Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are situations of emergency care for fever, when the child needs to give the medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and apply antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? Which medications are the safest?
Any battery has a limited lifespan, like any car part. The average period of operation of this element on average lasts 4-5 years. The battery life is affected by many factors. In particular, the brand of the car, operating conditions, timely maintenance of the car battery, etc. For serviceable performance of all functions by the accumulator, service plays a decisive role. This process can be done by yourself or with the help of a service center.
Factors affecting the battery life
Effect of car battery maintenance on service life
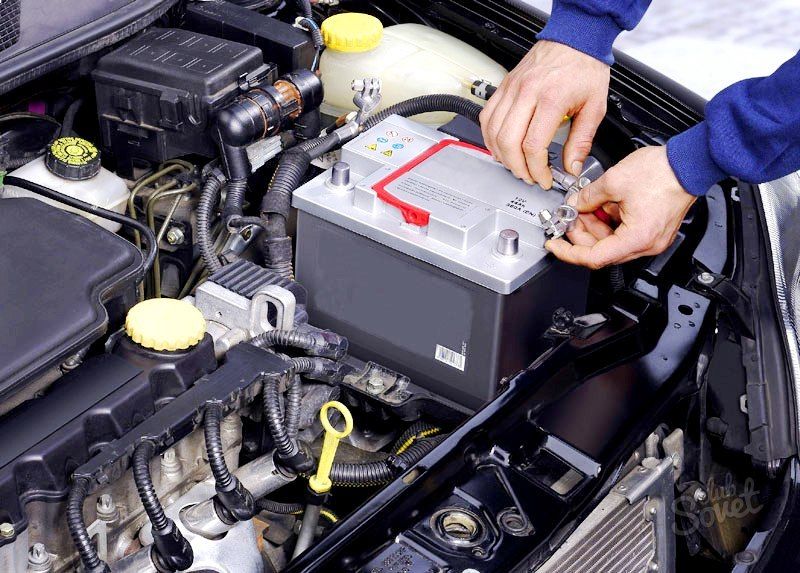 is determined by operating conditions and quality of service. Therefore, if the car is operated competently and in a timely manner to carry out maintenance by one's own hands, the duration of the battery can be increased. Buying a new battery will be expensive, therefore, it is beneficial to carry out preventive measures. The state of the battery with its own hands is checked at least twice a year.
is determined by operating conditions and quality of service. Therefore, if the car is operated competently and in a timely manner to carry out maintenance by one's own hands, the duration of the battery can be increased. Buying a new battery will be expensive, therefore, it is beneficial to carry out preventive measures. The state of the battery with its own hands is checked at least twice a year.
It is necessary to try to exclude the use of a discharged battery. This is especially true for the winter period of time. At low temperatures, the load is significantly increased by the battery, since it requires energy for heating the vehicle, working the headlights, etc.
In addition, in winter, the launch is much more difficult, which also entails considerable energy costs. In this regard, in order to increase the battery life, periodically after operation it is necessary to conduct all the electric consumers from the battery by themselves and start the engine without them. This will make it possible to produce the necessary.
 It is important to try to create conditions that will facilitate the start of the engine. So, it is not recommended to start the car, performing the voltage of the starter for more than 10-15 seconds. After an unsuccessful attempt, you should take a short time before starting up again.
It is important to try to create conditions that will facilitate the start of the engine. So, it is not recommended to start the car, performing the voltage of the starter for more than 10-15 seconds. After an unsuccessful attempt, you should take a short time before starting up again.
The battery should be taken care of. Periodically, the terminals need to be cleaned by hand. Purification is carried out using a special solution or a rag. The body of the device is treated with ammonia.
Always recharge the battery correctly. If it is long in a discharged state, then its plates are susceptible to destruction. For charging, a dedicated device is used.
How to service the battery by yourself?
- The battery is dismantled and cleaned of the electrolyte. Specify the volume of electrolyte in the banks.
- If necessary, compensate for the missing electrolyte by adding water. The water must be distilled.
- After this, it is necessary to charge the battery. But before that the battery needs to be thoroughly discharged.
- Continuing battery maintenance with our own hands, we perform electrolyte in cans.
The difference between the indices should not exceed 0.005 g / cm3. If the data does not comply with the established standard, an equalizing action is carried out. To do this, you need to charge the battery with a current of 1A.
Battery maintenance is best carried out after and before winter, since the operation of this car element in the summer is more sparing. Charging is best done using modern chargers.
12.2. Rescue the battery
12.4. A few more ways, based on the use of electric current
1. Technical introduction
The purpose of an automotive battery is understandable to anyone more or less knowledgeable in technical matters to a car enthusiast. With its first function - ensuring the engine starts - we come across every day. There is also a second - less commonly used, but no less significant - use as an emergency power source when the generator fails. In addition, the modern cars with electronics on board, the battery serves as a smoothing device for the voltage pulsations produced by the generator. It follows from this that care should be taken to disconnect the battery when the engine is running. The carburetor engine will not have anything, but how the computer that controls the modern engine will behave is unknown ... You can ruin the computer.
All starter batteries currently produced for cars are lead-acid. The basis of their work laid down since 1858, and to this day remains virtually unchanged, the principle of double sulphation.
As clearly seen from the formula, when the battery is discharged (right arrow), the active mass of the positive and negative plates interacts with the electrolyte (sulfuric acid), resulting in lead sulfate precipitating on the surface of the electrodes and water. As a result, the density of the electrolyte falls. When charging the battery from an external source, reverse electrochemical processes occur (arrow to the left), which leads to the recovery of pure lead on negative electrodes and positive lead peroxide on positive electrodes. At the same time, the density of the electrolyte increases.
Any car battery is a body - a container, divided into six isolated cells - cans (see Fig. 1).

