Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are situations of emergency care for fever, when the child needs to give the medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and apply antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? Which medications are the safest?
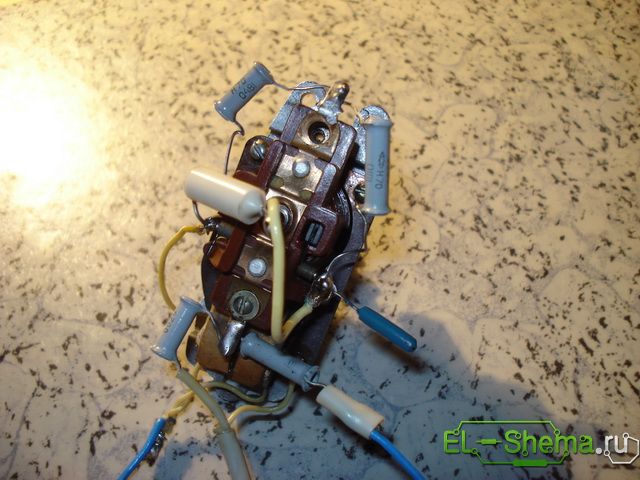
It became necessary to connect a universal collector motor. At first glance, there are no problems. Engine working, previously stood in the appropriate device and performed its intended function, that is, it was already connected. But the fact is that it was decided to use it in a completely different device. Conditions, possibilities of operation and requirements, both to his work, and to the service life have changed. After all, the mechanism in which it was supposed to re-engage the electric motor, will have to be assembled just for it. What to do with the existing harness? Can and most importantly, do you need to change something in it? In this particular case, this is an electric motor from an electric shaver.
The existing harness consists of capacitors and chokes designed to perform solely the functions of an interference suppression filter.

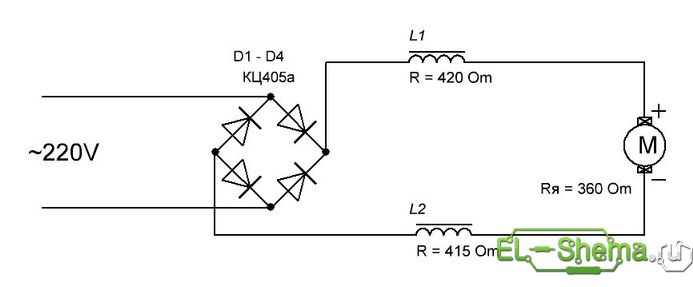
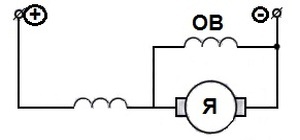
They do not influence the engine directly. It is known that the universal collector motor works equally well both on a constant and alternating current. Accordingly, without further ado, with the existing resistance of the stator winding sections (more than 800 ohms) plus the armature resistance (360 ohms), the connection can be made according to the following scheme:
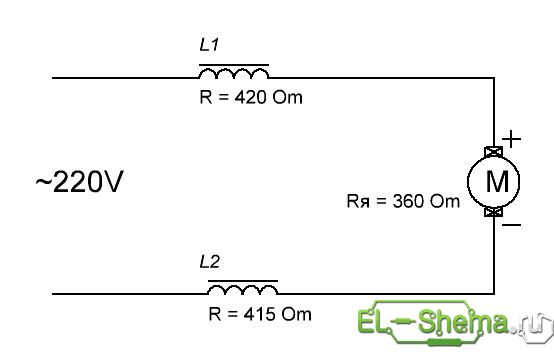
That was successfully tested.
![]()
However, at a constant current a little better. First, the efficiency of the motor with AC current is lower, secondly the service life of the brushes, the collector and the whole machine is shorter. The connection scheme will be as follows.
This version of the scheme was tested.
