Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are situations of emergency care for fever, when the child needs to give the medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and apply antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? Which medications are the safest?
Hello. I am glad to see you on my site. The theme of today's article: the device and the principle of operation asynchronous electric motors. I would also like to say a little about the ways to adjust their speed, and list their main advantages and disadvantages.
Earlier, I already wrote articles on asynchronous electric motors. If you are interested, then you can read. Here is the list:
Well, now let's move on to the topic of today's article.
At the present time, it is very difficult to imagine how all industrial enterprises would exist, if there were not asynchronous machines. These engines are installed almost everywhere. Even at home each person has such an engine. He can stand on your washing machine, on the fan, at the pumping station, in the hood, and so on.
In general, an asynchronous electric motor is a tremendous breakthrough in the world industry. All over the world, they produce more than 90 percent of the number of all produced engines.
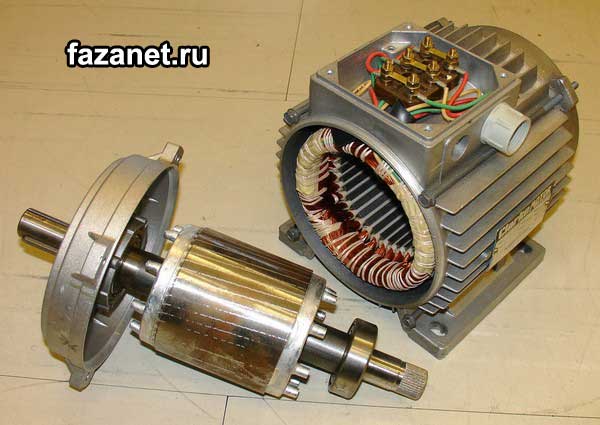

An asynchronous electric motor is an electric machine that converts electric energy into a mechanical one. That is, it consumes electric current, and in return gives a torque, with which you can rotate many units.
And the word "asynchronous" means non-simultaneous or does not coincide in time. Because at such engines the rotor speed slightly lags behind the rotational frequency of the electromagnetic field of the stator. Another thing called lagging is slip.
This slip is indicated by the letter: S
A slip is computed according to the following formula: S = (n1 - n2) / n1 - 100%
Where, n1 is the synchronous frequency of the stator magnetic field;
n2 is the shaft speed.
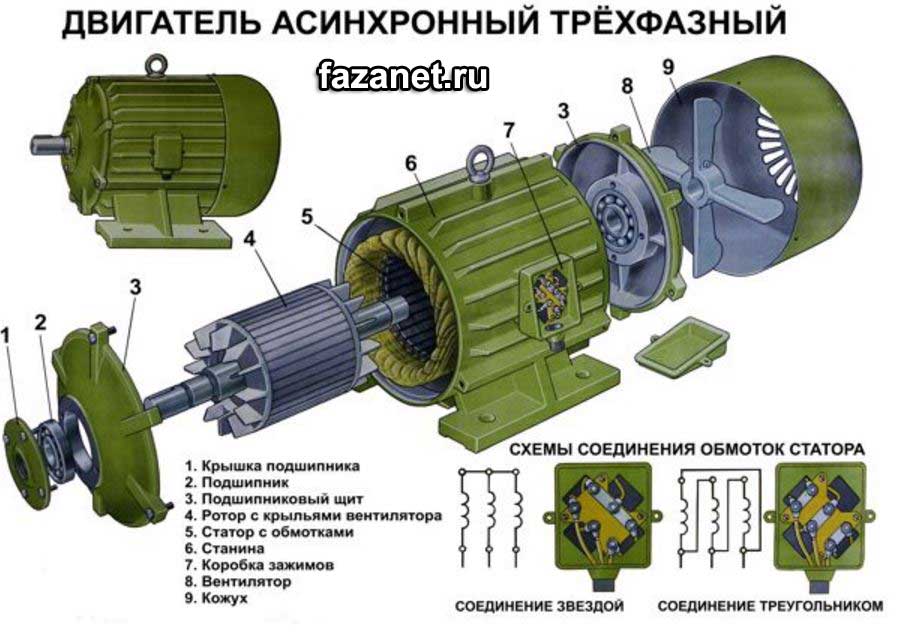
The device of the asynchronous electric motor.
