Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are situations of emergency care for fever, when the child needs to give the medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and apply antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? Which medications are the safest?
Incandescent lamps
Ordinary light bulbs, which are familiar to all of us, and their main advantage is the pleasant color of light that they emit. The colors of objects, as a rule, look more precisely under a lamp of this type. Incandescent bulbs spend a lot of electricity, as they produce a lot of heat.
Incandescent lamps produce 8-12 lumens of light per 1 W of consumed energy. The more powerful the incandescent lamp, the more lumens of light it produces per unit of power consumed. For example, one 100W lamp gives almost exactly the same amount of light (1360 Lumens) as there are two 60W lamps (1420 lumens).
The inconvenience of these lamps is that these lamps are ineffective in modern standards and have a relatively short service life (about 1000 hours). Incandescent lamps are available in a variety of shapes and sizes and have a variety of different socles.
Matte or transparent?

- The basic principle of choice between matt and transparent lamps is as follows:
- If the luminaire has transparent plafonds, use a transparent light bulb
- If the luminaire has matt plafonds, use matt light bulbs
- In the children's room, use matte light bulbs. Kids love to look at the lamp, and these lamps give a more comfortable for children's eyes light
- In crystal lamps, lamps with a large number of pendants, crystals and other light refractive parts, use transparent light bulbs, since the bright open spiral of a transparent incandescent lamp gives the necessary play of light
Reflector lamps
Reflector incandescent lamps have a silvered surface - this is their only difference from conventional incandescent lamps. The reflective surface directs light in a certain direction. Such lamps are usually designed for spotlights. The most common types of these lamps are R50, R63, PAR38.
Halogen light bulbs
Halogen bulbs - bulbs with filament filament, containing halogen gas. They give, like incandescent lamps, a very attractive light that resembles a sunlight. But they are somewhat more effective than incandescent lamps, since they produce 20% more light for power consumption and work longer, about 2000 hours.
The main advantage of a halogen lamp is its small size. The appearance of this lamp allowed the designers to create new designs for lamps and plafonds. Halogen lamp type GU10, with built-in reflector is the most common lamp for recessed luminaires. And it is used in many luminaires of directional light (spots).
The appearance of powerful linear halogen lamps type R7S, 300W power, made it possible to create a class of floor lamps that give a soft, pleasant reflected from the ceiling lighting, and illuminate the entire room. The main types of halogen lamps are: G9, G4, R7S, GU10. Each type is produced in several capacities.
Fluorescent lamps
They are - energy saving light bulbs. Contain gas in the tube and do not have a thread. They have been used everywhere for many years and are better known as long white pipes, which are usually found on the ceilings of public institutions.
The newest technologies have reduced the size and improved the efficiency of light bulbs. There appeared compact fluorescent lamps, which are now called in the wide use of Energy-saving ones. Now there are many different forms and options for the power of light bulbs.
The term "energy-saving" should be applied to other types of lamps with low energy consumption, such as LED.
Advantages of compact fluorescent lamps - low energy consumption due to the allocation of a small amount of heat - consume 20% of the energy of a conventional light bulb, with the same emitted light flux. Long service life, up to 8000 hours.
Compact fluorescent lamps produce 50-60 lumens per W, five times more light per unit of power consumed than incandescent lamps. They are ideal for use where light should be switched on for a long time. Many leading manufacturers of lamps have "warm white" lamps, with an improved color of light. The color, color impression that the fluorescent lamp creates during operation is characterized by the Color Temperature parameter. Unit of measure Kelvin.
- For fluorescent lamps, the color temperature is divided into the following main categories:
- Below 3300 K - white, warm light
- 3300-5000 K neutral light
- Over 5000 K "cold" light
Information on the color temperature of fluorescent lamps is placed on their packaging.
The disadvantages of this type of lamp are their high cost and not as pleasant as incandescent lamps, light. Also, practically with all energy-saving fluorescent lamps, you can not use a dimmer (rheostat power). Only a few of the world's leading manufacturers of lamps, in particular Philips, have in the range of several items of fluorescent lamps that can work with dimmers.
Due to the small heat emission, energy-saving lamps can be used (if they fit the size of the plafond) to increase the amount of light from the luminaires. For example, a chandelier designed for 5 x 40 W incandescent lamps = 200 watts. We want more light from her. We can not use more powerful incandescent lamps, since we have a limitation on the lamp power in the cartridge. (From a more powerful lamp the cartridge can melt). But if in this chandelier use five energy saving lamps, each power is 20W, then due to the fact that a 20W energy saving lamp gives a light like a 100W incandescent lamp, such a chandelier will give light as a chandelier with 5 * 100W incandescent.
On the popular wave of movement to reduce energy consumption, modern manufacturers are now paying much attention to the development and production of series of lamps designed specifically for use with energy-saving lamps and sold in the kit immediately with these lamps.
LED Light Bulbs
LED lamps are made on the basis of LED.
An LED is a semiconductor that converts an electric current into light. The basis of the LED is a semiconductor crystal. During the passage electric current Through this crystal there is light radiation. The color of the radiation can be different, depending on the composition of the crystal. In LEDs for household lighting, a semiconductor crystal of gallium nitride is used, this crystal gives a blue color. To obtain white light on the crystal, a phosphor is applied. Luminophor is a complex chemical substance that is excited by the light of a crystal and gives its own emission of yellow light. In this case, the phosphor absorbs only a part of the light from the semiconductor crystal, and passes a part. As a result of mixing blue light from gallium nitride, which has passed through the phosphor, and yellow light from the phosphor, white light is obtained.
LED light sources have huge advantages over all other lamps:
- Economical. LEDs convert to light radiation up to 80% of the received electricity. Light output of the best modern LEDs has reached 160 lumens per watt of power. This is almost twice as much as energy-saving fluorescent lamps and almost twenty times greater than incandescent bulbs.
- Long service life - 50 thousand hours or more. This will ensure the operation of the LED lamp for about 20 years without replacement, when it is used 8 hours a day.
- High mechanical strength - unlike all lamps made from glass, the LED is resistant to external influences.
- The number of on / off switches has no effect on the life of the LED.
- Small size, compact - unlike conventional lamps, which constructively needs a bulb - the LED is just a small plate. The small size of the LED opens up the possibility of creating new types of luminaires. It is possible that the expanding use of LEDs in household lighting can change the very approach to all forms and types of fixtures. Now, most of the LEDs for household lighting are placed inside lamps with the usual shapes and with a standard cap.
Distribution of LED lamps is restrained only, so far, by a high price. But the prices for light-emitting diodes decrease every year and in the near future, as many predict, all illumination in a life will be created by means of light-emitting diodes.
Modern technologies in lighting significantly expanded, but at the same time complicated the choice of light bulbs for home use. If earlier in 90% of the apartments, apart from the usual incandescent bulbs from 40 to 100 W, there was not much that happened, today there are a lot of varieties and types of lighting lamps.
Buy in the store the right kind of lamp for the lamp is not such a simple task.
What do you want from high-quality lighting in the first place:
- comfort for the eyes
- energy saving
- harmless use