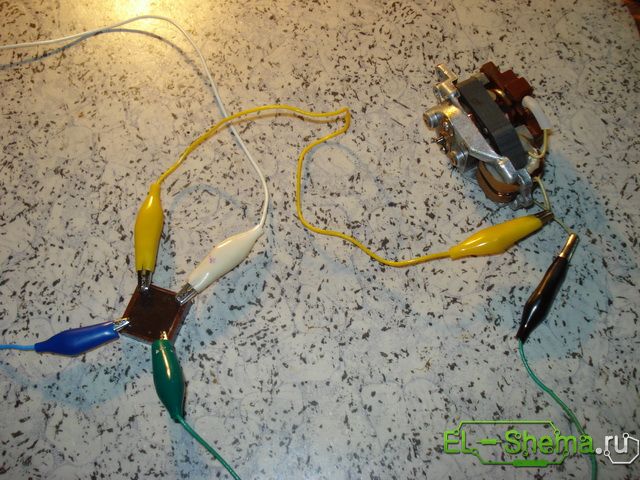

The sparks of the collector brushes became noticeably smaller. I decided to stop at this, but I was advised that when using this DC motor, a capacitor should be added after the diode bridge.
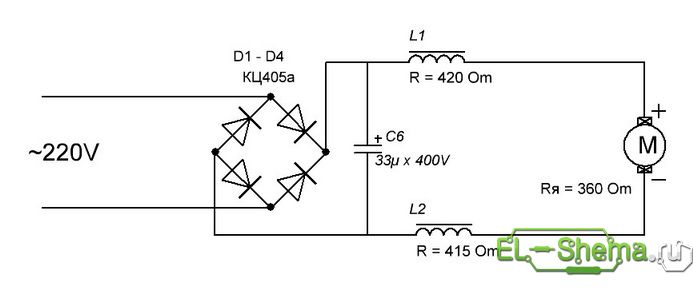
The capacitance of the capacitor was originally calculated from the formula, which seemed suitable for the given case. When connecting a capacitor with an estimated capacity of 200 mkf, the engine roared like a small electric drill, which made it necessary to reduce the capacity. The formula for calculating that did not justify itself, I do not see "sharing" the meaning.
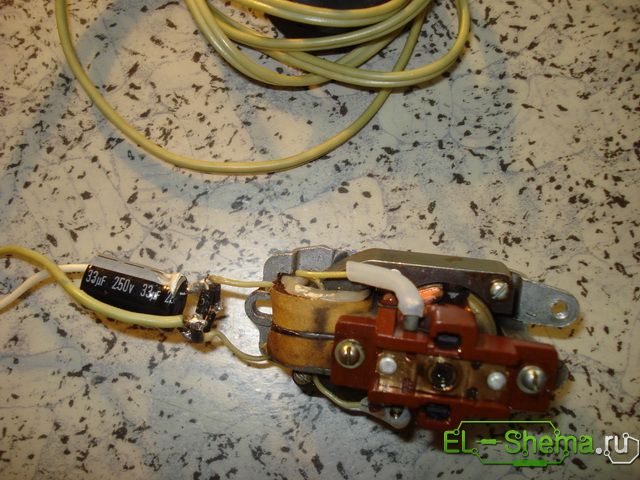

He stopped at a capacitor 33mkf x 250V and a diode bridge of diodes 1N4007 (as more compact). The work of the electric motor is satisfied.
Video of work of the electric motor
Nothing unusual, but it's really better to see than to hear (in this case, read) how he "buzzes" there, how he "sparkles" there. I wish you successful experiments, Babay.
In the household you rarely find a motor working on a direct current. But they are always installed in children's toys, which fly, ride, walk, etc. They always stand in cars: in different drives and fans. In electric transport, they are often used too.
In other words, motors are used direct current where a wide range of speed control and accuracy is required.
Electric power in the motor is converted into a mechanical one, causing it to rotate, and some of this power is expended on heating the conductor. The design of the electric DC motor includes an armature and an inductor that separate the air gaps. The inductor, consisting of additional and main poles, and the frame, is designed to create magnetic field. Anchor, assembled from separate sheets, winding working and collector, thanks to which the direct current is supplied to working winding, form a magnetic system. The collector is a cylinder, mounted on the shaft of the engine, assembled from copper plates isolated from each other. To its protrusions the ends of the armature winding are soldered. The current from the collector is removed by means of brushes fixed in a certain position in the brush holders, thereby ensuring the necessary pressure on the collector surface. Brushes with engine housing are connected by a traverse.