The engine consists of the following parts:
1. Stator with windings. Or the frame inside which is a stator with windings.
2. Rotor. This is if short-circuited. And if the phase, then we can say that it is an anchor or even a collector. I think there will be no mistakes.
3. Bearing shields. On high-powered engines, bearing caps with seals are still in front.
4. Bearings. Can stand slipping or rolling, depending on the performance.
5. Cooling fan. It is made of plastic or metal.
6. Fan housing. Has a slot for air supply.
7. Sideboard or terminal box. For connecting cables.
These are all its basic details, but depending on the type, type and performance, it can vary slightly.
Asynchronous electric motors are mainly produced in two types: three-phase and single-phase. In turn, three-phase ones are further subdivided into subspecies: with squirrel cage rotor or a phase rotor.
The most common are three-phase with a squirrel-cage rotor.
The stator has a round shape and is recruited from sheets of special steel, which are insulated with one another, and this assembled structure forms a core with grooves. In the core grooves are wrapped windings, with a special winding, insulated with varnish wire. The wire is cast mainly from copper, but also from aluminum. If the engine is very powerful, then the windings make the bus. The windings are laid so that they are shifted relative to each other by 120 degrees. The stator windings are connected to a star or a triangle.
The rotor, as I already wrote above, is short-circuited or phase.
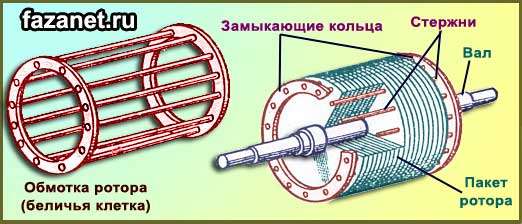
The short-circuited represents a shaft on which sheets are put on, also made of special steel. These typesetters form a core, in the grooves of which molten aluminum is poured. This aluminum evenly spreads through the grooves and forms rods. And along the edges, these rods are closed with aluminum rings. It turns out a kind of squirrel cage.
The phase rotor is a shaft with a core and three windings. Some ends, which are usually connected to a star, and the second three ends are connected to the current-collecting rings. And on these rings, with the help of brushes, electric current is supplied.
If a load resistor is added to the phase winding circuit, and when the motor is started to increase the active resistance, then this method can reduce the large inrush currents.
Operating principle.
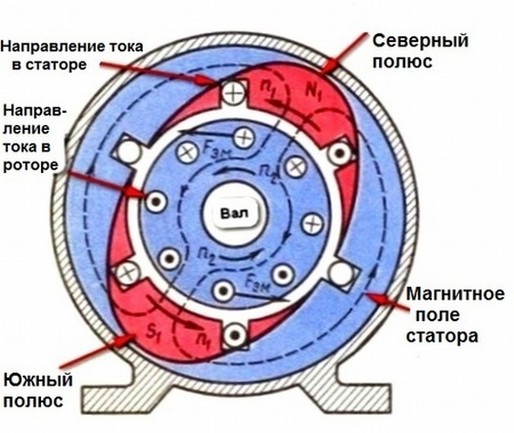
When an electric current is applied to the stator windings, an electrical current is generated in these windings. As you remember, from the above written words, the phases are shifted relative to each other by 120 degrees. And this flow in the windings begins to rotate.
And when the stator magnetic flux rotates, an electric current appears in the rotor windings, and its magnetic field. Two of these magnetic fields begin to interact and cause the rotor of the motor to rotate. This is if the rotor is short-circuited.
By the principle of robots, here is a video clip.
Well, with the phase rotor, in fact, the principle is the same. The voltage is applied to the stator and to the rotor. There are two magnetic fields that begin to interact and rotate the rotor.
Advantages and disadvantages of induction motors.
