Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are situations of emergency care for fever, when the child needs to give the medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and apply antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? Which medications are the safest?
People have been using electricity for a long time and almost never wonder what kind of current in the outlet is variable or permanent. The answer is quite simple, since 98% of all electricity produced belongs to the alternating current. This advantage is due to the ease of production and the possibility of transmission over long distances in comparison with direct current. During transmission, the AC value can be increased or decreased several times. Thus, most outlets work with alternating current. But, there are many consumers in the field of electronics, working from a direct current, voltage from 6 to 12 volts.
D.C
The concept of an electric current consists in the ordered motion of charged particles, which are affected by forces electric field or other outside forces. The direction of the current is the direction in which positively charged particles move.
If the value of the electric current strength and its direction remain unchanged, this current is assumed to be constant. Its existence requires free charged particles, as well as a current source that converts energy into the energy of the electric field. Under the action of external forces, the charged particles move. Their occurrence is due to various reasons. For example, for batteries and cells it will be chemical reactions. The generators produce a current using a conductor moving in a magnetic field. In photocells light affects the electrons of semiconductors and metals.
The direct current is used in industry, making it easier to start equipment with a large starting torque. Direct current motors are used for smooth speed regulation, with their help the starting torque is significantly smoothed out. The direct current is produced by batteries and batteries. Its value can vary from 6 to 24 volts.
Alternating current
Unlike direct current, the variable has the ability to vary in direction and magnitude at identical intervals of time. It is produced. In which the occurrence of electromotive force occurs under the influence of electromagnetic induction.

Alternating current is widely used in various areas, thanks to the ability to convert its strength and voltage with minimal energy loss. It can be single-phase and three-phase. In the latter case, the electrical system includes three circuits with the same frequency and EMF, shifted in phase by 120 degrees.
Using alternating current, transmission electric power long distances. During wire transfer, there are certain losses in the amount proportional to the square of the current. To reduce losses, you need to reduce the voltage. Reduced current causes a significant increase in voltage. Therefore, electricity is transmitted over long distances only when there is a high voltage. Conversion of currents to the necessary parameters is carried out with the help of transformers, which are electromagnetic devices of a reducing or boosting type.
Types and parameters of outlets
Electric sockets are fairly simple devices. Nevertheless, they have important functions, first of all, provide reliable contact between household appliances and the power grid. Sockets reliably protect against contact with live parts, provide reliable insulation. Most modern rosette models have a protective grounding function, performed by a separate contact.

All electrical outlets are divided into several types. In accordance with the applied fastening, they can be open or hidden. For example, outdoor wiring requires overhead outlets open type. They are easy to install and do not require holes for the junkets. Embedded models of sockets are attractive appearance, reliable fastening and a high degree of protection against electric shock due to the arrangement of current-carrying parts in the depth of the wall.
Sockets differ among themselves and in magnitude of current. Most modern outlets is designed for a current of 6, 10 and 16 amperes. Maximum current old Soviet models was only 6.3 amps. Consumers with high power are connected to special outlets that have high resistance to high currents. As a rule, this is stationary equipment. Maximum allowable current The outlet should correspond to the power of the consumer being connected to the electrical network.
How to measure the AC voltage in the outlet
On the Internet and various other sources, a lot of information on how to learn how to use a multimeter, how to measure voltage, current, resistance. All show, tell, but novice masters continue to make mistakes in making measurements. These errors are costly - the measuring devices fail, sometimes the devices that make measurements are burned, or worse, people get electric shocks and other injuries. The purpose of this article is to show with concrete examples and explain intelligibly why it is impossible to do certain things during measurements. A person should not remember why it is impossible, but understand, as it should be and why it can not be otherwise.
Let's start with the purposes for which sake measurements.
It is impossible visually, by external inspection, to determine the operating modes of elements electrical circuit or schemes.
For this purpose, measurementsi.e. determine whether there is an overload individual elements, whether the supply voltage corresponds to the norm, etc.
And now the main thing, the measuring device should not influence the circuit at its connection to it, otherwise the measured values will not correspond to those values which they actually have. In other words, the state of the circuit without the connected meter must remain the same after the instrument is connected.
How it is implemented in different modes:
- Measurement of voltage. Voltage Is the potential difference between two points. For example, there are two points A and B.
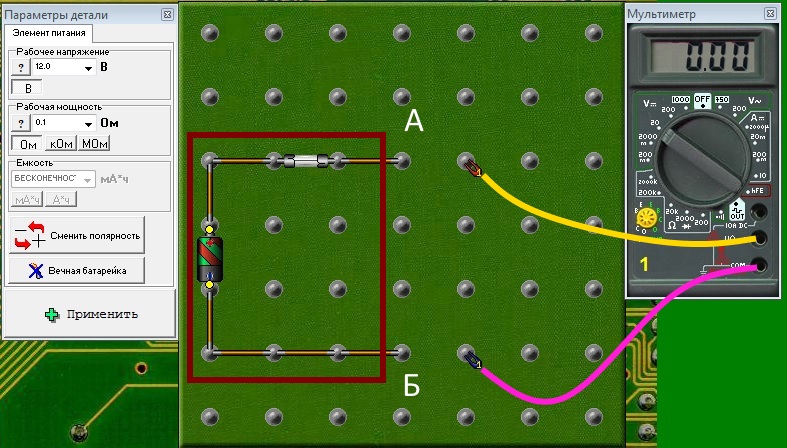
Their potentials are different, hence - there is tension between them. We need to measure it. To measure it, you need to connect a voltmeter to these points. Voltmeter should not change the state of points A and B when connected. This is possible when the voltmeter will have an infinitely large resistance (actually it is tens or even hundreds of megaohms) and when it is connected to points A and B there will be practically no current, otherwise the presence of a current will affect the value of the potentials of the points. The higher the class of the voltmeter, the higher its internal resistance and the less influence on the circuit during the measurement.