Brushes, in the course of work, glide over the surface of the rotating manifold, passing from one plate to the other. In this case, in parallel armature winding sections, a current change occurs (when the brush short-circuits the turn). This process is called commutation.
Under the influence of its magnetic field, an EMF of self-induction occurs in the closed section of the winding, causing an additional current that distributes the current unevenly on the brush surface, which leads to sparking.
Rotation frequency - one of its most important characteristics. It can be regulated in three ways: by changing the excitation flux, changing the magnitude of the applied voltage to the motor, changing the resistance in the anchor chain.
The first two methods are encountered much more often than the third, because of its inefficiency. The excitation current is regulated by any device, which is capable of changing the active resistance (for example, a rheostat). Adjustment by means of voltage variation requires the presence of a direct current source: a converter or a generator. Such regulation is used in all industrial electric drives.
Braking of an electric DC motor
For braking of electric drives with DPT there are also three options: Inhibition by opposing, dynamic and recuperative. The first is due to a change in the polarity of the current in the armature winding and the voltage. The second is due to the short-circuiting (through the resistor) of the armature winding. Electrical engine while working as a generator, converting it into electrical energy stored by it, which is released as heat. This braking is accompanied by an instant engine stop.
The latter occurs if the electric motor, included in the network, rotates at a speed that is higher than the idle speed. The EMF of the motor winding in this case exceeds the value of the voltage i in the network, which leads to a change in the opposite direction of the current in the motor winding, i.e. The engine gives energy to the network, switching to the generator mode. At the same time there is a braking torque on the shaft.
Advantages of DC motors
Comparing them with asynchronous motors, it is necessary to note excellent starting qualities, high speed (up to 3000 rpm), and also good adjustment. Of the shortcomings can be noted? Complexity of design, low reliability, high cost and repair and maintenance costs.
Principle of action of DPT
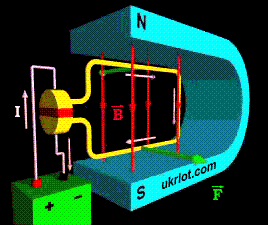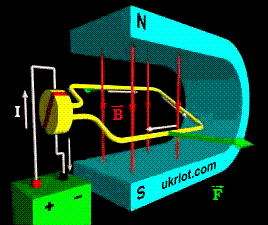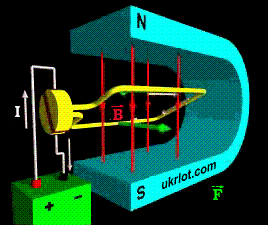
DPT, like any modern motor, operates on the basis of the "Rule of the Left Hand", with which everyone is familiar with the school and Faraday's law. When the current is connected to the lower winding of the armature in one direction, and to the winding of the upper one in the other, the armature starts to rotate, and the conductors placed in its grooves are pushed out by the stator magnetic field or the windings of the DC motor housing. The lower part is pushed to the right, and the upper part is pushed to the left. As a result, the anchor rotates until its parts are exchanged. To achieve continuous rotation, the polarity of the armature winding must be regularly swapped. This is exactly what the collector, switching at the rotation of the armature winding, does. The collector is supplied with a voltage from a source through a pair of pressure brushes made of graphite.
Principal schemes of DPT
Engine alternating current connects simply, in contrast to DPT. Typically, these high and medium power motors have separate terminals in the terminal box (from the winding and the armature). The armature is usually supplied with a full voltage, and on the winding - a current that can be regulated by a rheostat or a voltage variable. From the value of the current present on the excitation winding, the RPM of the AC motor is directly proportional.
Depending on which DC motor connection scheme is used, the electric motor can be a DC current, divided into self-excited and independent excitation (from a separate source).