The main advantages of an asynchronous electric motor with a squirrel cage rotor:
1. Very simple device, which allows you to reduce the cost of its production.
2. The price is much less compared to other engines.
3. Very simple circuit launch.
4. The speed of rotation of the shaft practically does not change with increasing load.
5. Well tolerates short-term overload.
6. Connectivity three-phase motors in a single-phase network.
7. Reliability and ability to operate in almost any conditions.
8. Has a very high efficiency and cos φ.
Disadvantages:
1. It is not possible to control the rotor speed without loss of power.
2. If you increase the load, the torque decreases.
3. The starting torque is very small compared to other machines.
4. When the underload is increased, the index cos φ
5. High indicators of starting currents.
Advantages of motors with a phase rotor:
1. Compared to short-circuited motors, has a sufficiently large torque. That allows it to run under load.
2. It can work with a small overload, and thus the frequency of rotation of the shaft practically does not change.
3. A small starting current.
4. You can use automatic starting devices.
Disadvantages:
1. Large dimensions.
2. The efficiency and cos φ are less than for squirrel-cage motors. And with underload, these indicators have a minimum value
3. You need to maintain the brush mechanism.
On this I will finish my article. If it was useful to you, then share it with your friends on social networks. If you have any questions, then ask them in the comments and subscribe to the updates. Till.
Sincerely, Alexander!
Electric motors are built-in elements of the working units of technology, and they provide them with proper work. It does not matter whether it is a warehouse equipment or a washing machine - these devices can not do without the use of an electric motor and, most often, asynchronous electric motors.
Electric motors of this type today have quite a wide scope of application, than they are obliged, first of all, to their operating characteristics. The fact is that their feature is the almost complete independence of the rotational speed of the shaft from the load on it.
Asynchronous motors consist of two parts: rotor 1 and stator 2. Its internal part is called a rotor, this part rotates and carries a winding on itself. The outer part is the motor casing and is called the stator, it is stationary, inside it there are special grooves (magnetic core), where phase windings (sections) of windings (stator winding) are arranged per phase. The phases of the stator windings can be connected by a "star" or a "triangle".
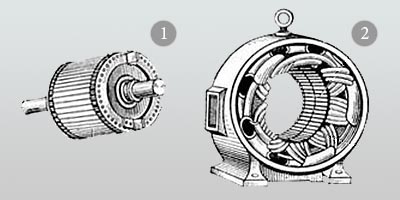
Both these parts are assembled from insulated sheets of stamped steel with a thickness of about 0.35-0.5 mm. For high-power machines, the gap between the rotor and the stator is made as small as possible, of the order of 1-1.5 mm, in low-power engines even less. The shaft rotates in the bearings located in the bearing shields.
Kinds asynchronous electric motors. Consider the types of induction motors and their device. Depending on the design of the rotor, asynchronous motors can be divided into two types: with short circuited and phase rotor. The main difference between these types of electric motors is only in the arrangement of the rotor.
Asynchronous electric motors with squirrel-cage rotor. These engines have a rotor that looks very much like a squirrel cage. Their stator winding is a rod made of aluminum or copper, closed from the ends of the rotor by two rings. To date, electric motors of small and medium power (up to 100 kW) are equipped with a "squirrel wheel" made of aluminum, by pouring it under pressure into the grooves of the rotor.
Asynchronous motors with phase rotor. The windings of the phase rotor are connected, most often, with each other by a "star". The motor with a phase rotor has one more name - engine with contact rings, this name was due to the fact that the ends of the windings are connected to three copper rings, which are electrically insulated not only from the motor shaft but also from each other. The rings are attached to the core of the rotor through insulating gaskets. They are superimposed with special brushes that even when rotating have electrical contact with the windings of the motor rotor. To change the speed, the brushes are connected to the rheostat.
 The principle of operation of induction motors. The supply voltage is supplied to the stator winding, forming a rotating magnetic field, which, in turn, acts on the winding of the rotor (rods), induces an EMF in it, creating an electric current.
The principle of operation of induction motors. The supply voltage is supplied to the stator winding, forming a rotating magnetic field, which, in turn, acts on the winding of the rotor (rods), induces an EMF in it, creating an electric current.