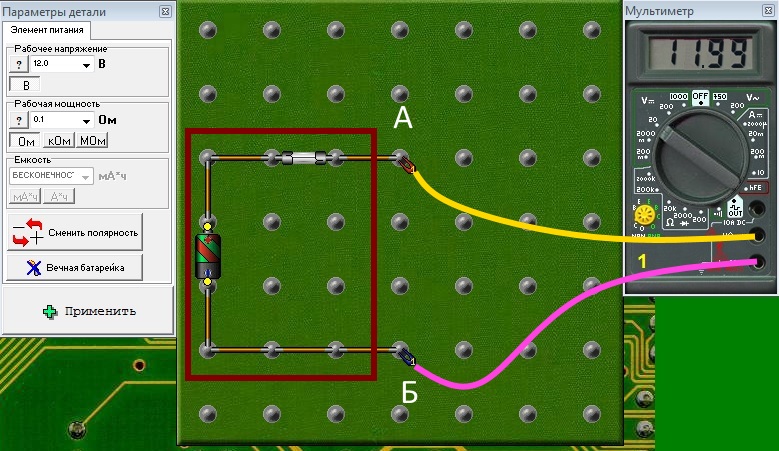
Conclusion– voltmeter has an infinitely large internal resistance, is connected to the measured points in parallel, with the power turned on. Before measuring, you must select the mode - constant pressure or variable, set the limit above the expected measurement result and make a measurement.
- Current measurement. Electricity Is the directed motion of electrons. For the current flow between points A and B, it is necessary to fulfill two conditions: the presence of a potential difference (voltage) between points A and B and the presence of an electrical circuit connecting these points. The magnitude of the current will be determined by the magnitude of the voltage between the points A and B and the magnitude of the resistance of the electrical circuit. This is Ohm's law I =U /R. In the figure below, the electrical circuit is a light bulb, its characteristics are 12V and 5A.
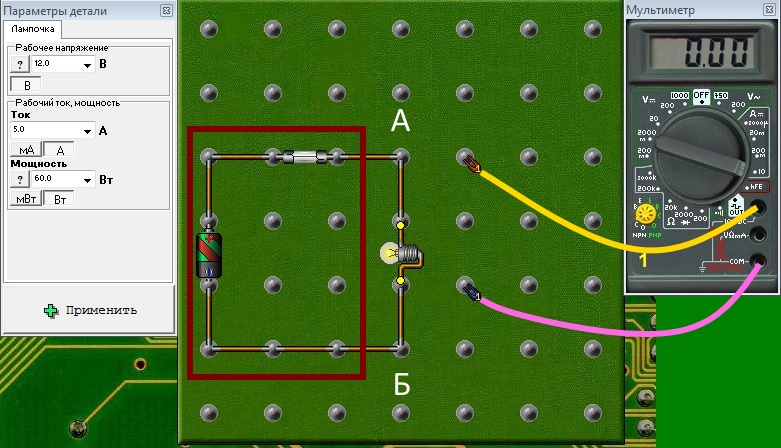
To measure current ammeter need to be included in the circuit. To do this, it needs to be broken and the current of the bulb through ammeter. According to the principle of minimal influence on the electrical circuit, it is clear that the resistance of the ammeter should be minimal. Really, the resistance of a good ampere meter is a fraction of Om, sometimes even a thousandth. In fact, we will replace the piece of wire with an ammeter.
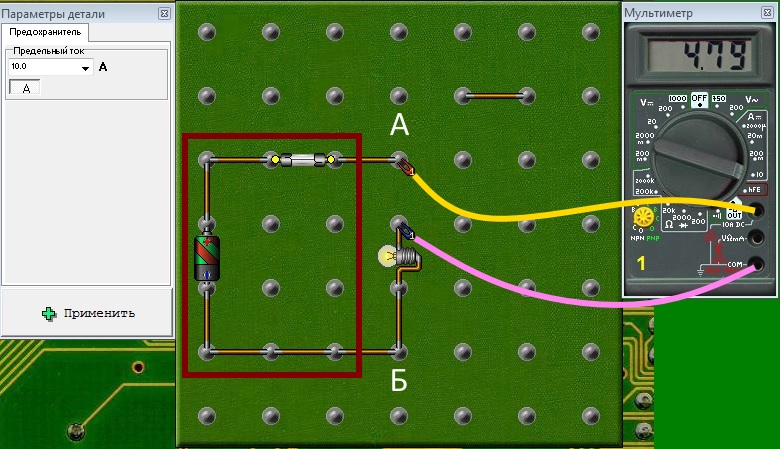
Conclusion– ammeter has an infinitesimally small internal resistance, is connected to the rupture of the existing electrical circuit, with the power turned off. Before measuring, you must select the mode - d.C. or variable, set the limit above the expected measurement result, turn on the power and make a measurement.
And now the most important thing. There is an outlet, it has two points, let's call them the same, A and B. The socket says ̴ 6 A, 220 V.