Each bank is a complete power source with a voltage of about 2.1 V. The bank has a set of positive and negative plates separated from each other by separators. As is known from the school course of physics, two discharged plates are in themselves a source of constant voltage, while their parallel connection increases the current. Sequential connection of six cans and gives a battery with a voltage of the order of 12.6 V. Any of the plates, both positive and negative, is nothing more than a lead lattice filled with active mass. The active mass has a porous structure so that the electrolyte enters the deepest possible layers and covers a larger volume. The role of the active mass in the negative plates is carried out by lead, in positive - lead peroxide.
Weight of a flooded battery with a capacity of 55 Ah is about 16 kg. This figure consists of the mass of the electrolyte - 5 kg (which corresponds to 4.5 liters), the mass of lead and all its compounds - 10 kg, as well as 1 kg, attributable to the tank and separators.
2. Main characteristics of batteries
2.0. Electromotive force (EMF)
The dependence of the EMF (roughly speaking voltage on the battery terminals) on the density of the electrolyte looks like this:
E = 6 * (0.84 + p),
where E is the emf of the battery, V
p is the electrolyte density reduced to 5 ° C, g / ml
2.1. Water flow rate
Indicator, directly related to the degree of serviceability of the battery. It is determined in laboratory conditions. A battery is considered to be maintenance-free if it has a very low water consumption in operation. Maintenance-free batteries do not require refilling of distilled water for a year or more, provided the voltage regulator is working properly.
The percentage of antimony in the lead lattices of the plates exerts a direct influence on the water flow. As is known, antimony is added to give the plates sufficient mechanical strength. However, every medal has a downside. Antimony promotes the splitting of water into oxygen and hydrogen, which results in the boiling-off of water and the reduction of the electrolyte level. In the batteries of the previous generation, the content of antimony reached 10%, in modern batteries this figure has been reduced to 1.5%.
Panacea from this trouble firms see in the development of the so-called. calcium technology - the replacement of antimony by calcium. Or replace antimony with calcium only in positive plates (so-called hybrid technology). Calcium in the lattice is a substance neutral to water, without reducing the mechanical strength of the gratings. That is why there is no decomposition of water and the electrolyte level remains unchanged.
The advantages of "calcium" batteries - can be installed in places that do not require convenient access for maintenance. It is not required (or very little is required) to add distilled water.
Lack of "calcium" batteries - with deep discharges there is the formation of insoluble calcium salts and the capacity of the battery is irreversibly lost. Hence it follows: in any case not to expose the calcium battery to the control training cycles! The manufacturers of the battery try to eliminate this deficiency by adding silver and other components to the battery, the result is not yet completely clear.
2.2. Battery durability
The average lifetime of modern batteries, provided that the rules of operation are observed - and this prohibition of deep discharges and recharges, including the fault of the voltage regulator - is 4-5 years.
The most harmful for batteries are deep discharges. The light devices left for the night or other consumers are capable of discharging it to a density of 1.12-1.15 g / cm 3, i.е. practically up to water, which leads to the main trouble with batteries - the sulfation of lead plates. Plates are covered with white coating, which gradually crystallizes, after which the battery is almost impossible to restore. Hence the main conclusion is that it is necessary to constantly monitor the battery condition and periodically measure the density of the electrolyte. This is especially true in the winter. It should be noted that sulphation within certain limits is a normal phenomenon and is always present. (Remember - based on the theory of double sulphation, the principle of battery operation is built). But with a small discharge and subsequent charging, the battery is easily restored to its original state. This is possible even with a deep discharge of the battery, but only if the charge immediately follows. If the battery is discharged for a long time without giving it a "recharge," a drop in density below the critical value inevitably leads to the formation of lead sulphate crystals that do not react under any circumstances. And this means that an irreversible process of sulfation has begun.
Dangerous for the battery and recharge. This occurs when the voltage regulator is faulty. In this case, the electrolyte begins to "boil" - there is a decomposition of water into oxygen and hydrogen and a decrease in the electrolyte level. That's why you need to monitor the charging voltage. Naturally, this is not difficult, if there is a voltmeter on the instrument panel. If it does not exist? In this case, connect the tester (in voltmeter mode) between the battery's "+" and "ground." Normal battery charging mode is provided in the range of 14.2 ± 0.7V. In older cars, the voltage was normally about 14 V, in modern ones closer to the upper limit of 14.5 ... 14.8 V. If the voltage is less - it is worth checking the belt tension, the reliability of the electrical connections of the power supply system. If this does not help, the fault must be sought in the voltage regulator. Also, the fault falls on the regulator, if the voltage exceeds 14.6 ... 15 V.
In recent years, widely spread pocket-type separators - the so-called. convertible separators. Their name speaks for itself - in these envelopes put the plates of the same name. Thus, the active mass crumbling during operation remains in the envelope, thereby preventing the plates from closing.
A battery that has not been operated for a long time (4-5 months) needs recharging. This is due to the fact that batteries are characterized by a phenomenon such as self-discharge. The diagrams in Fig. 2.3 show the self-discharge characteristics for different batteries. In the first case, this is a decrease in the density from the storage time, in the second case, the voltage drop.


However, often recharging requires a battery in use. The density of a fully charged battery is 1.27-1.28 g / cm 3, the voltage is 12.7 V. The battery is judged by the density of the electrolyte. The lower the density of the electrolyte, the stronger the battery is discharged. Reducing the density by 0.01 g / cm 3 compared to the nominal means that the battery is discharged by about 6 - 8%. Using the graph (see Fig. 4), it is possible to estimate the dependence of the degree of battery discharge on density. Degree of discharge is determined by the bank in which the density of the electrolyte is minimal. Everyone knows the axiom, nevertheless let's repeat it again - the battery discharged in the summer by more than 40%, and in winter more than 25%, it is necessary to remove it from the car and charge it. It should be remembered that a reduced density in winter is more dangerous, because among other things, can lead to the freezing of the electrolyte. Thus, at an electrolyte density of 1.2 g / cm 3, its freezing point is about -20 ° C.