Type of socle
Before buying a light bulb in the first place it is important to determine the type of socle required. Most household lighting fixtures use two types of threaded base:

They differ in diameter. The numbers in the notation and indicate its size in millimeters. That is, E-14 = 14mm, E-27 = 27mm. There are also adapters for fixtures from one lamp to another. 
If the chandelier plafonds are small, or the luminaire has some specificity, then a pin base is used.
It is indicated by the letter G and a number that indicates the distance in millimeters between the pins.
The most common are:
- G5.3 - which simply plug into the connector of the luminaire
- GU10 - first inserted and then rotated a quarter turn

The projectors use the R7S socket. It can be for both halogen and LED lamps. 
The power of the lamp is selected based on the limitation of the lighting device in which it will be installed. Information on the shape of the cap and the power limitation of the lamp used can be seen:
- on the box of the purchased lamp
- on the plafone of the already established
- or on the bulb itself

Flask shape
The next thing you need to pay attention to is the shape and size of the bulb. 
A flask with a threaded base can have:

Pear-shaped are designated by nomenclature - A55, A60; ball-type - the letter G. The numbers correspond to the diameter.
Candles are marked with a Latin letter - C. 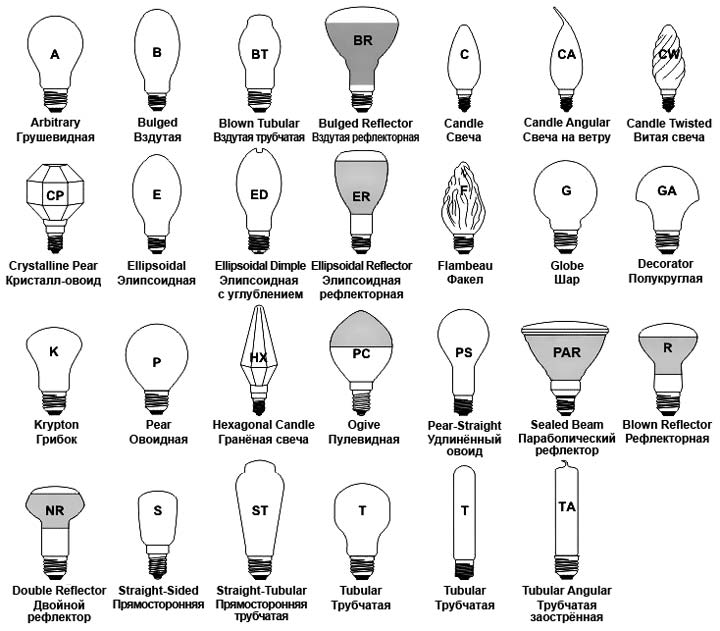
A flask with a pin cap has the form:
- small capsule
- or flat reflector
Norms of illumination
Brightness of lighting is an individual concept. However, it is commonly believed that for every 10m2 at a ceiling height of 2.7m, a minimum illumination of the equivalent of 100W is required. 
The illumination in lux is measured. What is this unit? In simple words - when 1 lumens illuminates 1m2 of the area of the room, then this is 1 suite. 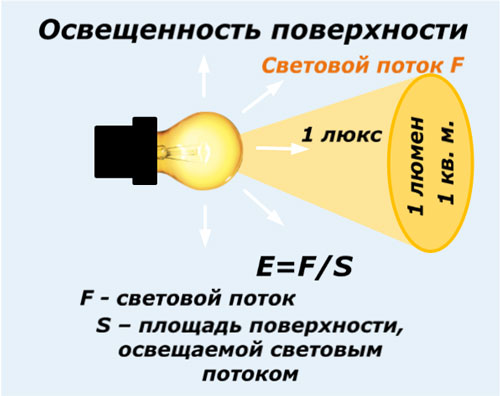
For different rooms the norms differ. 
The illumination depends on many parameters:
- from the distance to the light source
- colors of surrounding walls
- reflection light flux from foreign objects
Illumination is very easy to measure with the help of familiar smartphones. It is enough to download and install a special program. For example - Luxmeter ( link) 
True, such programs and camera phones are usually lying compared to professional devices luxmeters. But for domestic needs, this is more than enough.
Incandescent and halogen light bulb
The classic and most inexpensive solution for lighting an apartment is everyone habitual lamp incandescent, or its halogen version. Depending on the type of socle - this is the most affordable purchase. Incandescent and halogen light bulbs give comfortable warm light without flicker and do not emit any harmful substances. 
However, halogen lamps are not recommended to be touched by the flask. Therefore, they should go packed in a separate bag.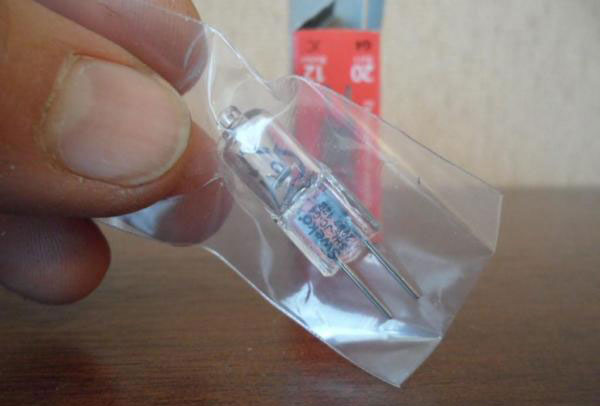 
When the halogen burns, it heats up to a very high temperature. And if you are touching her bulb with greasy hands, then a residual tension will form on it. As a result of this, the spiral in it will burn much faster, thereby reducing its service life. 
In addition, they are very sensitive to voltage surges and often because of this burn out. Therefore, they are put together with soft start devices or connected through dimmers.
Halogen lamps are mostly produced for work from single-phase network with a voltage of 220-230 volts. But there are also low-voltage 12 volts, which require connection through a transformer for the appropriate type of lamps. 
Halogen shines brighter than usual, about 30%, and power consumes the same. This is achieved due to the fact that it contains a mixture of inert gases.
In addition, during operation, particles of tungsten elements return back to the filament. In a conventional lamp, there is a gradual evaporation over time and subsidence of these particles on the flask. The light bulb dims and works half as much as the halogen lamp.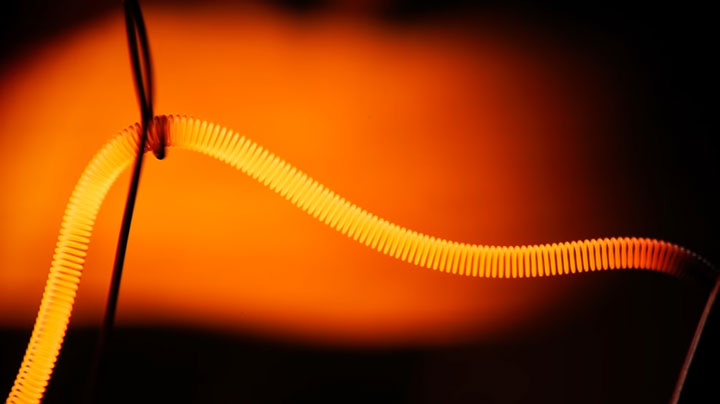 
Color transmission and light flux
The advantage of conventional incandescent lamps is a good color rendering index. What it is?
Roughly speaking, this is an indicator of how much light in the scattered stream contains light close to the solar one.
For example, when sodium and mercury lamps illuminate the night streets, it's not entirely clear what color cars and clothes people have. Since these sources have a poor color rendering index - in the region of 30 or 40%. If we take an incandescent lamp, then the index is already over 90%. 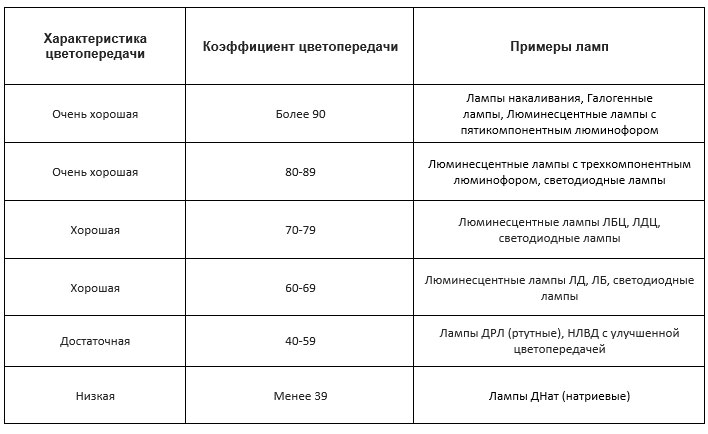
Now the sale and production of incandescent lamps over 100W are not allowed in retail stores. This is done for reasons of preserving natural resources and saving electricity.
Some still erroneously choose lamps guided by the inscriptions of power on the package. Remember that this figure does not speak about how bright it shines, but only about how much electricity it consumes from the network.