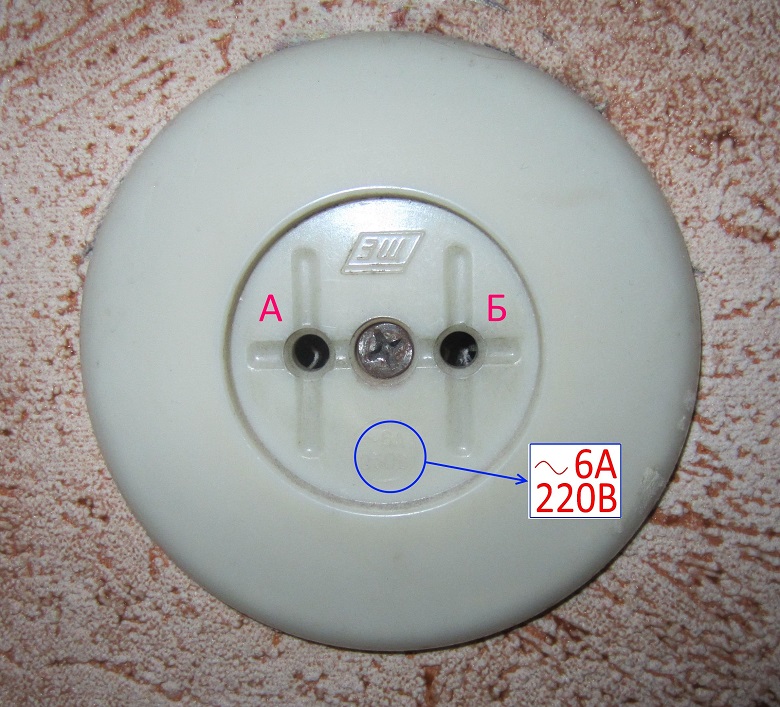

Some novice masters seeing this thinking, but I'll check my purchased device.
See inscription ̴ 220 V. It sets the mode of measurement of alternating voltage, the limit sets more than this value, for example, 750 V, and the test leads into the socket, sees the result of measurements of 220 V. Here everything is correct. This is analogous to our example of voltage measurement at the beginning of this article.
And now I measure the current, will he show me these 6 A, as indicated on the outlet. The socket is written 6 A, puts the limit of the device by 10 A and probes in the socket! Sparks, bugs and the device is not present !!! Lucky if traffic jams work. How many devices are burned from such measurements. Here is how it looks when modeling the situation in the program "The Beginnings of Electronics":
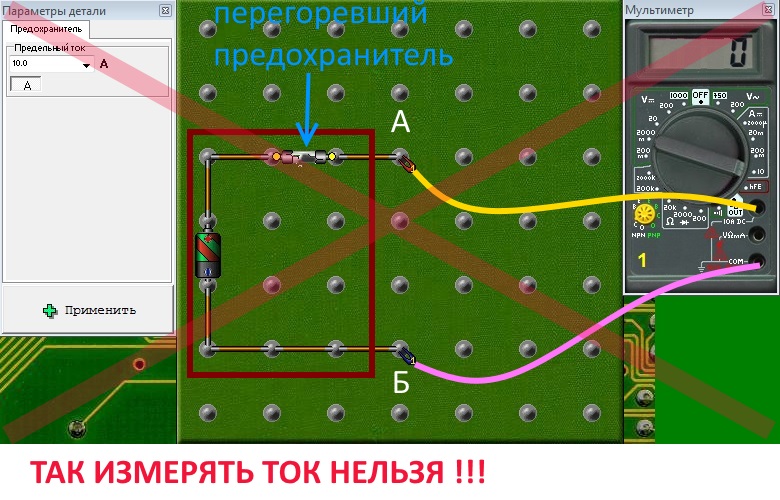
Let's analyze in detail why, not to remember that it is impossible, but understand.
For the flow of electric current, as mentioned above, two conditions are necessary: the potential difference and the electric circuit through which this current will flow.
The potential difference in the outlet is, we measured it, it is 220 V. There is no electrical circuit, nothing is connected to the outlet. When we hooked up ammeter to the socket, it became an electrical circuit, and since the resistance of the ammeter is minimal, only a fraction of Ohm, the current in the circuit consisting only of an ammeter according to Ohm's law ( I =U /R) tends to the largest possible value and will grow as much as the power of the power source or the strength of the circuit elements allow. Calculate what current will be if the resistance of the ammeter, for example, 0.01 Ohm. According to Ohm's law, I = 220 V: 0.01 Ohm. It turns out 22000 Ampere. The resistance of the wiring does not substantially limit this current, for example for copper, with a cross section of 2.5 mm / sq, it is 0.007 ohm / m. Naturally, this value will not reach this value, because at 10 A the automaton will work, and if there is a "bug" there, the wire will burn in the thinnest place. That's the reason for the accident. In other words, such an ammeter connection is equivalent to a short circuit.
The inscription on the socket 6A and 220V indicates that the socket contacts and its insulation are rated for currents up to 6 A and voltage up to 220 V. This means that this load socket can not be connected to a load that consumes more than 6A. At a voltage of 220 V, this corresponds to a power of up to 1320 watts.
To check the condition of the electrical network of the service operation, measurements are taken of the phase-zero loop. One of the special devices that is used for this purpose is called MZC-300 (from Sonel). The principle of the device is based on measuring the voltage drop on the calibrated load resistance, as recommended by GOST 50571.16-99.
The meaning of these measurements is that, in accordance with the requirements of the PTEP (rules for the technical operation of electrical installations of consumers) and PUE (rules for the installation of electrical installations), the short-circuit current of the electrical network must exceed the operating current of automatic switches in order to prevent fires.