Also it is necessary to recharge the battery if the density in different banks differs by more than 0.02 g / cm 3. It is optimal to charge the battery with a current equal to 0.05 of its capacity. For a battery with a capacity of 55 Ah, this value is 2.75 A. The lower the charging current, the deeper the charge. However, do not go to extremes - at a very low current, the battery simply does not "boil", in addition, the charging time will be incomparably greater. On the contrary, at a very high current, the battery "boils" much faster, but it will not have time to recharge by 100%. Signs of the end of charging are the rapid release of gas (the so-called "boiling") and the constant density of electrolyte for 1-2 hours.
For an approximate estimate of the time required to charge the battery, you can use the following algorithm. 
Initially, using the graph (Fig. 4), it is necessary to determine the degree of battery discharge based on the actual density of the battery measured by the hydrometer. Then, by the degree of discharge, we determine the lost capacity (or the capacity that the battery must be taken).
Then, choosing the value of the charging current, calculate the approximate charging time according to the formula:

Here it should be noted that not all energy goes to increase the capacity. The process efficiency is 40-80%, the rest is spent on heating. Therefore, real time increases about twice as much as calculated (which is taken into account by the coefficient "2" in the formula).
I must say that the use of this algorithm is justified only to facilitate the procedure, but in no way relieves the control over the progress of charging. The process of charging, and especially its termination, you need to control yourself, so as not to miss the beginning of a violent boiling.
Another option is the use for these purposes of automatic chargers, differing in design. The essence is one - on the voltage at the terminals of the battery, the current at each time and time of charging is calculated by the charger and provides the optimum current for charging. In this case, the charger stops giving power when the battery is fully charged.
For example, let's define the charging time of a battery with a capacity of 55 Ah with a current of 5 A, the density of which is 1.25 g / cm 3. As can be seen from the graph, at a given density, the battery is discharged by 25%, which means a loss of capacity by an amount

Thus, the approximate charging time

The optimal way to charge the battery, is its charge from on-board network car (naturally, provided the serviceability of the latter). With this method, first, it is impossible to reload, and secondly, there is a constant mixing of the electrolyte and its fullest penetration into the inner layers of the active mass.
However, it would be erroneous to assume that the battery charge starts immediately after the engine starts and continues all the time while the engine is running. Studies show that the battery takes charge in a strong dependence on the heating of the electrolyte. This is what a fairly common way of exploiting vehicles is dangerous. Cold start in the winter with a half-hour traffic to work, and then a few short trips throughout the working day do not allow to warm up the electrolyte and, therefore, to charge your battery. Thus, the discharge of the battery increases from day to day and in the end can lead to a sad result.
The physical processes that occur when the engine is started differ from the processes when the battery is discharged by consumers. When starting up, not all of the active mass and electrolyte is involved, but only that part that is on the surface of the plates and contacting the surface of the electrolyte plates. Therefore, after an unsuccessful attempt to start the engine, you should wait a while for the electrolyte to mix, its density leveled, it penetrated into the pores of the active mass. Normal start of the engine with a single rotation of the starter within 10s takes a capacity of 300A x 10s = 3000 Ac = 0.83 Ah, which is about 1.5% of the capacity of the battery.
With a slow discharge, not only the surface layers of the active mass participate, but also deep layers, so the discharge is deeper. However, this does not mean that the starter modes are not so destructive for the battery - the starter can also exactly discharge the battery to a critical value.
What are the signs of a battery failure? The battery does not charge, the density is low and does not increase during charging. Large self-discharge - the battery is charged, but does not hold a charge. You can try to train the battery, but if the active mass of the plates is shed or the lead sulfate crystallizes, then this can not be corrected.
In general, to master the way to assess the degree of possible discharge of the battery from any actions (including those that are conscious) will not be very difficult. It is necessary to learn several truths and memorize a few numbers.
- The battery begins to take more or less charge only after the electrolyte is warmed to a positive temperature (as you understand, at an air temperature of -20 ° C, the temperature of the electrolyte in the battery of the car stored in the fresh air will be approximately the same.)
- The efficiency of the charging process is approximately 50%.
- Each car generator is characterized by the following indicators:
- current of generator recoil when the engine is idling.
- current recoil generator when the engine at rated speed.
For VAZ cars these figures have the following meanings:
Table 1
As can be seen from the table, on the latest models of cars of the Volga Automobile Plant, generators are installed that have recoil current characteristics that are twice as large as the characteristics of the generators of the first models.
And finally, the approximate consumption of energy by car consumers:
table 2
Thus, the dimensions left for 3 hours will "eat" 4A x 3h = 12 Ah of battery capacity, which corresponds to the discharge by approximately 20%. It's not scary for one time. However, after repeating this one more time, you already risk not having your car, especially if it happens in winter, because the discharge will be of the order of 40% (especially since in the winter the batteries are usually operated more discharged).
Similarly, you can estimate what you have when the engine is idling for a long time. As already shown above, the recoil current of the VAZ-2108 car generator is idle at 24A. We subtract from this quantity 2A necessary for servicing the ignition system. There remains 22A. Using Table 2, it's easy to figure out what can be included so that at least a little would get to the battery.
For owners of cars with automatic transmission, the picture is even more complicated. Usually, standing in a traffic jam or at a traffic light, you do not switch to neutral, but push your foot on the brake. This reduces the engine speed from the standard 800-900 rpm. up to 600-700 rpm, which, accordingly, will lower the current produced by the generator, and the stop signals will add a couple more amperes of current consumption. Yes, and rear window heating for Germans, for example, is much more powerful than that of domestic cars.
You should know that the winter conditions of the car are in principle very heavy for the battery. Certainly the following data will be useful. The results of the research show that when the car is used in very difficult conditions (tests on the so-called "city-winter-night" regime) the battery gets about 1Ah per hour. Therefore, if, as in the example above, when starting the engine (in winter, when the starter is running for 10 seconds), 0.83 Ah of battery power is consumed, then in order to replenish this energy, the engine must run 0.83 * 1 = 0.83 h = 50 minutes.