The main indicator here is the luminous flux, which is measured in lumens. It is on him and you need to pay attention when choosing. 
Since many of us used to target the popular 40-60-100W capacities, manufacturers for modern economy lamps always on the package or in the catalogs indicate that their power corresponds to the power of a simple incandescent bulb. This is done solely for the convenience of your choice. 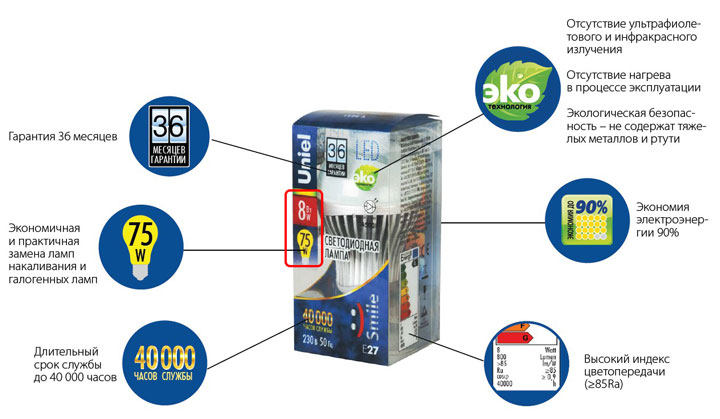
Luminescent - energy-saving
Fluorescent lamps have a good level of energy saving. Inside of them there is a tube from which a bulb is made, powder coated with a phosphor. This provides a glow of 5 times brighter than incandescent lamps at the same power. 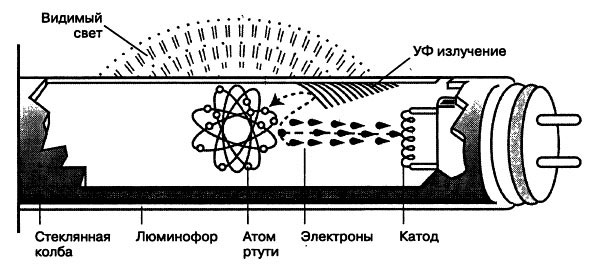
Luminescent is not very eco-friendly due to the spraying of mercury and the phosphor inside. Therefore, careful disposal through certain organizations and containers of reception of used bulbs and batteries is required.
They are also subject to flicker. Check it easily, just look at their glow on the display through the smartphone's camera. It is for this reason that it is not advisable to place such bulbs in living quarters where you are constantly on.
LED Light
LED lamps and lamps of various shapes and designs are widely used in various spheres of life. 
Their advantages:
Electricity saving for LEDs is more significant than for luminescent and energy-saving ones. They consume about 8-10 times less than incandescent lamps. 
If we roughly take the averaged parameters for power and light flux, then we can obtain such data: 
These results are exemplary and in reality will always differ, as much depends directly on the level of voltage, the brand of the manufacturer and many other parameters.
For example, in the United States, in one fire station, a regular incandescent bulb, which is more than 100 years old, still burns. Even a special website was created, where you can watch it through a web camera, online. 
Everybody is waiting for when it will burn to fix this historic moment. You can see.
Light flow
LED and energy-saving lamps have the ability to give different colors of light.
In order not to search for incomprehensible numbers and quickly distinguish the magnitude of the light flux, manufacturers often on the packaging produce visual color designations:
This is precisely its feature and advantage, which is widely used in open luminaires. 
For example, if we are talking about crystal chandeliers, then when using an ordinary LED lamp in it, because of its matte surface, the crystal will "play" and will not overflow. It shines and reflects light only when the ray is directed.
In this case, the chandelier does not look very rich. The use of filaments in them, reveals all the advantages and beauty of such a lamp. 
These are all the main types of lighting lamps widely used in apartment and apartment building. Choose the option you need according to the above characteristics and recommendations, and equip your home correctly and comfortably.
Among all wiring and wiring products, lighting equipment has the richest assortment. This is because the lighting elements carry in themselves not only purely specifications, but also design elements. The possibilities of modern lamps and luminaires, their design diversity are so great that it is no wonder to get lost. For example, there is a whole class of fixtures designed exclusively for gypsum plasterboard ceilings.
Numerous types of lamps have a different nature of light and are operated under unequal conditions. In order to understand what kind of lamp should stand in this or that place and what are the conditions for its connection, it is necessary to briefly study the main types of lighting equipment.
All lamps have one common part: the plinth, by means of which they are connected to the lighting wires. This applies to those lamps in which there is a socket with a thread for mounting in the chuck. Dimensions cap and cartridge have a strict classification. It is necessary to know that in household conditions lamps with 3 kinds of socles are used: small, medium and large. In technical terms, this means E14, E27 and E40. The plinth, or cartridge, E14 is often called the "minion" (in the figure with the French - "small").
The most common size is E27. E40 is used in street lighting. Lamps of this marking have a power of 300, 500 and 1000 W. The figures in the name denote the diameter of the cap in millimeters. In addition to the plinths, which are screwed into the socket by thread, there are other types. They are of the pin type and are called G-socles. Used in compact fluorescent and halogen lamps to save space. Using 2 or 4 pins, the lamp is attached to the lamp socket. There are many kinds of G-socles. The main ones are: G5, G9, 2G10, 2G11, G23 and R7s-7. Lamps and lamps always indicate information about the base. When choosing a lamp, you need to compare this data.