- Resistance measurement. The principle of measuring resistance is based on measuring the current flowing through the element of the circuit, the resistance of which we measure. The current source is the battery of the device. Hence, the conclusion is that there should not be other sources of current or voltage, in other words, the power supply of the circuit whose elements we check must be turned off. Otherwise, the value of the measured resistance will not correspond to reality or, worse, the device may fail. And one more important detail when measuring resistance - the measuring current from the battery of the device must flow only through one element of the circuit, the one whose resistance we measure. To do this, you need to remove from the general scheme at least one contact of the element being checked.
Resistance measurement example:
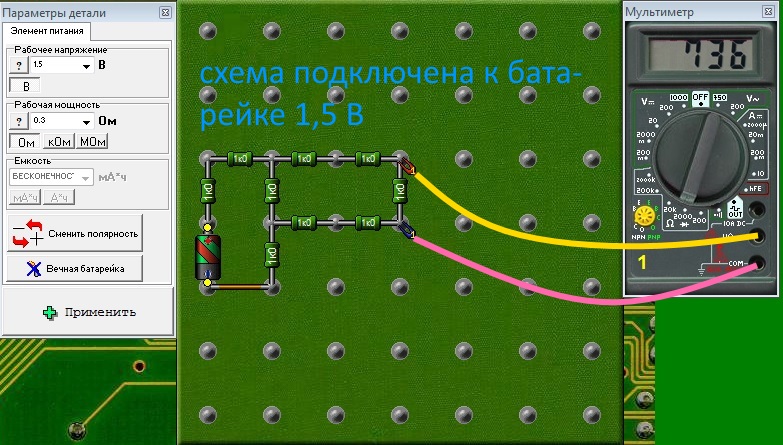
All resistors are rated 1kΩ.
Measurement of the resistance when the power supply of the circuit is connected, only 1.5 V. The device shows 736 Ohm, not 1 kΩ. There are two reasons:
- A battery is connected in the circuit, which creates an additional current through the measured resistance.
- In parallel to the measured resistance, additional resistances are connected and through them also the measured current flows.
Measuring the resistance when the circuit power is off, but the measured resistor is not dropped from the circuit. The instrument shows 833 ohms, not 1 kOhm. The reason is that the battery in the circuit is disconnected, but the connected resistors remain in parallel.
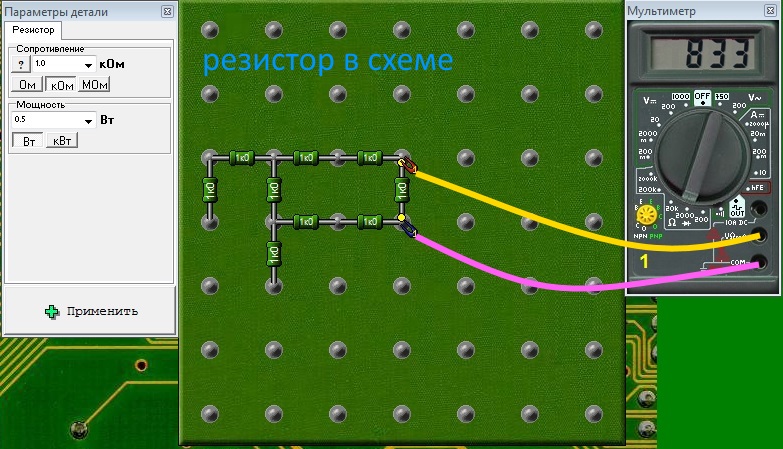
Resistance measurement with at least one output disconnected. This is the correct method of measuring resistance, on the device we see the true resistance value of the resistor being tested, 1000 Ohm, which is 1 kOhm. The ohmmeter current flows only through the measured resistance.

When using capacitor capacitance meters and inductance meters, the above rules must be observed.
Article material is duplicated on video:
From the point of view of specialists in the field of electrical engineering, the question "what current is in the socket?" Is not entirely correct. The fact is that if the consumer is not connected to the electric grid, then no current flows in it, since in this case the electrical circuit is open.
However, if you do not enter into disputes about the adopted terminology, the rated current is the most important parameter of any electrical equipment. The choice of the elements of the electric network, the ways of their installation, as well as the characteristics of consumers should be carried out taking into account these parameters.
Main characteristics of electricity in household networks
To date, there are several criteria that determine the quality of electricity household electrical networks, having a voltage of 220 V. All these characteristics are clearly defined in GOST 32144-2013. The most important of them are:
- Frequency deviation.
- Slow changes, as well as fluctuations and voltage dips.
- Nonsinusoidal stress.
- Unbalance of voltage in three-phase networks.
With your own apartment there is no need to take into account all the parameters of the quality of electricity. It is enough to know its basic characteristics, which can be checked with the use of simple and reasonably cheap measuring instruments.

These parameters include the frequency of the mains supply (permanent or alternating current), the voltage value, as well as the power of the connected consumers.
At present, AC power is used to supply most consumers. Its wide distribution was facilitated by the possibility of transmitting such energy over long distances. This quality is ensured by the ability of an alternating current to flow in electrical circuits containing capacitive resistances, which are inevitably present in extended power lines. As is known from the general course of physics, direct current does not have the ability to flow through a circuit that has capacitors in its composition.
Since AC power is used in the sockets, one of its most important characteristics is frequency.

In our country, it is customary to use AC power with a frequency of 50 Hz.