3. Terminology
Accumulator battery - one of the main elements of the electrical equipment of the car, as it accumulates and stores electricity, provides engine start-up under various climatic conditions, and also supplies electrical appliances with the engine stopped.
Automotive lead-acid 12-volt battery consist of 6 consecutively connected elements (cans), united in a common housing. From each bank vent is carried out, the structures can differ significantly.
Electrolyte is a solution of sulfuric acid in distilled water (for the central strip of Russia with a density of 1.27-1.28 g / cm 3 at t = + 20 ° C). Boiling of electrolyte - a rapid release of gas in the electrolytic decomposition of water with the release of oxygen and hydrogen. This occurs while the battery is charging.
Self-discharge - spontaneous decrease in the capacity of the battery when idle. The rate of self-discharge depends on the material of the plates, chemical impurities in the electrolyte, its density, the purity of the upper part of the battery case and the duration of its operation.
Voltage of a fully charged battery without load (EMF - electromotive force) should be within 12.6-12.9 V. Voltage in the vehicle's on-board network with the engine running is slightly higher than on the battery terminals, and should be within 13.8-14.8 V (0.2 V from extreme values). Voltage value below 13.8 V leads to a low battery, and above 14.4V - to a recharge, which adversely affects its service life.
Battery polarity - a term that determines the location of current collectors on its housing. On foreign batteries, the polarity can be direct or reverse, that is, the orientation of the positive and negative terminals relative to the housing can be different. According to the Russian standard (if viewed from the side of the conclusions) the negative (-) should be on the right, positive (+) on the left.
Battery capacity - The ability of the battery to receive and give energy - measured in ampere-hours (Ah). To estimate the capacity of the battery, a 20-hour discharge technique with a current of 0.05C 20 (ie, current equal to 5% of the nominal capacity) is adopted. Ie, if the battery capacity is 55 Ah, then discharging it with a current of 2.75 A, it will be completely discharged in 20 hours. Similarly, for batteries with a capacity of 60 Ah, a full 20-hour discharge will occur at a slightly higher discharge current - 3A.
This characteristic determines the ability to feed consumers in an extreme situation (in the event of a generator failure). Characterized by the volume of the active mass.
Cold start current at -18 ° C (DIN) - The amount of current that the battery is capable of giving when the engine is started at -18 ° C. The most important characteristic, directly affecting the start-up of the engine. After all, at -20 ° C, the current consumed by the starter is about 300A. (To start the hot engine in summer, the same figure is 100-120A.) The value of the starting current is determined by the design of the battery, plates, separators. The lower the internal resistance of the battery, the higher the starting current, the more reliable starting of the engine at low temperatures.
Backup capacity - the time during which the battery can provide the work of consumers in emergency mode. The size of the reserve capacity, expressed in minutes, has been increasingly shown by battery manufacturers after the cold start current value.
The case of modern batteries is made of plastic, in most cases translucent, allowing to control the level of electrolyte.
Maintenance free battery. At once it is necessary to make a reservation that this term should not be understood literally and be perceived as a guide to inaction. This name speaks for improved consumer properties of the battery. Maintenance-free batteries require water topping not more often than once a year, provided they are used on cars with serviceable electrical equipment and an average annual mileage of 15-20 thousand km. There are designs that exclude all interference throughout the life cycle, but they are particularly critical to the state of automotive electrical equipment.
Most of the maintenance-free batteries are manufactured by manufacturers, filled with electrolyte. Since these batteries have a much smaller self-discharge, they can be stored for 6 months to 1 year without recharging. Self-discharge of new unattended batteries for 12 months can be up to 50% of the nominal capacity.
4. Battery marking
The following markings are placed on modern batteries:

Some batteries have this marking:
![]()
Despite the fact that after the capacity is 280A, the figure that interests us and shows the cold start current according to our DIN standard is 255A.
The designations of the main characteristics on the batteries of different manufacturers differ from each other. Most European manufacturers and a significant part of them in Asia are guided by the industrial standard of Germany DIN 43539 Part 2, which specifies two main parameters: the battery capacity, measured in ampere hours (Ah) at + 25 ° C, and the starter current in amperes (A) at -18 ° C.
Batteries of American manufacturers are tested at the request of the American standard SAE J537g , which is included in the international standard BCI and also introduces two main parameters: the reserve capacity, measured in minutes at + 27 ° C, and the cold scrolling current in amps at -18 ° C. The SAE standard does not provide for the measurement of the battery capacity in ampere hours.
The first considers the battery's ability to prolong the discharge by lower currents, the second - discharge by high currents, but in a shorter period of time.
Recalculation of the current of the starter discharge according to the European DIN standard in the current of cold scrolling according to the American SAE standard can be carried out with the help of experimental coefficients. For batteries with a capacity of up to 90 Ah, the coefficient 1.7 is used, i.e. ISAE = 1.7 IDIN. For batteries with capacities from 90 to 200 Ah, the coefficient 1.6 is used, i.e. ISAE = 1.6 IDIN.
Currently in Europe, along with the German standard DIN introduced a new single standard En-60095-1 / 93 .
In addition, a corresponding inscription is placed on maintenance-free batteries. Most often in Russian, English or German (or in the language of the manufacturer, such as the Spanish batteries "Tudor").
5. Choice and purchase of batteries
Make sure that the battery you choose matches constructive features your vehicle (capacity, installation location, mounting method, polarity, shape and size of the current collectors). Specialized trading firms have catalogs of the entire assortment, in which information on modifications and technical characteristics.
Inadvisable on a car with an outdated electrical system, install a battery that does not add water. This will lead to a reduction in its service life or failure.
The battery capacity should not be significantly different from that specified by the vehicle manufacturer. Non-observance of this condition leads to a sharp reduction in the service of both the battery and the starter.