As a result of the interaction of the magnetic field of the rods caused by this electric shock with the magnetic field of the stator, and a force is created creating a rotating electromagnetic moment, i.e. rotation of the rotor.
The frequency of rotation of the shaft of induction motors depends primarily on the number of pairs of poles, determined by the number of coils per phase. So, three winding coils create a bipolar magnetic field (one pair of poles). At a standard frequency of 50 Hz, the rotor speed will be of the order of 3000 rpm. As the magnetic field increases along the poles, the speed of rotation of the rotor decreases, for example, the magnetic field at six poles has a speed three times less than for a two-pole pole.
At the present time, the use of squirrel-cage rotor motors has become more common, due to the simplicity of the device, and thus, in many respects - the simplicity of repair, maintenance and ease of use. Engines with a phase rotor are used much less often.
Perhaps there is not a single serious mechanism or machine that does not use electric motors. In the car, with a washing machine, agricultural equipment and small household appliances - everywhere used electrical engine. The most widespread is an asynchronous electric motor and we will talk about it today.
Synchronous and asynchronous motors in mechanical engineering and in everyday life
Due to its simplicity and economy, an asynchronous electric motor can come in handy not only in mechanical engineering and in everyday life, but we will consider exactly such engines that are found most often. The reason for the popularity of an induction motor alternating current became its availability, the ability to connect to any power outlet without any rectifiers and matching devices, as well as ease of maintenance and repair in which case.
There are two types of asynchronous electric motors - with a squirrel-cage rotor and with a phase rotor. But to begin with it is necessary to understand the design and learn the principle of operation of an induction motor with a squirrel-cage rotor, after which the reason for its popularity will become clear. Although asynchronous motor was developed back in the late 19th century, so far its design has not undergone any particular changes.
Advantages of the engine
![]()
The main feature of the characteristics of this engine and the most valuable of their manifestation, consider the fact that the load on the engine is virtually independent of the rotational speed of the shaft. Magnetic fields and electromotive force have been studied for about two hundred years, and our induction motor has become the best confirmation of this, it is one of the most effective methods transformation of energy.
The principle of operation of this motor is just based on the interaction of a moving magnetic field and a conductive element located inside this field. The engine, as is known even from the school bench, consists of two basic nodes - the rotor and the stator. The stator just generates a rotating magnetic field. Structurally, the stator is a metal core, wound on it with a copper wire with thermo-lacquered insulation.
Inside the stator, inside its magnetic field, is placed a rotor, which is a shaft with a core and a winding. The figure below shows the schematic of the device of an asynchronous motor.
Under the scheme it is clear that the stator consists of a set of plates and several windings, which are wound on a plate-shaped core. These windings can be connected in different ways, depending on the type of voltage. Each of their windings is shifted relative to each other by 120 degrees. And the rotor of such an engine can be basically of two types.
The rotor of the phase type does not differ fundamentally from the stator. This is a three-phase winding, the ends of which are connected according to the "star" scheme. The free ends of the windings are connected to the current collector rings. The rings come into contact with the conductor by means of brushes and therefore it is possible to install an additional limiting resistor in the connection circuit.

Resistor as a device smooth start, serves to be able to reduce the values inrush current, which can reach quite large values.
Short-circuited rotor and its features
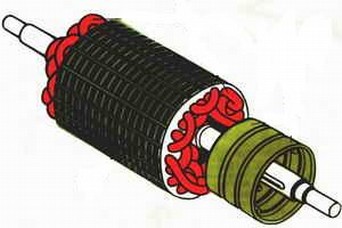
The short-circuited rotor is a composite core made of special sheet steel. The core has channels that do not isolate the windings from each other, but on the contrary - they are flooded with molten light-fusible light metal, and it forms rods that are fixed in the ends at the ends.
The metal from which these bars are made and to which the spaces between the cores are poured depends on the required characteristics of the engine and this can be both copper and aluminum.
How the magnetic field works
The engine operates on the basis of the process of obtaining mechanical work as a result of the action of a moving magnetic field on the conductor. A voltage is applied to the stator winding, each phase forming its own magnetic flux. The frequency of the magnetic flux depends directly on the frequency of the current supplied to the ends of the winding.