Power lamps - one of the most important characteristics. On the cylinder or socle, the manufacturer always indicates the power on which the luminosity lamp. This is not the level of light that it radiates. In lamps of a different nature of light, the power is quite unlikely.
For example, powersave lamp at a specified power of 5 watts will shine no worse incandescent lamps in 60 watts. The same applies to fluorescent lamps. The luminosity of the lamp is calculated in lumens. As a rule, this is not indicated, so when choosing a lamp, it is necessary to focus on the advice of sellers.
Light output means that for 1 W of power the lamp gives so many lumens of light. Obviously, an energy-saving compact fluorescent lamp is 4-9 times more economical than incandescent. It is easy to calculate that a standard 60 watt lamp gives about 600 lumens, whereas a compact lamp has the same value at a power of 10-11 W. So it will be more energy-efficient.

Incandescent lamps
(LON) - the very first source of electric light, which appeared in the home. It was invented in the middle of the 19th century, and although it has undergone many reconstructions since that time, the essence remained unchanged. Any incandescent lamp consists of a vacuum glass bulb, a plinth on which contacts and a fuse are located, and filaments that emit light.

Spiral of incandescence is made of tungsten alloys, which easily withstand an operating combustion temperature of +3200 ° C. To the thread does not burn out instantly, in modern lamps, some inert gas, for example argon, is pumped into the cylinder.
The principle of the lamp is very simple. When passing a current through a conductor of small cross-section and low conductivity, part of the energy goes to the heating of the helix-conductor, which causes it to glow in visible light. Despite such a simple device, there are many kinds of PESs. They vary in shape and size.

Decorative lamps (candles): the balloon has an elongated shape, stylized as an ordinary candle. Usually, they are used in small lamps and sconces.
Painted lamps: glasses of cylinders have a different color for decorative purposes.

Mirror lamps called lamps, part of the glass cylinder which is covered with a reflective composition for the direction of light by a compact beam. Such lamps are most often used in ceiling lamps to direct light down without lighting the ceiling.
Lamps for local lighting work under voltage 12, 24 and 36 V. They consume a little energy, but the lighting is appropriate. They are used in hand lanterns, emergency lighting, etc. LON still remain in the forefront of the light source, despite some shortcomings. Their minus is a very low efficiency - no more than 2-3% of the energy consumed. Everything else goes into heat.

The second disadvantage is that the LONs are not safe from the fire point of view. For example, an ordinary newspaper, if put on a 100-watt bulb, flashes in about 20 minutes. Needless to say, in some places, LON can not be exploited, for example in small lampshades made of plastic or wood. In addition, such lamps are short-lived. The lifespan of PES is about 500-1000 h. Among the advantages can be attributed to cheapness and ease of installation. PES do not require any additional devices to work, like fluorescent ones.
Halogen lamps

Halogen lamps little different from incandescent lamps, the principle of operation is the same. The only difference between them is the gas composition in the tank. In these lamps, iodine or bromine is mixed with the inert gas. As a result, it becomes possible to raise the temperature of the filament and to reduce the evaporation of tungsten.

That is why halogen lamps can be made more compact, and their service life rises by 2-3 times. However, the temperature of glass heating increases very significantly, therefore halogen lamps are made of quartz material. They do not tolerate contamination on the flask. Touching an unprotected hand to the balloon is impossible - the lamp will burn very quickly.

Linear halogen lamps Used in portable or stationary searchlights. They often have motion sensors. Such lamps are used in gypsum plasterboard constructions.

Compact lighting devices have a mirror coating.
To cons halogen lamps it is possible to attribute sensitivity to voltage drops. If it "plays", it is better to purchase a special transformer, equalizing the current.

Fluorescent lamps
Principle of operation fluorescent lamps seriously differs from PECs. Instead of a tungsten filament in a glass bulb of such a lamp, mercury vapor is ignited by an electric current. The light of a gas discharge is practically invisible, since it is emitted in the ultraviolet. The latter causes the phosphor to glow, with which the walls of the tube are covered. This light we see. Externally, and by the method of connection, fluorescent lamps also differ greatly from PON. Instead of a threaded cartridge on both sides of the tube, there are two pins fixed as follows: they must be inserted into a special cartridge and rotated in it.