It is very good to know the recommended value inrush current starter for your car. On many cars, starters with a reducer are installed. This allows you to significantly reduce the amount of starting current in the first moments of launch, especially in severe frosts, and therefore significantly prolong the life of your battery.
Carefully study the text of the warranty card. Pay special attention to those sections, which list: cases that exclude warranty service; addresses of warranty workshops; Operating conditions.
The battery marking must have a reference to the standard (DIN, SAE, En or others). In the marking according to the SAE standard, the value of the capacitance in ampere-hours (Ah) is not indicated. Specifying the capacity in Ah in the SAE standard is an indirect sign of forgery. The most prone to falsification are expensive batteries of well-known manufacturers, so it is better to buy them in trading companies that are trustworthy.
Most manufacturing companies code the date of release of the battery. Modern maintenance-free batteries allow for long enough storage without significant loss of their consumer properties, so the date of manufacture is less relevant. It is more preferable to purchase a battery filled with a high-quality factory electrolyte. It is ready to work, easy to test. A non-filled dry-charged battery requires additional time and costs to prepare for operation.
Do not rush to give money! You have the right to require a battery check. First of all, remove from it a protective wrapping film, no matter how beautiful it may be, and make sure that the case is not damaged - this happens quite often. Then ask the seller to measure the density of the electrolyte - it should not be below the nominal value by more than 0.02 g / cm 3 and the same in all banks, which corresponds to approximately 80 percent of the battery charge. The last test should be carried out with a load fork - its voltmeter should show 12.5-12.9 V when the load is off, and when it is on - do not go below 11V for 10 seconds.
In the event of a deviation from these values, the battery may be partially or completely unusable.
If you are refused to check the battery, can not confirm the quality of the goods with a certificate, a guarantee coupon, then it is better to refuse the purchase.
6. Battery installation
Before installing the battery, be sure to completely remove the plastic wrap. The vent openings must be open. Pay attention to the correct connection. It is recommended to clean the battery terminals and afterwards fix it with petroleum jelly. This is done to protect the contacts from moisture ingress and oxidation of the contact site. Especially it concerns power wires with copper (but not lead) tips.
It is very important to pay attention to the wires. The terminals must be cleaned not only from the side of the battery, but also from the other side. The place where the massive wire (-) should be also carefully cleaned from paint, oil and other dirt. Contact tight tight. The same applies to the terminal on the starter. Inattention to wires and contacts can very much "come out sideways" in the winter in the cold.
The battery should be stiff in its place. Bolting it in the fasteners is unacceptable. Additional vibration will affect the battery life. Closure and shedding of plates in jars most often occur precisely because of vibration.
Note that on many cars, the battery is quite close to the exhaust manifold. That is, it will be quite hot in the summer, and this is very bad for the battery! On the "right" machines provides thermal insulation of the battery from the engine.
Operating conditions have a significant effect on battery life. Frequent engine starts and trips for short distances, electrical equipment malfunctions (starter, generator, relay-regulator), additional power consumers, untimely maintenance, unreliable battery attachment can greatly shorten the life of the battery.
With continued movement along the road, the battery can be recharged (boiled) - in a city with small runs and "traffic jams" it is usually discharged (see above).
Generator (at idle engine) in winter does not provide the work of most regular consumers, not to mention additional. The heated rear window and the heater fan are added to the included parking lights, low-beam headlights, stop lamps, direction indicators, audio equipment. The daily undercharging of the battery gradually reduces its capacity, which eventually leads to the inability to start the engine with a starter.
A battery failure can also be caused by a leakage current in the vehicle's electrical equipment. This happens when, when all consumers are disconnected, one or a part of them remains in the electrical circuit (the switch or relay is faulty). The culprit can be an alarm. After a deep discharge, the battery may not recover its original nominal capacity. The battery will not be able to work properly if the engine requires a prolonged start-up of the starter (power, ignition).
7.1. Maintenance of batteries during operation is reduced to verification and adjustment in accordance with the requirements: the level and density of the electrolyte; cleanliness and reliability of fastening electrical connections batteries with the car body, electrical equipment parameters, battery fastening. It is also necessary to monitor the correct tension of the alternator belt, clean and lubricate the terminals and terminals, and keep the battery clean. Wipe the upper surface with an aqueous solution of baking soda. The electrolyte density is brought to the required value by charge the battery from a stationary charger .
The value of the charging current in amperes (A) should not exceed 1/10 of the battery capacity (simplified).
7.2. Extending the life of a new battery
It is difficult to say briefly about this. First of all, it is necessary to fill the electrolyte, which exactly corresponds not only to the climatic zone, but also to the season of operation. If the battery will work only in the warm season, then the density of the electrolyte can be 1.20 g / cm 3, and if to -15 ° C - 1.24 g / cm 3, etc. This accuracy, of course, will reduce the rate of plate sulphation, hence, increase the battery life.
The service life of the battery is significantly affected by the average degree of charge, which depends on the serviceability of the relay-controller. It is necessary that this value is maintained at least 75%.
reference:
It is established that the deviation of the regulated voltage by 10 ... 12% up or down from the optimum reduces the battery life by 2 ... 2.5 times.
First x, adjust the motor so that it can be easily started from half a turn. This will protect the battery from a deep discharge. When starting the engine with a starter, a current of several hundred amperes passes through the battery, which does not contribute to its longevity. Therefore, the easier it is to start the engine, the better for the battery: it will last longer.
reference:
Reducing the time of the starter twice in six or eight daily starts increases the battery life by about 1.5 times.
Secondly , adjust the relay-regulator if necessary, so that the voltage is within 13.8 ... 14.4V. This is one of the most important conditions. Thirdly , never allow the electrolyte level to drop below the required level.
reference:
The late filling of distilled water in batteries can reduce battery life by 30%.
These simple tips will prolong the life of the battery.
In addition, experts advise if you have a charger at any opportunity (for example, at night) to put the battery for recharging with a small current - about 1 ... 2A. To do this, you can not remove the battery from the car. Only this operation, if done regularly, at least once a month, increases the battery life by at least a year.