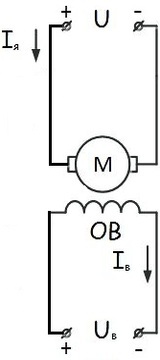
Scheme for connecting a motor with parallel excitation
It is similar to the previous one, but does not have a separate power source.
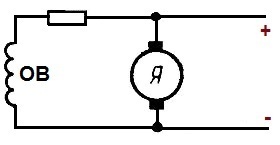
When you need a large starting current, engines with excitation are used in a series: in city electric transport (trolley buses, trams, electric locomotives).
![]()
The currents of both windings in this case are the same. Disadvantage - a constant load on the shaft is required, since when it is reduced by 25%, the speed of rotation sharply increases and the engine fails.
There are still motors that are rarely used - with mixed excitation. Their scheme is presented below.
Direct current electric motor with parallel excitation
Under the term "excitement" is understood the creation in electric machines The magnetic field, which is necessary to make the engine work. Excitation schemes are several:
- With independent excitation (the winding is powered from an extraneous source).
- Direct current electric motor with parallel excitation (power supply of the field winding and armature are connected in parallel) - shunt.
- With sequential excitation (both windings are connected in series) - serial.
- With mixed excitation - compound.
Brushless motors
But, the engine with brushes that wear out quickly and lead to sparking can not be used where high reliability is required, therefore, electric motors (electric bicycles, scooters, motorcycles and electric cars) have the most application of brushless electric motors. They are characterized by high efficiency, low cost, good specific capacity, long service life, small size, quiet operation.
The work of this engine is based on the interaction of the magnetic fields of the electromagnet and the permanent one. When the window is 21 century, and around full of powerful and inexpensive conductors, it is logical to replace the mechanical inverter with a digital one, add a sensor for the position of the rotor, decides at which point a particular coil needs to apply voltage, and get a brushless DC motor. As a sensor is more often used Hall sensor.
Since brushes are removed in this engine, it does not need regular maintenance. The DC motor is controlled by means of the control unit, which allows to change the speed of the motor shaft rotation, to stabilize the revolutions at a certain level (regardless of the load on the shaft).
There is a control unit consisting of several units:
- Systems of pulse-phase control of NRFU.
- The Regulator
- Protection.
Where to buy the electric motor
Many companies with world names produce today a 220 V DC electric motor. You can buy it in online stores, the managers of which will provide comprehensive online information regarding the chosen model. A large selection of models of such engines on the site http://www.aliexpress.com/w/wholesale-brushless-dc-motor.html, in the catalog of which it is possible to get acquainted with the cost of models, their description, etc. Even if there is no interesting engine in the catalog, you can order its delivery.
Collector AC motors are widely used as power units for household appliances, hand power tools, electrical equipment for cars, and automation systems. The circuit of connection of the collector motor of an alternating current, and also its device remind the scheme and the device of the electric motor of a direct current with consecutive excitation.
The field of application of such motors is due to their compactness, low weight, ease of operation, relatively low cost. The most demanded in this production segment are low-power electric motors with high speed.
- Simplified wiring diagram
- Engine management
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Typical malfunctions
Features of the design and principle of operation
In fact, the AC collector motor is a fairly specific device that has all the advantages of a DC machine and, therefore, has similar characteristics. The difference between these motors is that the AC motor stator housing for reducing eddy current losses is made from separate electrical steel sheets. The excitation windings of the alternating current machine are connected in series to optimize the operation in the domestic 220v network.