It is worth noting. Some consumers operate on high-frequency voltage. This allows to significantly reduce their mass-dimensional indicators and improve some specific specifications. To supply such devices, frequency converters are used, which are built-in or are purchased separately.
Check the frequency in the network can be using special instruments - frequency meters, but for practical purposes, such measurements are used rarely. It is much more important to know how many amperes flow in the electrical network and what is the magnitude of its voltage.
Voltage of the network
Most people know that the usual AC voltage is 220 V.

To supply more powerful consumers, a three-phase network can be used. In this case, the potential difference between the phases is 380 V, and between phase and zero - the same 220 V. As a matter of fact, the state power system is built on the use of three-phase mains. Separation of them into single-phase lines occurs immediately before connecting consumers.
Due to the uneven load at different phases, there may be a skew that causes current flow in the common zero wire, as well as a decrease or increase in the voltage on individual consumers.
Important! If the voltage in the outlet goes beyond the permitted limits, there may be significant difficulties in the operation of the electrical equipment, up to the disconnection of its built-in automatic protection or the failure of the electrical installation.
Rated current of the consumer
Any device used in AC or DC electrical networks has certain parameters. One of them is the rated current.
This characteristic shows how many amperes can be passed through the main circuit of the device for a long time.
In this regard, electrical outlets do not constitute an exception to the rules. They can also be divided according to the rated current. The standard values for single-phase devices household purposes are 6, 10, 16, 25 and 32 amperes.
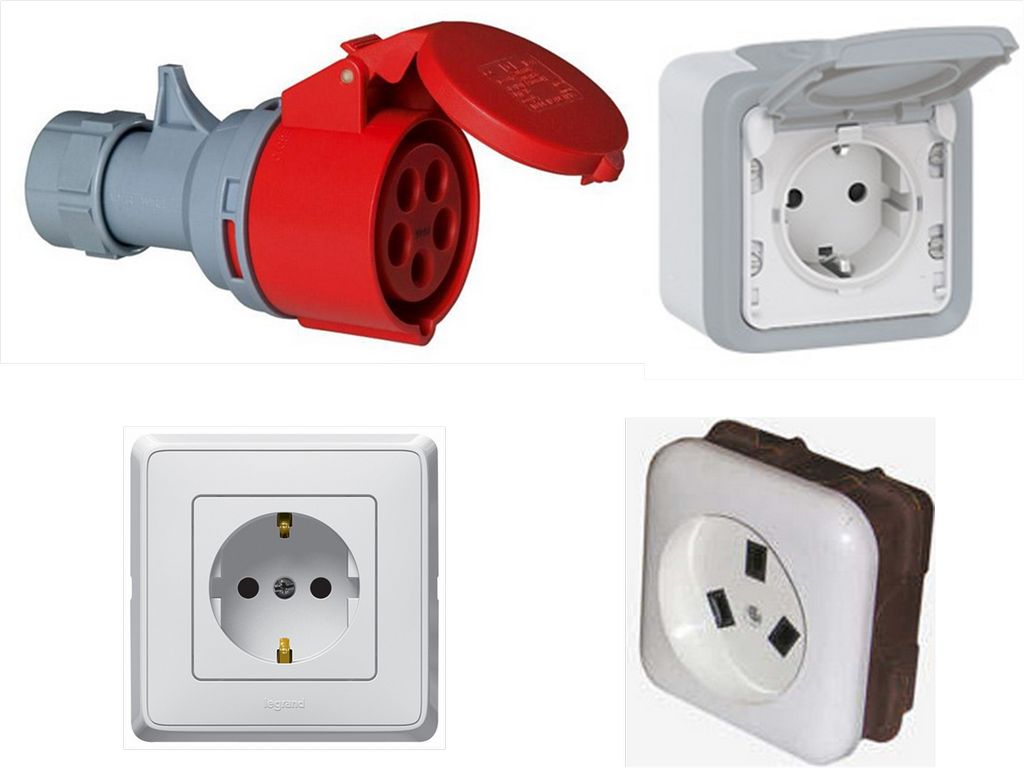

Sockets for 6 - 16 amperes are used most often and can be combined into groups receiving power along a dedicated line from the apartment switchboard. Devices with a nominal current of 25 amperes are designed to power more powerful consumers.
As for sockets for 32 amperes, they are produced in most cases in a three-phase version and are designed to connect particularly powerful consumers, such as electric stoves or cooking surfaces.
Rated current calculation
When the electrical current flows, the conductor becomes substantially heated, which is often the cause of the failure of the mains and even leads to a fire. The intensity of heating depends on two factors: the square of the current value, as well as the electric resistance of the load. It is easy to guess that the most powerful consumers have a minimum resistance, allowing to pass significant currents.
where P is the active power of the consumer, W.
U is the mains voltage, V.
This formula is equally suitable for determining the current at alternating and constant voltage.
Methods for measuring voltage and current
To check the conformity of the voltage of the mains to the established requirements, and also to find out how many amperes flow through one or another of its elements, various devices for measuring current and voltage are used.
Indicator screwdriver
The cheapest device that allows you to check the availability of potential on the contacts of the outlet is an ordinary indicator screwdriver. In this case, you can not find out how many volts are applied between the contacts.

In a normally functioning network, when the indicator is touched to the phase contact of the socket, the LED in the handle of the voltage indicator glows brightly, when touched zero wire such a glow is absent. This method can be used only to determine the presence of voltage in the phase conductor.
Its essential disadvantages are the impossibility of monitoring the integrity of the zero conductor, the magnitude of the voltage, as well as the susceptibility of measurement accuracy to the influence of "pickups" generated magnetic fields passing by electrical wires. Thus, the indicator can be illuminated even if there is no rated voltage on the phase contact of the outlet.