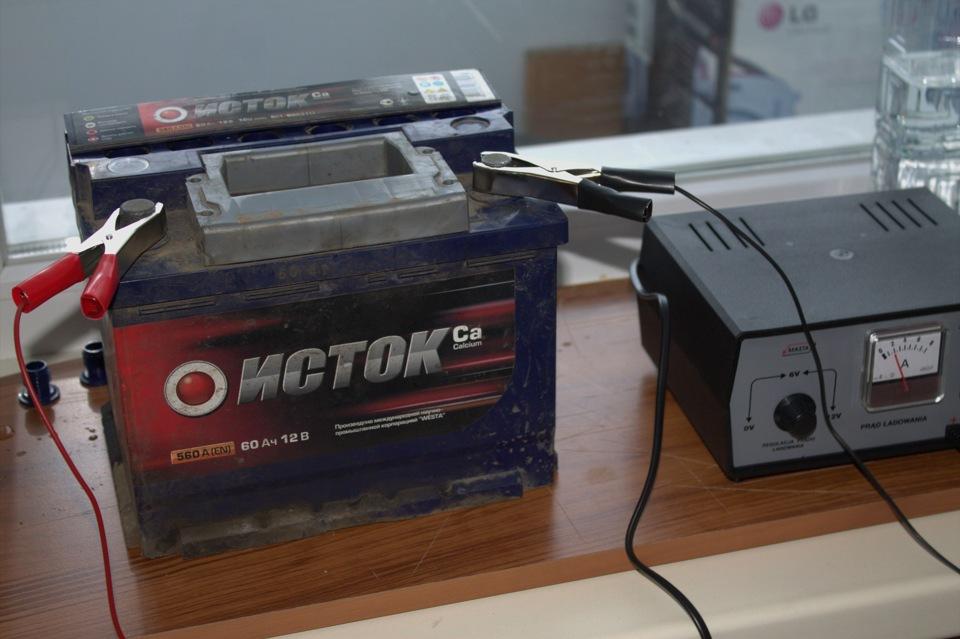
7.3. Charging the battery with a charger
Well, now how to charge? For this purpose, rectifiers direct current. Motorists call them chargers. They come with manual adjustment or automatic. Before charging, it is necessary to open all the gas channels: remove the plugs, remove the lid of the cans. When charging, three parameters are important: voltage, charge current and time. The maximum rectifier voltage should not be too high, it is better if it is regulated. When the battery is partially 25 percent discharged, the initial charge current when the rectifier is turned on can jump up sharply. Adjust it to a rating not exceeding 1/10 of the battery capacity or less, if the voltmeter already shows a voltage close to 14V. Ie, if you have a battery labeled 55Ah - maximum current 5.5. Further, during the charging process, the voltage will increase and the current will decrease. It is considered, if the current does not decrease within the last 2-3 hours, then the battery is charged. It is important to remember that you can not charge a high current for more than 25 hours. The electrolyte will heat up strongly and boil away, the plates from heating can lead and they are closed on each other. Usually the normal time of full charge is about 15 hours.
Sometimes it is necessary to align the density with a small current. For example, if the density of electrolyte in different banks is 1.23, 1.25. By turning on the rectifier, set the charging current to about 2A. Sometimes below, I'm guided by a voltmeter: again, not higher than 14V. The time of such charging is up to two days. Especially it is necessary to do this after the battery is discharged to zero by futile attempts to start the engine. With what, do it right away, until the sulfatization of the plates began.
 Batteries that do not add water should only be charged by devices with automatic charge voltage maintenance. Failure to do so will result in a reduction in their service life. Fortunately, now the chargers are sold many types. Among them there are quite intelligent (for example, "Pendant"), allowing you to monitor the current, charge voltage, time and total charge capacity. And these chargers are not at all expensive - about half the price of a decent battery.
Batteries that do not add water should only be charged by devices with automatic charge voltage maintenance. Failure to do so will result in a reduction in their service life. Fortunately, now the chargers are sold many types. Among them there are quite intelligent (for example, "Pendant"), allowing you to monitor the current, charge voltage, time and total charge capacity. And these chargers are not at all expensive - about half the price of a decent battery.
Specific requirements for charging, operation and maintenance must be stated in the instruction manual or the warranty card accompanying the batteries.
Manufacturers do not provide for the addition of stabilizing and improving drugs to the electrolyte. To bring the electrolyte level to normal it is inadmissible to use electrolyte! In the battery pack only distilled water . Do not use water of doubtful origin. In case of frequent boiling, check the electrical equipment of the vehicle.
It is necessary to know that when the electrolyte level is greatly reduced, a dangerous concentration of the gas mixture can form inside the battery case. To exclude the possibility of an explosion, one should not bring an open flame (even a cigarette) to the battery and allow sparking of electrical contacts. Gas discharge systems of some modern batteries are more explosion-proof. In the central strip of Russia, batteries do not require an adjustment of the electrolyte density during the change of seasons.
Before the winter operation of the car, do not only service the battery (see above), but also the systems that affect the engine start. Be sure to fill in the engine oil corresponding to the season. To facilitate starting the engine in severe frosts, bring the battery for several hours in a warm room.
Before long winter parking also serve the battery, but do not store it in a warm room, but leave it in the car with the terminals removed. The lower the temperature, the lower the rate of its self-discharge.
It is inadmissible to leave a discharged battery in the frost. Electrolyte of low density will freeze, and ice crystals will render it unfit for use. The density of the electrolyte of a discharged battery can be reduced to 1.09 g / cm 3, which will lead to its freezing already at a temperature of -7 ° C. For comparison, an electrolyte with a density of 1.28 g / cm3 freezes at t = -65 ° C.
Tilting the battery and draining the electrolyte can lead to the closure of the plates and its failure.