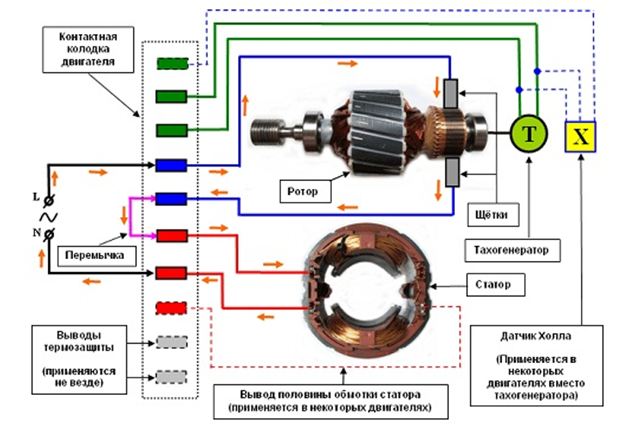
They can be either single-phase or three-phase; thanks to the ability to work from a constant and alternating current are also called universal. In addition to the stator and rotor, the structure includes a brush-collector mechanism and a tachogenerator. Rotation of the rotor in the collector motor results from the interaction of the armature current and the magnetic flux of the excitation winding. Through the brushes, the current is fed to a collector assembled from trapezoidal sections and is one of the rotor assemblies connected in series with the stator windings.
In general, the principle of operation of the collector motor of alternating current can be visually demonstrated using the experience known from school with the rotation of the frame placed between the poles of the magnetic field. If a current flows through the frame, it starts to rotate under the action of dynamic forces. The direction of movement of the frame does not change when changing the direction of current flow in it.
Sequential connection of the field windings gives a large maximum torque, but there are large idling speeds, which can lead to premature failure of the mechanism.
Simplified wiring diagram
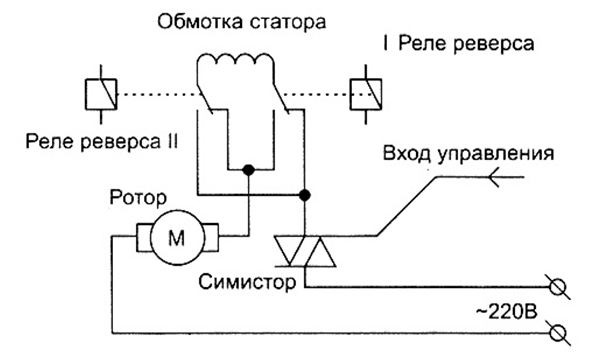
A typical circuit for connecting an AC collector motor can provide up to ten output contacts on the contact strip. The current from the phase L flows to one of the brushes, then it is transferred to the collector and the armature winding, after which the second brush and the jumper goes to the stator windings and goes to neutral N. This method of connection does not include the reverse of the motor due to the consequent connection of the windings leading to simultaneous replacement of the poles of magnetic fields and as a result the moment always has one direction.
The direction of rotation in this case can be changed only by changing the places of the output of the windings on the contact strip. The engine can be "directly connected" only with the stator and rotor connections connected (via a brush-collector mechanism). The half winding output is used to turn on the second speed. It should be remembered that with this connection, the motor runs at full power from the moment it is turned on, so it can be operated for no more than 15 seconds.
Engine management
In practice, engines with different ways regulation of work. The collector motor can be controlled using electronic scheme, in which the role of the regulating element is performed by a triac that "passes" the specified voltage to the motor. The triac works like a quick-wrench, on the gate of which control pulses come and open it at a given moment.
In circuits using a triac, the principle of action based on the full-wave phase control is implemented, in which the magnitude of the voltage applied to the motor is tied to pulses arriving at the control electrode. The frequency of rotation of the armature is directly proportional to the voltage applied to the windings. The operation principle of the collector motor control circuit is described in simplified terms by the following items:
- the electronic circuit sends a signal to the gate of the triac;
- the gate opens, current flows through the stator windings, giving the motor armature M rotation;
- tachogenerator converts into instantaneous electrical signals instantaneous values of the rotational speed, as a result, feedback is generated with the control pulses;
- as a result, the rotor rotates evenly under any load;
- the reverse of the electric motor is carried out by means of relays R1 and R
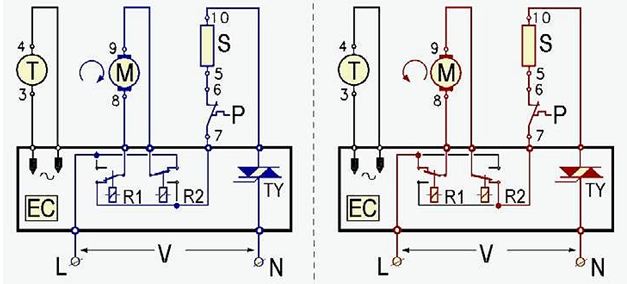
In addition to the triac, there is a phase-pulse thyristor circuit management.