Asynchronous motor Is an asynchronous AC electric machine in the driving mode, in which the rotational frequency of the stator magnetic field is greater than the rotor speed.
The principle of work takes the basis of creation rotating stator magnetic field , about what more you can read from the link.
Asynchronous motors are one of the most common electric machines, and often are one of the main converters of electrical energy into mechanical energy. The greatest advantage is the lack of contact between the moving and moving parts of the rotor, I mean the electrical contact, for example, in engines direct current through brushes and a collector. However, this is true only for short-circuited rotors, in asynchronous motors with a phase rotor, this contact takes place, but more on this later.
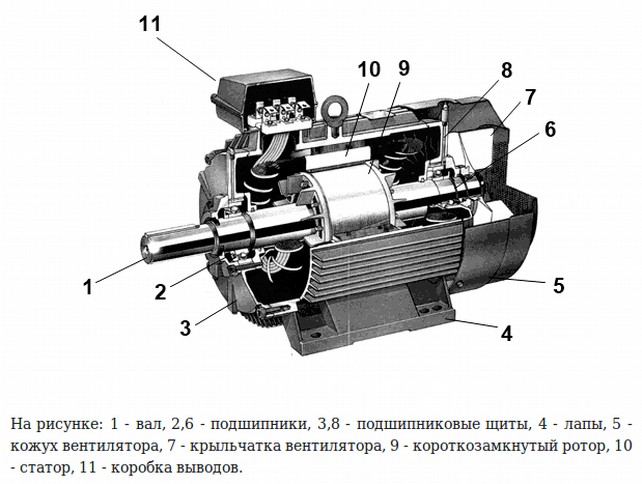
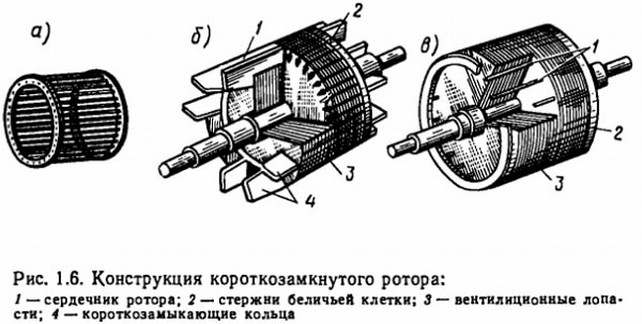
Consider the design, an example is an asynchronous motor with a squirrel-cage rotor, but there is also a phase rotor type. The induction motor consists of a stator and a rotor between which an air gap. The stator and rotor, in turn, also have so-called active parts - excitation winding (separately stator and separately rotary) and magnetic core (core). All other parts of the AD, such as: shaft, bearings, fan, housing, etc. - purely structural parts that provide protection from the environment, strength, cooling, the ability to rotate.
Figure 1 - Design of an asynchronous motor.
The stator is a three (or many) -phase winding, the conductors of which are uniformly packed in grooves along the entire circumference, with an angular distance of 120 el. degrees. The ends of the stator winding are usually connected according to the "star" or "triangle" schemes, and are connected to the network supply voltage . The magnetic circuit is made of electrotechnical laminated (recruited from thin sheets) of steel.
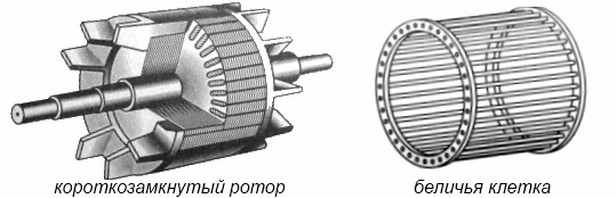
As I said earlier, in an asynchronous motor there are only 2 types of rotors: it is a phase type of the rotor, and short-circuited. The magnetic circuit of the rotor is also made of a bonded electrical steel. The short-circuited rotor has the form of a so-called "squirrel cage" because of the similarity of its design to this cell. This cell consists of copper rods, which are short-circuited by rings. The rods are directly inserted into the grooves of the rotor core. To improve the starting characteristics of the AD with this type of rotor, use a special form of the groove, this makes it possible to use the effect of current displacement, which affects the increase in the active resistance of the rotor winding during start-up (large slip). By themselves, the AD with a squirrel-cage rotor has a small starting torque, which adversely affects the area of their use. The most widespread they found in systems that do not require large starting points. However, this type of rotor differs in that less maintenance is spent on servicing it than on servicing the motor with a phase rotor, due to the lack of physical contact in the rotor type of a squirrel cage.