8. Features of battery operation in winter
First of all, we measure the density of electrolyte in all banks without exception. The norm is 1.27-1.28 g / cm 3. Do you far from it? So, we remove the battery and put it on charging. And this is unequivocal! In no case are we trying to increase the density of the electrolyte by adding concentrated acid, no matter how low its density. The desired result - the increase in the capacity of the battery will not occur.
Further. It is compulsory to audit all power wires, terminals and contacts. Clean the terminals with a fine sandpaper. Contacts on the battery, too, to clean and tighten. You can then lubricate with lithol so that moisture does not get to the contacts. On the other side of the power wires, also check the contacts.
8.1. Lighting from another car
For Russian car owners a normal situation, when a neighbor asks to "light" his battery. For this simple procedure, in addition to a car with a charged battery, correct wires. Those wires that are sold in the markets have simply awful quality. Not only that these wires are copper and a sufficiently large cross section. Very high quality "crocodiles" are needed, providing a large contact area and a high clamping force, and good contact between the wire and the "crocodile" is necessary. Do not forget that on these wires we will have about 200 amperes!
In order not to damage the complex electronic systems of your own machine, this seemingly elementary procedure requires a strict sequence of actions.
1. Connect the red cable to the (+) terminal on the charged battery.
2. Connect the other end of the red cable to the (+) terminal on the "ground" battery.
3. Connect the black cable to the (-) terminal on the charged battery.
4. Connect the other end of the black cable to a clean ground point on the engine block or chassis, most importantly away from the battery, carburetor, fuel hoses, etc. At the time of connection, be prepared for a small spark.
5. Ensure that both cables do not touch moving parts.
6. Start the car with the charged accumulator and allow it to work not less than one minute.
7. Try to start the car with a "seeded" battery. If the engine does not start, wait a few minutes and try again. If it does, let it run for a few minutes in this position.
8. Turn off the car with the charged accumulator.
9. When disconnecting the cable, follow the above procedure in reverse order.
By car, from which a light (source), you need to cut the stove (fan) to full speed - both in winter and in summer. The fact is that the inductive (reactive) nature of the resistance of the running electric motor almost completely extinguishes the very voltage surge (on the machines with "ringing" wiring (Avdotya 100, Subaru Legashi before 1996 and many others) can kill the on-board computer .
9. Features of battery operation in summer
Do not be surprised if one day it will be difficult or not to start a car in hot weather. Warm season - the same test as the cold. Heat accelerates chemical processes. Malfunctions and defects in the electrical system of the car or battery will immediately affect the battery condition. But, most likely, you will find out about it at the most inopportune moment. For example, at night during a rain, when it is necessary to include lighting, ventilation and windshield wipers. So do not relax. Summer is the most suitable period for buying a new battery.
In the summer, the motorist will not immediately notice that in the accumulator the density of the electrolyte and its level in the banks are insufficient. But the higher the ambient temperature, the more active the electrochemical processes. As a result of electrolysis, oxygen interacts with the plates, and the hydrogen that has become free evaporates. Thus, water disappears from the electrolyte. As soon as the solution level is below the plate level, the sulfation of the plates begins (lead sulfate dissolves in the electrolyte, and then settles on the surface of the plates already in the form of large insoluble crystals and the plates are electrolyte-insulated). The capacity of the battery decreases. Electrochemical reactions stop. The battery is out of order.
Keep in mind that during long-term storage of the battery occurs self-discharge (decrease in capacity). Leaving the battery in a discharged state is not recommended: in this case the water evaporates and the plates open. And then everything, as described above.
Acceleration of electrolysis helps to compact the active mass. This "disease" affects the negative plates, the active mass of which gradually becomes compacted during operation, and its porosity decreases. Access to the electrolyte inside the negative plates is difficult, which reduces the capacity of the battery. In addition, the consolidation of the active mass can be accompanied by the formation of cracks and peeling.
Plates crumble when the charging current increases, short-circuiting, lowering the electrolyte level, frequent and prolonged starting of the starter, when the battery is loaded with a high-power discharge current. Often, positive plates are subject to warping, while cracks form in their active mass, and it (the active mass) begins to fall out of the lattices.
The reason for the loss of active mass from the lattices of the plates can be a prolonged recharge, poor plate attachment, vibration, etc. The crumbling active layer eventually closes the plates, reduces the power and the service life. AT modern batteries plates are placed in an envelope-separators; the precipitate falls out, but a short circuit can be avoided.
In summer, the ventilation holes are clogged with dust. To prevent the battery from bursting and exploding, keep the battery clean. Fill plugs must be tightly closed.
First, monitor the electrolyte level and regularly add distilled water. Secondly, do not leave the battery uncharged. Third, watch for the cleanliness of the case. Fourth, monitor the condition of the electrical system of the car. A defective starter and generator completely imperceptibly "prepare" the battery for the winter and with the first frosts it will refuse.
If you plan to replace the battery, it is better not to wait until the fall. In the season, the choice is much less, the prices are higher, and there are more willing. In any case, the assistance of a trained sales consultant will be required. In the summer he can give you more time.
10. Security Considerations
Remember that the danger of ignition of oxygen and hydrogen released during charging (and also after its completion) is quite real.
Although most serious manufacturers equip battery caps with flame arresters designed to prevent it from getting inside the battery, this likelihood still persists.
Remember also that a spark arises not only when the terminal is disconnected. Static electricity from synthetic clothing can be enough to cause an explosion.
The explosion of the battery can be compared in power with a shot from a 12mm gun. The result is an eerie sight, and it happens more often than you can imagine. For example, in cautious America, there are more than ten thousand such cases per year.
While the explosion probably will not be fatal, it can seriously injure you, especially the person, as the plastic shards scatter in all directions. Therefore, always be in safety glasses.