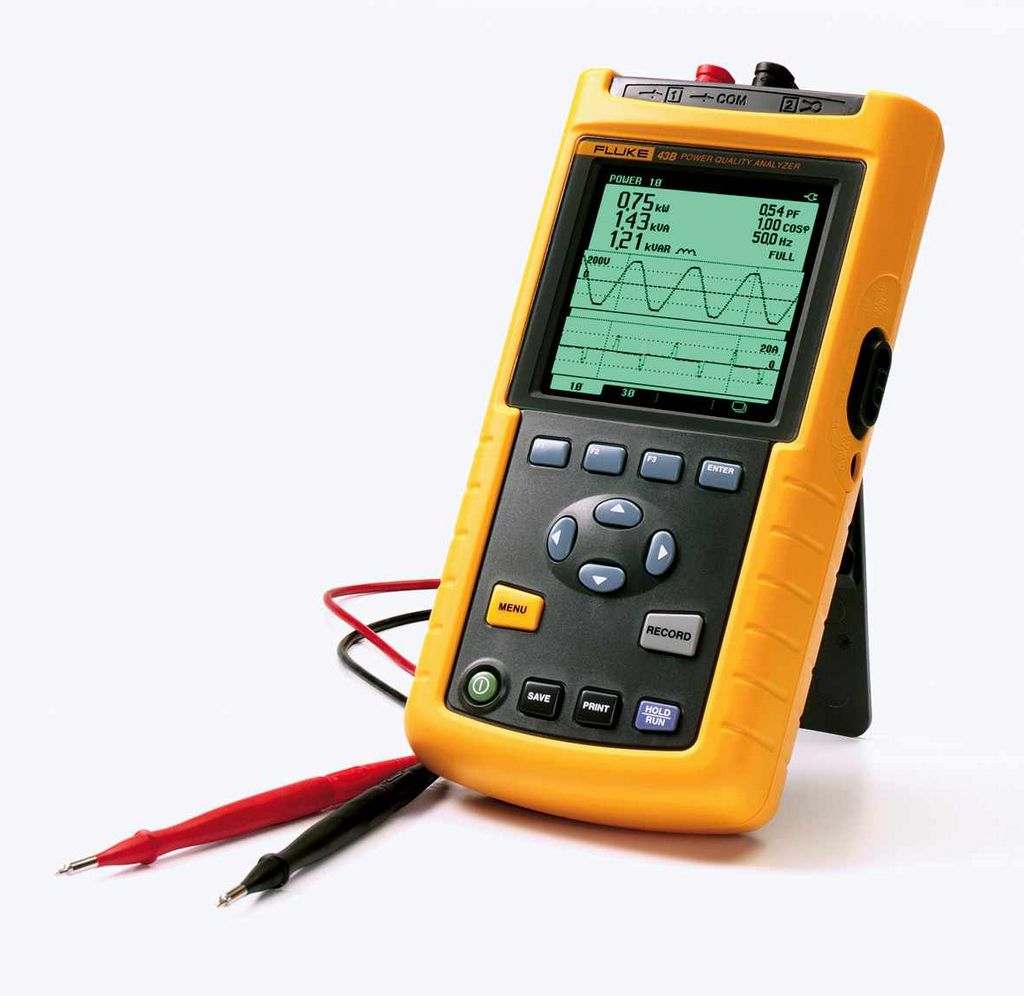
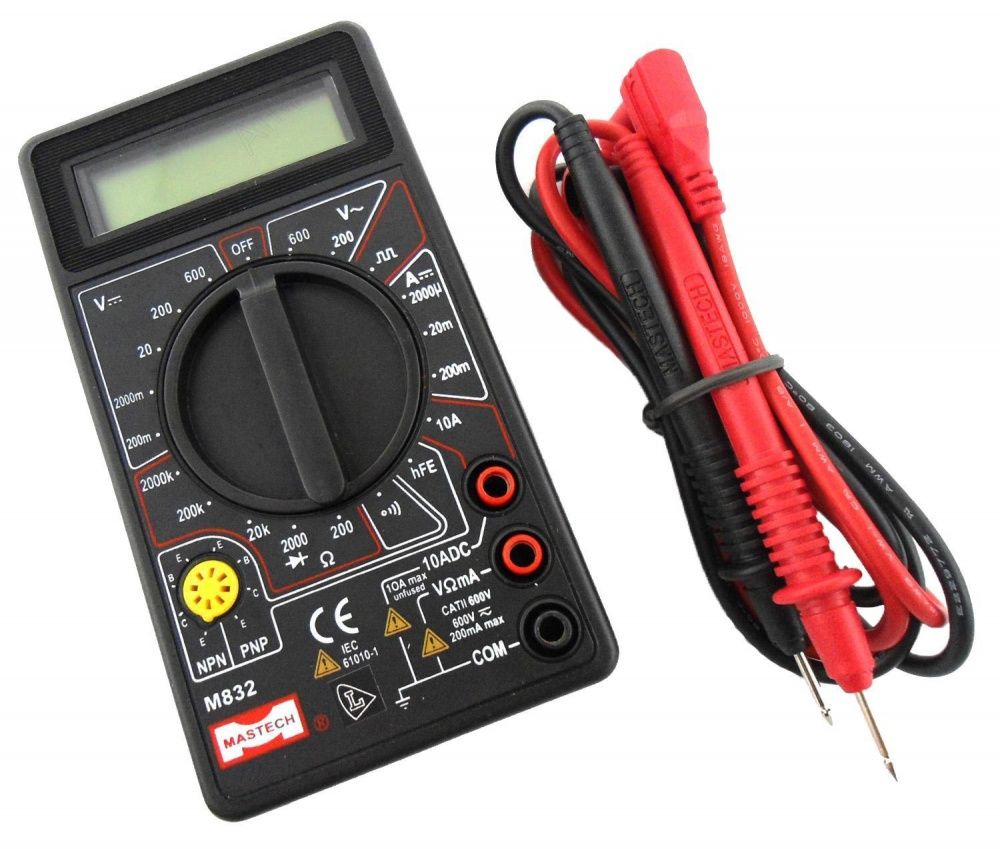
A more accurate method of voltage measurement is the use of special instruments - voltmeters (often used testers or multimeters that allow measuring several quantities: voltage, current, resistance, capacitor capacitance, etc.).