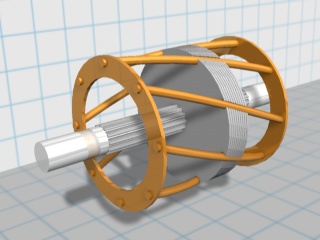
Figure 2 - Rotor AD "squirrel cage"
The phase rotor consists of three-phase winding, often connected by the "star" scheme, and outputted to the contact rings, which rotate together with the shaft. The brushes are made of graphite. The phase rotor provides many advantages, such as star-delta start , rotational speed control by changing rotor resistance.
Modes of operation
Read more
To convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, apply special devices. In particular, this is an asynchronous motor with a squirrel-cage rotor, which is the simplest device of this type.
What it is
An asynchronous motor is a device that is used to convert the energy of electricity into a mechanical one. Powered by AC power. The main difference from a synchronous machine is that of this engine the stator speed is greater than the rotor frequency. This electric motor is very popular due to its reliability and ease of use.
Three-phase and single-phase motor consists of a stator and a short-circuited rotor, this is perfectly demonstrated by the drawing below. The stator consists of separate cylindrical sheets of steel and a rotor. In the grooves there is a winding, which is equipped from the usual power cable. The winding of each groove is in relation to the other at an angle of 120 degrees, in the section it becomes evident that during operation the grooves become a star or a triangle.
Photo - asynchronous motor
The rotor is the core that is inside the stator. It is also assembled from separate steel sheets that are connected together by a molten aluminum alloy. Due to this, the entire structure is formed by studs (rods). They, in turn, are connected by short rings, which are fastened to the ends of the rods. Such a squirrel cage can also be connected by copper rings, but then the engine is used at lower voltages in order not to melt the metal.
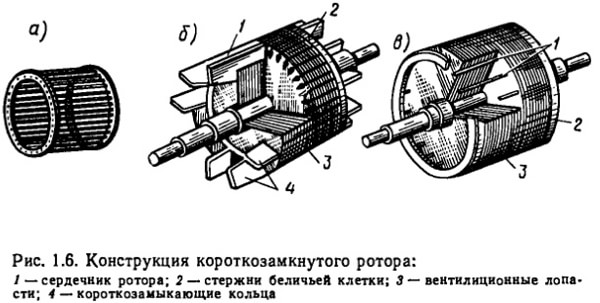
Photo - rotor design
It should be noted that thanks to this design, maintenance of the engine with an asynchronous type of operation is simpler than synchronous. Due to the absence of brushes, the operation of the device is considerably prolonged.
Instruments can be in closed and open versions. The explosion-proof device is in a special casing, it is protected from fire when the network is unstable. Also, depending on the location of the rotor, the devices are of the following type:
- Horizontal;
- Vertical.
Pluses:
- Availability. Comparatively with synchronous machines, asynchronous machines cost much less. In addition, they are very common. They can be found in specialized shops, markets, Internet portals;
- Reliability. In addition to the absence of brushes, which are rubbed considerably extends the period of use, the device also lends itself to slight overloads. This is necessary if the engine is used in powerful plants where voltage drops are possible;
- Ease of use. Start is performed by simple intuitive actions. For inclusion, a simple scheme is used;
- High efficiency, compared with synchronous machines.
Photo types of engines
In this case, an induction motor with a squirrel-cage rotor has disadvantages:
- High inrush current at rated speed. At the first start, strong electric network overloads are possible;
- Low level of protection. Despite the protected performance of the windings, motors of this type are susceptible to breakage. In particular, the winding often burns at constant voltage drops;
- The slip factor is too low.