Advantages and disadvantages
The undeniable advantages of such machines include:
- compact dimensions;
- increased starting torque; "Universality" - work on alternating and constant stress;
- speed and independence of the network frequency;
- soft speed control in a wide range by varying the supply voltage.
- reducing the longevity of the mechanism;
- sparking between and collector and brushes;
- increased noise level;
- a large number of collector elements.
Typical malfunctions
The most attention to self requires a brush-collector mechanism, in which sparking is observed even with the operation of the new engine. The used brushes should be replaced to prevent more serious malfunctions: overheating of the collector sipes, their deformation and flaking. In addition, it can occur interturn closure winding of the armature or stator, as a result of which there is a significant fall of the magnetic field or a strong arcing of the collector-brush transition.
Avoid the premature failure of the universal collector motor can be the competent operation of the device and the professionalism of the manufacturer in the process of assembling the product.
Due to its compact dimensions, the collector motor is widely used in the construction of hand power tools. It is successfully used instead of capacitor single-phase asynchronous. Mass application of collector motors is due to their high power, ease of operation and maintenance. Regardless of external differences and types of fasteners, they all have the same operating principle.
The device and the principle of operation
First of all, this is single-phase electric motor, where there is a consecutive excitation of the windings. For its operation, alternating or direct current can be used. For this reason, the collector motor is considered universal.
Most of these motors have in their design the basic elements in the form of a stator along with the excitation winding, as well as the rotor and two brushes as a sliding contact. A large role in the entire design is assigned to the tachogenerator. Its magnetic rotor is fixed at the end of the rotor shaft, and the coil is fixed by means of a locking ring or cover.
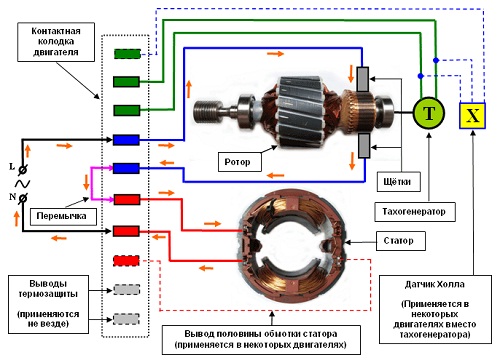
All the components of the electric motor are combined in a common design. They are connected by two aluminum covers, which directly form the motor housing. To output the contacts present in all elements, a terminal block is used, which makes it easy to include them in the general electrical circuit. To operate the belt drive, a pulley is pressed onto the rotor shaft.
Connection and management
The work of this type of motors is based on the interacting fields present in the stator and rotor, when passing through them electric current. The collector motor has a series circuit, through which windings are connected. The terminal block allows you to use up to ten contacts, increasing the number of connection options.
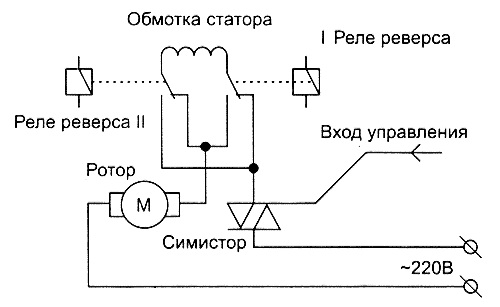
The simplest connection can be made, knowing only the location of the leads in the stator and brushes. With a normal connection, electrical protection means and devices are installed to limit the current. Therefore, direct connection from the network should be no more than 15 seconds.
The collector motor is controlled by a special electronic circuit. In this scheme, all power adjustment is performed by supplying voltage to the motor in the required quantity and connected in series with it.