Fluorescent lamps have a low operating temperature. To their surface, you can safely rest your palm, so they are installed anywhere. A large surface of the glow creates an even scattered light. That is why they are also called lamps daylight . In addition, varying the composition of the phosphor, you can change the color of light, making it more acceptable to the human eye. In terms of service life, fluorescent lamps outnumber incandescent lamps by almost 10 times.

Minus fluorescent lamps is impossibility direct connection to the mains. You can not just throw 2 wires on the ends of the lamp and plug the plug into the outlet. For its inclusion, special ballasts are used. This is due to the physical nature of the glow of the lamps. Along with electronic ballasts, starters are used, which, as it were, ignite the lamp at the moment of switching on. Most luminaires for fluorescent lamps are equipped with built-in glow mechanisms like electronic ballasts (ballasts) or throttles.

Marking of fluorescent lamps not similar to the simple designations of PECs, which have only a power index in watts.
For the lamps under consideration, it is as follows:
- LB - white light;
- LD - daylight;
- ЛЕ - natural light;
- LHB - cold light;
- LTB - warm light.
The numbers following the lettering indicate the first digit - the degree of color rendition, the second and third - the luminescence temperature. The higher the degree of color rendition, the more natural is the lighting for the human eye. Consider an example related to the glow temperature: a lamp labeled LB840 means that this temperature is 4000 K, the color is white, daytime.
The following values mean the marking of the lamps:
- 2700 K - the superheated white,
- 3000 K - warm white,
- 4000 K - natural white or white,
- more than 5000 K - cold white (daytime).
Recently, the appearance of compact fluorescent energy-saving lamps in the market has produced a real revolution in lighting equipment. The main shortcomings of fluorescent lamps were eliminated - their bulky dimensions and the inability to use conventional rifled cartridges. The ballasts were mounted in the lamp socket, and the long tube curled into a compact spiral.

Now the variety of types of energy-saving lamps is very large. They differ not only in their power, but also in the form of discharge tubes. The advantages of such a lamp are obvious: there is no need to install electronic ballast for launch, using special luminaires.
Cost-effective fluorescent lamp replaced the usual incandescent lamp. However, it, like all fluorescent lamps, has drawbacks.

The disadvantages of fluorescent lamps are several:
- such lamps do not work well at low temperatures, and at -10 ° C and below they begin to shine dimly;
- long start-up time - from a few seconds to several minutes;
- a low-frequency rumble is heard from the electronic ballast;
- do not work together with dimmers;
- relatively expensive;
- do not like frequent on and off;
- the lamp includes harmful mercury compounds, so it requires special disposal;
- if you use the backlight indicators in the switch, this lighting equipment starts to flicker.

No matter how hard the producers try, the light of fluorescent lamps is not very similar to the natural one yet and cuts the eyes. In addition to energy saving lamps with ballasts, there are many varieties without built-in electronic ballast. They have completely different types of socle.
Principle of luminescence high pressure mercury lamp (DRL) - arc discharge in mercury vapor. Such lamps have a high luminous efficiency - at 1W there are 50-60 lumens. They are started by means of ballasts. The disadvantage is the spectrum of luminescence - their light is cold and sharp. Lamps DRL most often used for street lighting in luminaries such as "cobra".

LED lamp
LED lamp - this high-tech product was first constructed in 1962. Since that time lED lamp began to be gradually introduced to the market of lighting products. The LED by the principle of action is the most common semiconductor, in which part of the energy in transition p-n is reset in the form of photons, that is, visible light. Such lamps have simply stunning characteristics.

They are ten times superior to PACs for all indications:
- durability,
- light output,
- economy,
- strength, and so on.
They have only one "but" - this is the price. It is about 100 times higher than the price a conventional lamp incandescent. However, work on these unusual light sources continues, and we can expect that soon we will rejoice in the invention of a cheaper model than its predecessors.

Note! Due to the unusual physical characteristics of the LEDs, they can be used to make real compositions, for example in the form of a starry sky on the ceiling of the room. It is safe and does not require much energy.
Currently, there is a wide selection of different lamps, each of which has its own unique characteristics. For certain conditions you can choose the most appropriate lighting device.
The following basic types are on the market:
- Incision:
- vacuum;
- halogen;
- krypton;
- Gas Discharge:
- mercury
- DRL;
- DRE (metal halide);
- xenon;
- neon, argon, etc.
- mercury
- LED Light.
Characteristics

In the detailed description, we will consider the following characteristics:
- base (cartridge) - the place of attachment of the bulb;
- color rendition;
- light output (light efficiency);
Light output
Indicates how many lumens give a light source at a power of 1W. For example, a standard incandescent lamp has a luminous efficiency of 10 lm / W, a luminescent lamp - 70 lm / W, so at the same power, the latter will glow 7 times brighter.
In a talk about light output, it is necessary to mention the so-called energy-saving technologies.
Essentially, energy saving means: little consume - a lot of shining. In this context, sodium light sources have the highest energy efficiency (see comparative table).
However, it is customary to call either LED or fluorescent lamps.
Color Rendering Ratio (Ra)

Shows how natural colors look in the emitted light. The larger the given number, the better the source characteristics, the closer its light to natural light.
The qualitative gradations of the coefficient are indicated in the table:
| Ra | color rendering quality |
| <39 | not enough |
| 40–59 | is sufficient |
| 60–79 | oK |
| >80 | very good |
Colorful temperature

Determines the color of the luminous object, measured in degrees Kelvin (K). Depending on the temperature of light, the surrounding objects look somewhat different.
An ordinary white sheet of paper can have shades from warm and yellowish at 2500 K (candle), to radiant blue at a temperature of 6500 K.
Distinguish the following shades of light:
The light of different temperatures affects the perception of man differently (let us recall at least theatrical productions and various installations where light plays an essential role in the transmission of the emotional state).
Warm white (2700 - 4200 K) light helps to relax, adjusts to a calm mood. Suitable for lighting bedrooms, living rooms and dining rooms.
Daylight (4200 - 5500 K) helps to concentrate on the tasks, most suitable for office premises and for lighting the work area (including in the kitchen), for make-up.
Cold white light (5500 - 6000 K) is quite energetic, suitable for bathrooms, kitchens (working surface, but not a dining table).
Classification
Incandescent lamps
In the recent past, the most common type. Lighting devices of this type can be used both on stationary and portable devices (for example, hand lanterns).
Light emits a heated tungsten filament, placed in a flask (balloon), from which air is pumped (hence the term "vacuum").
Incandescent bulbs on the composition of gas in the balloon are divided into the actual vacuum, krypton, halogen.
Vacuum