Such a device is connected in parallel to the network (its probes are inserted into the outlet in the absence of consumers connected to it). Using such devices it is possible to find out how many volts of DC or AC voltage is applied to the contacts of the socket.
The current in the socket can be measured using a multimeter connected in series in the network as an ammeter.
Important! The device configured for current measurement can not be connected in parallel to the network. It can break down.
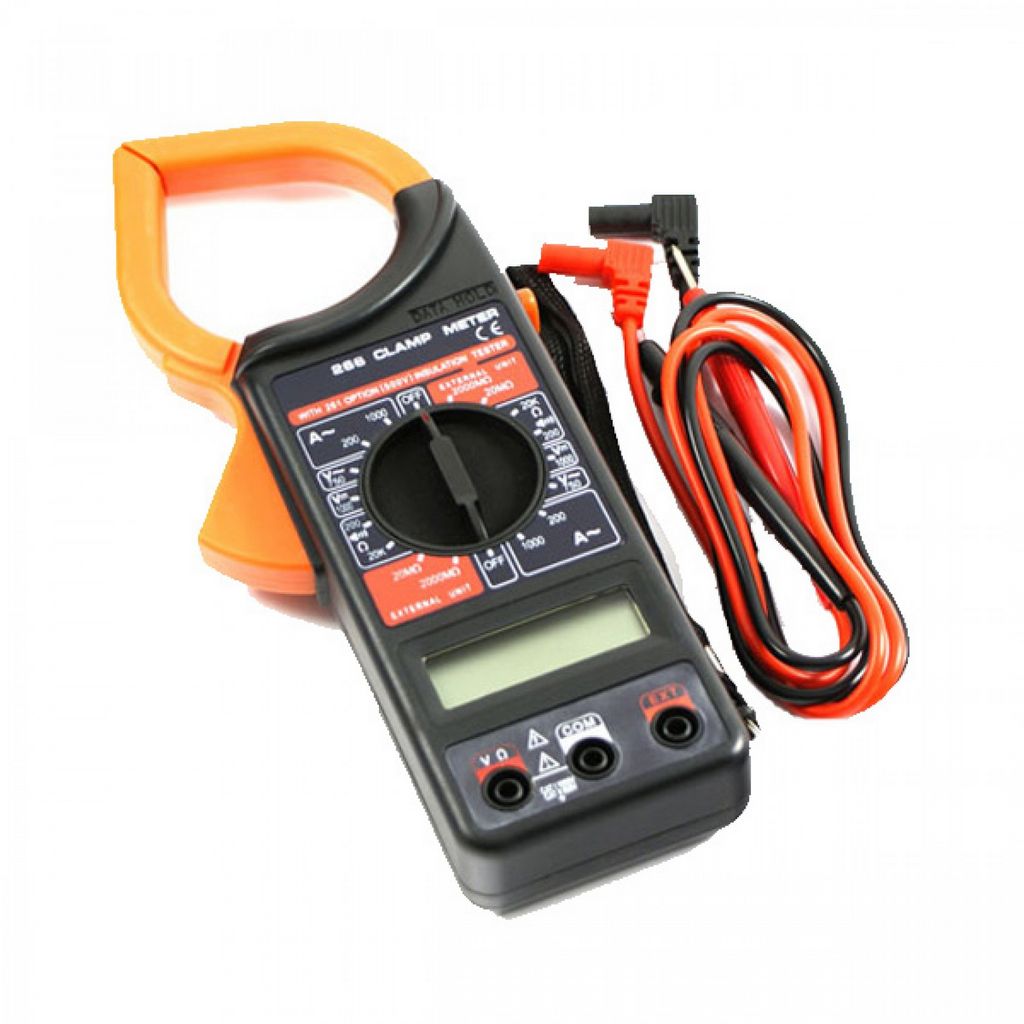
The main disadvantage of using an ammeter is the difficulty of its connection. Therefore, in many cases, in order to check how many amperes flow in the wire, you can use measuring pincers. The main advantage of this device is the absence of the need to open the circuit and disconnect the electrical equipment when it is used.

Thus, among all the characteristics of electricity in household electrical networks, the most important are frequency, voltage, and also rated current.
When conducting electricity in a new house, owners have to buy outlets. But how to choose them correctly to ensure the normal operation of all electrical appliances, not everyone knows. After all, for this you need to take into account not only how many volts in the socket, but also the number of amps, because more powerful technology delivers the network enhanced overload.