In household electrical equipment, where electric motors are used, as a rule, electromachines with mechanical commutation are installed. This type of engine is called collector (hereinafter referred to as CD). We offer to consider different types of such devices, their operation principle and design features. We also talk about the merits and demerits of each of them, we will give examples of the scope of application.
By such a definition is meant an electric machine that converts electricity into a mechanical one, and vice versa. The design of the device assumes the presence of at least one winding connected to the collector (see Figure 1).
Figure 1. The collector on the rotor of the electric motor (marked in red)
In CD, this element is used to switch windings and as a sensor, which allows to determine the position of the armature (rotor).
Types of CD
Classify the data of the device is taken according to the type of power, depending on which there are two groups of CDs:
- Direct current. Such machines have a high starting torque, smooth speed control and a relatively simple design.
- Universal. Can operate as a permanent or alternating source of electricity. They are characterized by compact dimensions, low cost and easy operation.
The first, are divided into two subspecies, depending on the organization of the inductor, it can be on permanent magnets or special excitation coils. They serve to create the magnetic flux necessary to form a torque. CD, where excitation coils are used, are distinguished by the types of windings, they can be:
- independent;
- parallel;
- consistent;
- mixed.
Having dealt with the species, consider each of them.
CD of universal type
The figure below shows the appearance of the electric machine of this type and its main design elements. This performance is typical for almost all CDs.
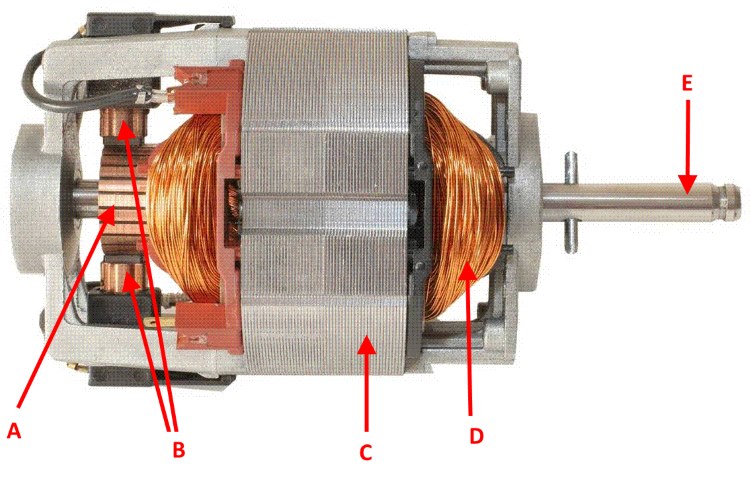
Notation:
- A is a mechanical commutator, it is also called a collector, its functions have been described above.
- В - brush holders, serve for fastening brushes (as a rule, from graphite), through which the voltage goes to the armature windings.
- C - Stator core (is recruited from plates, the material for which is electrical steel).
- D - Stator windings, this node refers to the excitation system (inductor).
- E - Anchor shaft.
In devices of this type, excitation can be sequential and parallel, but since the latter option is not currently produced, we will not consider it. As for the universal serial excitation CD, the typical scheme of such electric machines is presented below.

A universal CD can operate on an AC voltage due to the fact that when the polarity changes, the current in the field windings and the armature also changes direction. As a result, the torque does not change its direction.
Features and scope of universal CDs
The main disadvantages of this device are manifested when it is connected to alternating voltage sources, which is reflected in the following:
- reduction in efficiency;
- increased sparking in the brush-collector unit, and as a result, its rapid wear.
Previously, CDs have been widely used in many household electrical appliances (tools, washing machines, vacuum cleaners, etc.). At the moment, manufacturers have almost ceased to use this type of engines preferring brushless electric machines.
Now consider the collector electromachines working from sources of constant voltage.
CD with inductor on permanent magnets
Structurally, such electromachines differ from universal ones in that instead of excitation coils permanent magnets are used.