The surface of the bulb can be either transparent or matt, which allows for a softer light without the use of a protective cap. Also, the upper part of the cylinder can be covered with a mirror paint to direct the light stream downwards (in the case of ceiling lighting).
Lamps for portable sources operate from 12, 24, 36 V.
For stationary - 220 V, 50 Hz (city electric network).
The main disadvantage of such light sources is low efficiency: only 2-3% goes to lighting. The rest of the energy is dissipated in the form of heat (hence the low light output).
The type of fixing used is the Edison base (E-socle); differs in its diameter (in mm), indicated in the marking:
- E10 - used for pocket flashlights;
- E14, also called "minyon" (small);
- E27 - standard;
- E40 is used for outdoor lighting;
Pros:
- wide distribution of equipment;
- low price;
- convenience of installation;
Minuses:
- low efficiency;
- short working time (500-1000 hours);
- fire hazard (can not be used in plastic and wooden structures);
Characteristics:
Krypton lamps

The lamp is incandescent, in the cylinder of which is added krypton (inert gas). They have smaller dimensions and longer operating time than vacuum ones (1000-2000 h), they are not sensitive to voltage drops.
Characteristics:
Halogen lamps

As the name implies, the flask contains a pair of halogens (elements of group 17 of the Mendeleev-bromine or iodine table). Addition of these gases can significantly increase the operating time and increase light output, compared with vacuum analogs.
Use the E or G-cap (see fluorescent lamps).
Pros:
- Service life up to 2000-4000 h.
- Small size, the possibility of use in gypsum plasterboard (for example, suspended ceilings).
Minuses:
- Sensitivity to contamination (the installation must be carried out in gloves, if grease gets to the surface of the bulb, the device very quickly fails).
- Sensitivity to voltage drops.
Currently, a new type of halogen sources with an infrared coating that transmits visible light and reflects thermal radiation has been developed, they have reduced power consumption and extended operating time compared to uncoated analogs.
Characteristics:
Gas-discharge lamps
The physical basis of luminescence is an electrical discharge passing through a gas sealed in a tube.
Depending on the inner contents of the tube, the following types are distinguished:
- Mercury:
- DRL;
- luminescent;
- Sodium.
- Neon, xenon, argon, etc.
The luminescence process must be started using a special ballast (PFM). At present, lamps are produced, where the PCM can be either integrated in the cartridge or mounted separately.
Mercury

All mercury-containing devices are highly toxic, they need to be disposed of through hazardous waste collection points. In accordance with the Minamata Mercury Convention, the production, export and import of some mercury-containing lamps will be banned from 2020, along with a similar ban on mercury-containing batteries and thermometers.
Lamp DRL (arc mercury luminescent)

Mercury lamp high pressure, should not be used in rooms where people are for a long time (apartments, offices).
Data lighting find their application in street lighting, in automated industrial shops, in agriculture.
Minuses:
- Low Ra: 40 – 59.
- Longer switch-on time (up to 15 minutes), depending on the temperature of the ambient air (the colder, the more time the process of exposure takes up).
- Strong heating of the tube.
- Sensitivity to voltage drops: at frequent short-term power outages the device will go out, and then, after a reclosure, for a long time to enter the operating mode.
The classic DRL is gradually getting out of use.
At present, for household use, devices of a combined type are manufactured (for example, by OSRAM).
Lamp DRI (mercury arc with radiant additives)

Also called metal halide.
Lamps DRL, in the flask of which are added halogenides of certain metals (sodium, indium, etc.).
The base E27, E40, R7S (the socket with recessed contact, is used mainly in high-intensity lighting installations, after marking the cap, the length of the bulb in mm is indicated as 78 or 118):
Mercury-quartz lamps (PRK, DRT)

Arc-type GDVD type DRT (arc mercury tubular, obsolete - direct mercury-quartz, PRT) are used in medical equipment (the very quartz of cabinets) for disinfection of air, products. Also, DRT are used in some technological processes (such as, for example, photopolymerization).
Fluorescent lamps

Or else a fluorescent lamp.
The marking of domestic instruments indicates a spectrum of luminescence:
After the lettering, the numbers follow: the first indicates the degree of color rendition (the higher it is, the more natural the light looks, the range is 6-9), the next two - the color temperature:
- 30 (3000 K) - warm white;
- 35 (3500 K) - white;
- 40 (4000 K) - cold white;
- 54 (5400 K) - daylight;
- 65 (6500 K) - cold daylight;
Used G-socle, which is a nest, where with the help of pins attached balloon. It is used for halogen and fluorescent compact lamps (to reduce the size). There is a large number of markings of this type of socle, so each time you need to compare the type of attachment (it is indicated on the bulb), the socles are not interchangeable.
Pros:
- Low operating temperature (you can safely touch).
- Soft light.
- Operating time up to 30 000 h.
- Modern Compact Models can be connected to a regular cartridge (the luminescent lighting of the previous generation were made in the form of tubes and required for their connection the use of special cylinders).
Minuses:
- Source work is not noiseless (the process of luminescence is accompanied by a rumble).
- Plus working temperatures environment.
- Toxicity - it is necessary to dispose to special polygons (for the population free of charge through the reception points of hazardous waste).
- Enough long turn-on period, during which the light reaches a maximum.
- Sensitivity to frequent on-off.
From the listed features it is evident that it is advisable to install such equipment in places where it is necessary to provide illumination for a long time with a minimum number of inclusions. For example, on the first floors of stairs.
If the mode of use implies a short period of work with frequent inclusions (for example, in bathrooms) - it is better to choose another source.
Characteristics:
Sodium lamps
Discharge lamps with sodium vapor

These lamps give a monochrome yellow light. They are used wherever a high color rendering index is not required: in street and road lighting, with lighting of buildings, etc. High pressure lamps (NLVD) are used in agriculture for additional illumination of plants in winter.
There are several markings of arc sodium (DN) light sources of domestic production:
- DNaT - DN tubular;
- DNaS - DN in a light diffusing flask, are a substitute for DRL;
- DNaMT - matted;
- DNaZ - mirror;
Xenon headlight