GOST for modern apartments
Why is it important to know how many amps are in the socket
Under the Soviet Union, the apartment was subject to a load limitation of up to 6 amps and 220V. But gradually the growth in the number of home appliances and its consumed capacities led to a revision of GOSTs, and today for apartments the standard load is 16 amperes.
We explain the difference. If you install a 6 amp socket, you can connect to it a technician whose power does not exceed 1.5 kW. Even small devices, for example, electric kettles today have already exceeded this figure, and many of the models have a power of about 2 kW. And if you stick such a kettle into this outlet, it will knock out traffic jams. Therefore, the optimal version of sockets for household appliances - at 16 amperes. They will pull the load to 3.5 kW per point.
On sale you can find and sockets with a load of 25 amps. Such models are in demand in houses where there are not gas, but electric cookers. When you turn on all the burners, they consume a large amount of electricity, so they require a powerful outlet.
If power lines are laid in workshops with woodworking machines and other similar equipment, then the voltage in 220V is already not enough. In this case installation is required three-phase network, having a voltage of 380V. For such an electric network, special three-phase sockets are designed for a load of 32 amperes. By the way, in private houses, such connectors are also found if the building is heated using electricity. However, it is necessary to strengthen and wiring.
Compare prices for - discounts up to 40%.
Is it important how much in a socket Hertz
Another factor affecting the operation of the technique is the frequency of the current. For people who are in the same country and do not travel anywhere, this indicator has no effect whatsoever, because according to generally accepted standards, the Russian power network uses a voltage of 50 hertz frequency. And all the devices are "sharpened" just under this indicator.
Another thing is if a person by occupation often goes abroad and carries with him the necessary equipment (laptop, phone, etc.). He may face the problem that there is another indicator of frequency and voltage where he has arrived. For example, in the US, the voltage is used at 120V with a frequency of 60 hertz. And to use in this country brought equipment, you will need an adapter, and sometimes an adapter, if the type of outlet does not fit your forks. Precisely such an incident can occur if you buy equipment abroad. Therefore, it is better to know in advance what voltage and amperage are used for the devices you are going to purchase.
To begin with, the crux of the matter is not correct! Namely, to say the voltage of the current is not correct, for comparison we can give the expression - hot ice. Let's take a closer look at such basic electrical concepts as tension, current and resistance. After that it will be quite clear what and how is called and what is the original meaning of electrical terms and concepts. So, let's take an example with ordinary water in the pipes.
There is water itself, consisting of atoms, there are pipes through which it flows, there are barriers that impede the flow of water. Electricity also consists of the tiniest particles, which are called electrons and move not in pipes, as water does, but in various electrical conductors (mostly metals). These electrically charged particles are acted upon by certain forces, some force them to move, while others, on the contrary, tend to obstruct their movement.
 What is wrong with the expression of the voltage in the network 220? Voltage and current are in some sense opposite concepts. Like water, in the absence of obstacles on its way, the water flows with maximum speed and flow. Also in electricity. The electric current is an ordered flow of charged particles (electrons) moving inside the conductor. The voltage arises (more precisely, it increases) if an obstacle appears in the path of the flow of particles in the form of a certain resistance. For water, this will be a reduction in the diameter of the channel through which it flows, which increases the water pressure. For electricity, this will be an obstacle in the form of various factors that slow down the movement of electrons (the molecular structure of the conductor, its temperature, etc.), which increases the voltage at some point between the two points (potentials).
What is wrong with the expression of the voltage in the network 220? Voltage and current are in some sense opposite concepts. Like water, in the absence of obstacles on its way, the water flows with maximum speed and flow. Also in electricity. The electric current is an ordered flow of charged particles (electrons) moving inside the conductor. The voltage arises (more precisely, it increases) if an obstacle appears in the path of the flow of particles in the form of a certain resistance. For water, this will be a reduction in the diameter of the channel through which it flows, which increases the water pressure. For electricity, this will be an obstacle in the form of various factors that slow down the movement of electrons (the molecular structure of the conductor, its temperature, etc.), which increases the voltage at some point between the two points (potentials).
Thus, we get that between two different points in the electrical circuit (between which we make our measurements) with increasing resistance, which prevents the current of charged particles in the conductor, increases electrical stress. Conversely, when it decreases, the voltage becomes smaller, and the current strength in the circuit increases. I think now more or less it became clear why talk voltage is not correct.
 In a typical household power supply, the standard AC voltage is 220 volts. But the current depends on the connected load. The more powerful the device we plug into the outlet, the more current will appear in the conductor connecting this device to the power network. At the same time, there will be some drop in the voltage on the network (not significant, unless, of course, the supplying substation is not overloaded by other people or by you). To this end, each consumer is given a certain power, which he can use without negative influences on the general electrical supply network (system).
In a typical household power supply, the standard AC voltage is 220 volts. But the current depends on the connected load. The more powerful the device we plug into the outlet, the more current will appear in the conductor connecting this device to the power network. At the same time, there will be some drop in the voltage on the network (not significant, unless, of course, the supplying substation is not overloaded by other people or by you). To this end, each consumer is given a certain power, which he can use without negative influences on the general electrical supply network (system).
In order to protect the network 220 from overloads, various protective devices are used, starting from the simplest ones in the form of fuses, and ending with all kinds of electrical and electronic devices. They cut off the load when the maximum permissible current or short circuit occurs.
P.S. Having the right idea of how exactly this or that system works, whether it is electrical, mechanical, hydraulic or other, it becomes possible to work with it correctly (maintenance, repair, improvement, etc.). So I think after this article, you will no longer talk about the current tension, but divide these concepts properly.