Video: Three-phase asynchronous motors
Principle of operation
At a time when electric Energy is fed to the stator, each phase begins to emit a certain magnetic field. Each of them is rotated 120 degrees relative to the other. Due to this, the total flux of the magnetic field becomes rotating. These magnetic fluxes in the stator create electromagnetic induction. Due to the fact that the winding of the rotor is short-circuited, a definite current appears in it. This current interacts with the magnetic field and there is a starting reaction. At the moment of maximum rotation speed, the rotor is first suspended, producing a braking torque, and then starts to rotate. Next, there is a starting slip.
Photo - start circuit
This is a mechanical value that determines the ratio of the frequency of the stator magnetic field and the rotor speed. It is measured in percent. This is a very important indicator, because by its size it is possible to determine the difference in rotation of the rotor and stator, and, consequently, the operation of the engine.
At the initial stage of operation, the slip equals zero, but after decreasing the electromagnetic induction, it decreases or increases depending on the type of work. For example, at idle the indicator decreases, while at maximum speed the slip increases. The maximum slip is called critical. After the device starts to rotate at maximum speed, you need to monitor the slip. Otherwise, if the specified level is exceeded, the stability of the operation is disturbed. This entails not only the failure of individual parts of the device, in particular, steel plates, overloaded from friction, but also a complete breakdown of the engine. The calculation is carried out using the formula:
S = ((n1 - n2) / n1) * 100%
Where n1 is the rotation of the stator field, and n2 is the rotation of the rotor.
If the induction motor with a squirrel-cage rotor fails, its specifications, as a result, it stops. The average level of slip is considered to be from 1 to 8 percent. In some types, a slight deviation from this norm is allowed. On this basis, the electric asynchronous models work due to the interaction of the stator magnetic fields with the currents that arise in the rotor windings.
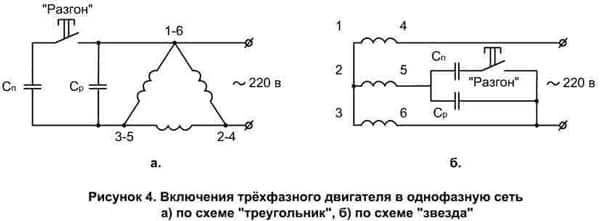
Photo - motor connection
Technical characteristics and designation
Each electric motor has its own operating parameters, so before you buy a device, you need to calculate the required data. Let us consider the technical characteristics of an asynchronous motor of the AIR type with a squirrel-cage rotor.
| Class | power, kWt | Current at maximum voltage 380, A | Turnovers, min -1 | Coefficient of efficiency,% |
| 56 A2 | 0,18 | 0,55 | 3000 | 66 |
| 56 V2 | 0,25 | 0, 73 | 3000 | 66 |
| 63 A2 | 0,37 | 0,9 | 3000 | 73 |
| 63 V2 | 0,55 | 1,3 | 3000 | 73 |
| 71 A2 | 0,75 | 1,3 | 3000 | 79 |
| 71 V2 | 1,1 | 2,6 | 3000 | 80 |
| 80 A2 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 3000 | 81 |
| 80 V2 | 2,2 | 5 | 3000 | 83 |
It is worth paying attention to the marking of engines. As you can see, after marking the engine mark, in the table above - this is the AIR series, followed by the letter and numerical definition of the engine class.
B - blown models, have protection from overheating, it is also called the motor-fan (for example, the ANM model);
B - built-in type;
C - high slip;
E - built-in brake;
E2 - manual stop;
3E - single-phase model with three-phase winding;
F - submersible motor engine;
Р3 - model for motor-generators;
Ш - sewing motor, but it will also be possible to connect to other similar devices of the required capacity;
К - crane performance;
П - possesses high indicators of accuracy at work, it is as much as possible protected from overloads;
A - used in nuclear production;
X - resistant to chemical attack.
Buy an induction motor with squirrel-cage rotor can be in a special electrotechnical store, the price will depend on its type and characteristics. On average, the cost varies from 800 rubles to several thousand.