Allow to get a very good color rendition.
They are used in car headlights, as well as in projectors, flashlights and other lighting devices.
Depending on the application, the price for them varies from several hundred to several thousand rubles. They have a narrow special purpose.
Characteristics:
Neon, argon, and others.
![]()
Gas-discharge lamps, the bulb of which is filled with an inert gas.
Have a long operation time (up to 80 000 hours), depending on the composition of the gas sweep, you can get light sources of different shades (from blue-green to red-orange). Used for advertising lighting, to indicate the voltage in the network.
LED lamp

They are also called LED.
This type of source has one significant drawback: high cost. However, they can further significantly reduce energy costs. In the economic plan, these lighting devices are very attractive, since they have a long period of operation.
At the moment, LEDs are used to illuminate streets, in common areas (often together with), to illuminate museum exhibits.
Pros:
- Ecological compatibility.
- Long service life (30 000-50 000 h.).
- Small size.
- Small heat source.
- Resistance to mechanical impact.
Minuses:
- The cost.
- The narrowly focused beam of light.
- By end of life the brightness of such sources decreases (the so-called burn-out of LEDs).
Characteristics:
Comparison table:
| A type | Price,r | Power, W | Light output, lm / W | Color renderingRa | Light temperature,TO | Service life, h | Key Features |
| vacuum | from 10 | 5 – 500 | 7 – 17 | more than 90 | 2 700 | 500 – 1000 | fire risk |
| halogen | from 20 | 20 – 1500 | 14 – 30 | more than 90 | 3 700 | 2000 – 4000 | can be mounted in gypsum board, high sensitivity to contamination of the surface of the bulb |
| krypton | from 40 | 5 – 500 | 8 – 19 | more than 90 | 2 700 | 1000 – 2000 | fire risk |
| DRI | from 500 | 20 – 2000 | 70 – 95 | more than 90 | 3500 – 6000 | 8000 – 10 000 | long switch-on time, toxicity, the bulb does not heat up (luminescence). |
| luminescent | from 100 | 4 – 140 | 40 – 90 | 60 – 90 | 3000 – 6000 | 30 000 | |
| sodium | from 200 | 50 – 100 | 150 – 200 | from less than 39 to 59 | 3000 – 6000 | 30 000 | plant illumination |
| lED Light | from 200 | 2 – 2000 | 40 – 120 | 60 – 89 | 3000 – 6000 | 30 000 – 50 000 | energy efficient |
When choosing the light sources, their operational characteristics must be taken into account.
The right choice will save you money and prolong the life of the lighting device.
Among all wiring and wiring products, lighting equipment has the richest assortment. This is because the lighting elements carry not only purely technical characteristics, but also design elements. The possibilities of modern lamps and luminaires, their design diversity are so great that it is easy to get lost (Figure 5.66).
For example, there is a whole class of fixtures designed exclusively for gypsum plasterboard ceilings. Numerous types of lamps have a different nature of light and are operated under unequal conditions. In order to understand what kind of lamp should stand in this or that place and what are the conditions for its connection, it is necessary to briefly study the main types of lighting equipment.
All lamps have one common part: the plinth, by means of which they are connected to the lighting wires. This applies to those lamps in which there is a socket with a thread for mounting in the chuck. Dimensions cap and cartridge have a strict classification.
It is necessary to know that in household conditions lamps with 3 kinds of socles are used: small, medium and large. In technical terms, this means E14, E27 and E40. Cap, or cartridge,
In addition to the plinths, which are screwed into the socket by thread, there are other types. They are of the pin type and are called G-socles. Used in compact fluorescent and halogen lamps to save space. With the help of 2 or 4 pins the lamp is fixed in the socket of the luminaire (Fig. 5.68).

Table 5.8. Light output of lamps of different types |
||||||||||||||||
|
There are many kinds of G-socles. The main ones are: G5, G9, 2G10, 2G11, G23 and R7s-7.
Lamps and lamps always indicate information about the base. When choosing a lamp, you need to compare this data.
Power is one of the most important characteristics of a lamp. On the cylinder or socle, the manufacturer always indicates the power on which the luminosity of the lamp depends. This is not the level of light that it radiates. In lamps of a different nature of light, the power is quite unlikely. For example, energy-saving at a specified power of 5 watts will shine no worse than an incandescent lamp of 60 watts. The same applies to fluorescent lamps. The luminosity of the lamp is calculated in lumens. Typically, this is not indicated, so when choosing a lamp, you need to look at the advice of sellers or look in the table. 5.8.
Light output means that at 1 watts of power the lamp gives so many lumens of light. It can be seen from the table that an energy-saving compact fluorescent lamp is 4-9 times more economical than incandescent. It is easy to calculate that a standard 60 watt lamp gives about 600 lumens, whereas a compact lamp has the same value at a power of 10-11 W. So it will be more energy-efficient. Incandescent lamp (JIOH) is the very first source of electric light that has appeared in the home. It was invented in the middle of the 19th century, and although it has undergone many reconstructions since that time, the essence remained unchanged. Any PES consists of a vacuum glass bulb, a cap on which contacts and a fuse are located, and filaments that emit light in Fig. 5.69).
The filament of incandescence is made of tungsten alloys, which easily withstand an operating combustion temperature of +3200 ° C (Figure 5.70). To instantly not burn out the thread, in modern lamps, some inert gas is pumped into the cylinder, for example argon.
The principle of the lamp is very simple. When passing a current through a conductor of small cross-section and low conductivity, part of the energy goes to the heating of the helix-conductor, which causes it to glow in visible light. Despite such a simple device, there are many kinds of PESs. They differ in shape and size (Figure 5.71).
Decorative lamps (candles): the balloon has an elongated shape, stylized as an ordinary candle (Figure 5.72). Usually, they are used in small lamps and sconces.
Painted lamps: glasses of cylinders have a different color for decorative purposes. Mirror lamps are called lamps, part of the glass cylinder is covered with a reflective composition for the direction of light by a compact beam. Such lamps are most often used in ceiling lamps to direct light down without lighting the ceiling. Lamps of local illumination work under voltage of 12, 24 and 36 V. They consume a little energy, but also the lighting is appropriate. They are used in hand lanterns, emergency lighting, etc. |
PES are still in the forefront of the light source, despite some shortcomings. Their minus is a very low efficiency - no more than 2-3% of the energy consumed. Everything else goes into heat. The second disadvantage is that the LONs are not safe from the fire point of view. For example, an ordinary newspaper, if put on a 100-watt bulb, flashes in about 20 minutes. Needless to say, in some places, LON can not be exploited, for example in small lampshades made of plastic or wood. In addition, such lamps are short-lived. The lifespan of PES is about 500-1000 h. Among the advantages can be attributed to cheapness and ease of installation. PES do not require any additional devices to work, like fluorescent ones. Halogen lamps little different from incandescent lamps, the principle of operation is the same. The only difference between them is the gas composition in the cylinder (Figure 5.73). In these lamps, iodine or bromine is mixed with the inert gas. As a result, it becomes possible to raise the temperature of the filament and to reduce the evaporation of tungsten. That is why lamps can be made more compact, and their service life rises by 2-3 times.
However, the temperature of glass heating increases very significantly, therefore halogen lamps are made of quartz material. They do not tolerate contamination on the flask. Touching an unprotected hand to the balloon is impossible - the lamp will burn very quickly. Linear halogen lamps are used in portable or stationary searchlights. They often have motion sensors (Figures 5.74 and 5.75).
Such lamps are used in gypsum plasterboard constructions. Compact lighting devices have a mirror coating (Fig. 5.76-5.77).
|
The minuses of halogen lamps include sensitivity to voltage drops. If it "plays", it is better to purchase a special transformer, equalizing the current. Principle of operation fluorescent lamps seriously differs from PECs. Instead of a tungsten filament in a glass bulb of such a lamp, mercury vapor is ignited under the influence of an electric current (Figure 5.78).
The light of a gas discharge is practically invisible, since it is emitted in the ultraviolet. The latter causes the phosphor to glow, with which the walls of the tube are covered. This light we see. Externally, and by the method of connection, fluorescent lamps also differ greatly from PON. Instead of a threaded cartridge, there are two pins on both sides of the tube, fixed as follows: they must be inserted into a special cartridge and rotated in it (Figure 5.79). Fluorescent lamps have a low operating temperature. To their surface, you can safely rest your palm, so they are installed anywhere. A large surface of the glow creates an even scattered light. That is why they are sometimes called daylight lamps (Figure 5.80). In addition, varying the composition of the phosphor, you can change the color of light, making it more acceptable to the human eye. In terms of service life, fluorescent lamps outnumber incandescent lamps by almost 10 times. |
The downside of such lamps is the impossibility of direct connection to the power grid. You can not just throw 2 wires on the ends of the lamp and plug the plug into the outlet. For its inclusion, special ballasts are used. This is due to the physical nature of the glow of the lamps. Along with electronic ballasts, starters are used which, as it were, ignite the lamp at the moment of switching on (Figure 5.81).