This kind of CD has received the greatest distribution in comparison with other electric machines of this type. This is explained by low cost due to the simplicity of the design, simple control of the rotation speed (depends on the voltage) and change of its direction (it is enough to change the polarity). Engine power directly depends on the field strength, created by permanent magnets, which introduces certain limitations.
The main scope of application is low-power drives for various equipment, often used in children's toys.

Among the advantages are the following qualities:
- high torque even at low speed;
- dynamism of management;
- low cost.
The main disadvantages are:
- low power;
- loss of magnets of their properties from overheating or over time.
To eliminate one of the main disadvantages of these devices (magnets aging), special windings are used in the excitation system, we turn to the consideration of such CDs.
Independent and parallel excitation coils
The former were given this name due to the fact that the windings of the inductor and the armature are not connected to each other and are fed separately (see A in Figure 6).

Figure 6. Circuit diagrams with independent (A) and parallel (V) excitation winding
The peculiarity of this connection is that the power supply U and U K must differ, otherwise the force moment will occur. If it is impossible to arrange such conditions, the armature and inductor coils are connected in parallel (see B in Figure 6). Both types of CD have the same characteristics, we considered it possible to combine them in one section.
The moment of force of such electromachines is high at low speed and decreases with its increase. Characteristically, the armature and coil currents are independent, and the total current is the sum of the currents passing through these windings. As a result, with a current drop of the excitation coil to 0, the CD with a high probability will fail.
The scope of such devices - power plants with a power of 3 kW.
Positive features:
- lack of permanent magnets removes the problem of their failure over time;
Minuses:
- the cost is higher than that of permanent magnet devices;
- the inadmissibility of a current drop below the threshold value on the excitation coil, since this will lead to a breakdown.
Serial excitation coil
The scheme of such a CD is shown in the figure below.

Since the windings are connected in series, the current in them will be equal. As a result, when the current in the stator winding becomes smaller than the rated current (this occurs with a small load), the power of the magnetic flux decreases. Accordingly, when the load increases, the power of the flow proportionately increases, up to the full saturation of the magnetic system, after which this dependence is violated. That is, in the future the increase in current in the coil winding of the armature does not lead to an increase in the magnetic flux.
The above feature is manifested in the fact that a CD of this type is not allowed to run at a load a quarter of the nominal. This can lead to the fact that the rotor of the electric machine will sharply increase the speed of rotation, that is, the engine will go "in raznos". Accordingly, this feature introduces limitations on the scope of application, for example, in mechanisms with belt transmission. This is due to the fact that when it breaks the electric machine starts to work in idle mode.
This feature does not apply to devices whose power is less than 200 W, they are allowed to fall loads up to idle mode.
The advantages of a CD with a serial coil are the same as those of the previous model, except for the simplicity and dynamism of control. As for the minuses, they should include:
- high cost in comparison with analogues on permanent magnets;
- low level of torque at high speed;
- since the stator and field windings are connected in series, there are problems with controlling the speed of rotation;
- work without load leads to a breakdown of CD.
Mixed excitation coils
As can be seen from the circuit shown in the figure below, an inductor on a CD of this type has two coils connected in series and parallel to the winding of the rotor.

Typically, one of the coils has a greater magnetizing force, so it is considered as the main, respectively, the second - an additional (auxiliary). Counter and co-ordinate inclusion of coils is permissible, depending on this, the intensity of the magnetic flux corresponds to the difference or the sum of the magnetic forces of each winding.
With the on-off, the characteristics of the CD become close to the corresponding parameters of the electric machines with sequential or parallel excitation (depending on which of the coils is the main one). That is, such inclusion is actual, if it is necessary to get the result in the form of constant speed of rotation or their increase with increasing load.
The consistent inclusion leads to the fact that the characteristics of the CD will correspond to the average value of the indicators of electric machines with parallel and consecutive excitation coils.
The only drawback of this design is the highest cost in comparison with other types of CD. The price is justified by the following positive qualities:
- magnets are not obsolete, in the absence of such;
- a low probability of failure in abnormal operating modes;
- high torque moment at low speed;
- simple and dynamic control.