Most luminaires for fluorescent lamps are equipped with built-in glow mechanisms like electronic ballasts (ballasts) or throttles.
The marking of fluorescent lamps is not similar to the simple designations of PECs having only a power rating in watts. For the lamps under consideration, it is as follows:
LB - white light;
LD - daylight;
ЛЕ - natural light;
LHB - cold light;
LTB - warm light. The numbers following the lettering indicate the first digit - the degree of color rendition, the second and third - the luminescence temperature. The higher the degree of color rendition, the more natural is the lighting for the human eye.
Consider an example related to the glow temperature: a lamp labeled L B840 means that this temperature is 4000 K, the color is white, daylight. The following values mean the marking of lamps: 2700 K - superheated white, 3000 K - warm white, 4000 K - natural white or white, more than 5000 K - cold white (daytime).
Recently, the appearance on the market compact fluorescent energy saving lamps made a real revolution in lighting equipment (Figure 5.82).

Fig. 5.82. Compact fluorescentenergy saving lamp with ballast
The main shortcomings of fluorescent lamps were eliminated - their bulky dimensions and the inability to use conventional rifled cartridges. The ballasts were mounted in the lamp socket, and the long tube curled into a compact spiral. Now the variety of types of energy-saving lamps is very large. They differ not only in their power, but also in the form of discharge tubes (Figure 5.83).
The advantages of such a lamp are obvious: There is no need to install electronic ballast for start-up, using special luminaires (Figure 5.84). An economical fluorescent lamp has replaced the usual PEC. However, it, like all fluorescent lamps, has drawbacks.
Minuses a few:
Such lamps do not work well at low temperatures, and at -10 ° C or lower they begin to dim dim;
Long start-up time - from a few seconds to several minutes;
A low-frequency rumble is heard from the electronic ballast;
Do not work together with dimmers;
Relatively expensive;
Do not like frequent on and off;
The lamp includes harmful mercury compounds, so it requires special disposal;
If you use the backlight indicators in the switch, this lighting equipment starts to flicker.
No matter how hard the producers try, the light of fluorescent lamps is not very similar to the natural one yet and cuts the eyes.
In addition to energy saving lamps with ballasts, there are many varieties without built-in electronic ballast. They have completely different types of socle (Figure 5.85).
Fig. 5.85. Compact fluorescent lampit is usually used in lighting fixtures,equipped with electronic ballast
The principle of glowing a high-pressure arc mercury lamp (DRL) is an arc discharge in mercury vapor (Figure 5.86). Such lamps have a high light output - at 1 Watt 50-60 lumens. They are started by means of ballasts. The disadvantage is the spectrum of the luminescence - their light is cold and sharp. LRD lamps are most often used for street lighting in "cobra" type luminaires (Figure 5.87).
 Fig. 5.86. Lamp DRL
Fig. 5.86. Lamp DRL
LED lamp - this high technology product was first constructed in 1962. Since that time, LED lamps have been gradually introduced to the market of lighting products (Figure 5.88).
 |
Fig. 5.88. LED flashlight is characterized bybright light and extremely low energy consumption |
LED by the principle of action is the most common semiconductor, for which part of the energy in the pn transition is reset in the form of photons, that is, visible light. Such lamps have simply amazing characteristics. They are ten times better than PAN for all indications: longevity, light output, economy, durability, etc. (Fig. 5.89).
They have only one "but" - this is the price. It is approximately 100 times the price of a conventional incandescent lamp. However, work on these unusual light sources continues, and we can expect that soon we will rejoice at the invention of a cheaper model than its predecessors
NOTE!
Due to the unusual physical characteristics of the LEDs, they can be used to make real compositions, for example in the form of a starry sky on the ceiling of the room. It is safe and does not require much energy.