If you suddenly needed to disconnect the battery on a car with a working motor (it's better, of course, not to subject your car to such tests), you first need to include as many consumers as possible: stove, lights, fog-lights, wipers. If this is not done, the voltage regulator can burn, and then the electrical equipment, including the engine control system, will fail. And first, take a look at the instructions: does it allow you to do such an operation at all? After all, on cars of some brands, stuffed with modern equipment, any disconnection of the battery disables complicated electronic systems.
11. Storage of the battery
So, if there is no possibility of recharging during storage of the battery, the following method can be recommended. Electrolyte in the battery should be replaced with a 5% solution of boric acid. Before replacing the electrolyte, the battery is fully charged, and then the electrolyte is drained for 15 minutes. Then it is immediately washed twice with distilled water, keeping the water for 20 minutes. After rinsing, pour a solution of boric acid, wrap the plugs with open air vents, wipe the battery and put it into storage. Self-discharge batteries with a solution of boric acid is practically absent.
reference
To prepare a 5 percent solution of boric acid, it is necessary to dissolve 50 g of boric acid in 1 liter of distilled water, heated to 50 ... 60 ° C. The solution is poured into batteries at a temperature of 20 ... 30 ° C.
Store the battery at a temperature of at least 0 ° C, since a poured 5 percent solution of boric acid can freeze. And for the introduction of such a battery, a solution of boric acid is poured out of it for 15 ... 20 minutes, and a sulfuric acid electrolyte with a density of 1.38 ... 1.40 g / cm 3 is immediately filled in for our zone. After a 40-minute impregnation of the plates with electrolyte, the battery can be installed on the car if the density of the electrolyte does not decrease below 1.24 ... 1.25 g / cm 3. If it became lower, the density should be corrected by selecting a weak solution and adding an electrolyte with a density of 1.40 g / cm
12. Annexes
12.2. Rescue the battery
July 17, 2017One of the important parts of the car is the battery. He accumulates electricity and gives it to the on-board system of the machine. Without it, the starter will not start.
Experienced motorists know how to ensure the battery life for five to six years. If you do not service this element, its service life will not exceed three years. It is always more economical to conduct periodic maintenance than to purchase a new battery.
In this article, we will talk about the reasons for reducing the life cycle and the stages of battery diagnostics, testing the density and ways to increase it.
Reasons for shortening the battery life
Forewarned is forearmed. It is this principle that will prolong the life of the car battery, prioritize maintenance. It is important to know what causes can lead to a reduction in efficiency.
Periodic discharged state
The correct state of the battery is charged. In this case, when starting, the accumulated energy is recirculated to the starter. Further recharging occurs from the generator while the vehicle is moving.
Modern vehicles, stuffed with a lot of appliances, consume energy in such quantities that the battery can not cope with the replenishment of the stock. Especially negative impact on the state of the battery has a tense urban driving style, when you often have to be in traffic jams. Therefore, it is important to remember to recharge the battery.
Ambient temperature
It is technically provided that the battery in a charged state fully emits energy at a temperature regime of 15-20 0С. The charge starts to get lost when the temperature drops by 1 ° C.
Non-observance of operating rules
Most often during the winter operation of the car, in a discharged battery in the frost, the electrolyte freezes. What are the consequences for the battery? The most serious are complete failure. When the electrolyte freezes, the lead plates, the body, are permanently damaged.
 In the summer in the heat, motorists face the evaporation of water from the electrolyte. In this situation, the plates suffer again (there is a short circuit), shortening the battery life.
In the summer in the heat, motorists face the evaporation of water from the electrolyte. In this situation, the plates suffer again (there is a short circuit), shortening the battery life.
Faulty on-board network
Its important components: the generator and the voltage regulator should work flawlessly. Any of their malfunctions drastically reduces the performance of the battery.
Another point, the voltage level of the on-board network. Increased level leads to a constant recharge of the battery and the boiling of the electrolyte. A low level will lead to a chronic discharged battery. What will be the consequences, it was said above.
Low-quality consumables
Inside the battery, corrosion processes are inevitable. The fight against this phenomenon is carried out by the producers. What can a motorist do? To fill up the accumulator exclusively with high-quality electrolyte and distilled water. The latter experts recommend taking in pharmacy chains.
Sulphation of plates is also inevitable. In our power only to reduce the intensity of this process, resorting to desulphation. The occurrence of this problem is indicated by a rapid drop in capacity, overheating, increased voltage on the battery terminals.

When should I service?
It is important to know not only how to maintain the car battery, but also when to do it. Service consists of service operations and diagnostics. If service maintenance is better conducted in car-care centers, then diagnostics can and should be done independently. Only so the motorist will know about the actual state of the battery.
It is reasonable to carry out the diagnosis of the battery condition at the time of checking the oil level, filling the washer tank, etc. This approach will prevent some problems with batteries.
What is included in the diagnosis:
- checking the voltage at the terminals with the battery disconnected;
- checking the voltage when the engine is running;
- determination of the electrolyte level;
- check for dirt and surface damage.
Service maintenance
When the maintenance operations are carried out by the employees of the service station, the car owner does not think what they are doing. But if the motorist performs maintenance of the car battery with his own hands, he should study what operations need to be carried out.
Let's consider five basic actions.
1. When the car is used continuously, it is recommended that the battery be recharged every three months using the network chargers. In this case, the maximum charge level is reached, and the problem with the discharged state of the battery is eliminated. Periodic recharging is performed automatically in constant voltage from the generator of cars.
Recharging can be unplanned. In situations where the owner forgets to turn off the headlights or a long simple car happens, then the charge level drops to zero. In this case, charging is done in DC mode. This operation must be carried out under control.
 2. Check the load of the battery by using a load fork. This device will show the real working capacity of the battery. The check should be carried out in two stages: no load and no load.
2. Check the load of the battery by using a load fork. This device will show the real working capacity of the battery. The check should be carried out in two stages: no load and no load.
The first step is to disconnect the battery from the charging source. Then connect the load plug and check the data of the built-in voltmeter with the matching table.
To the second stage proceed only at 100% level of charging. With the load connected, the measurement is made at the fifth second of operation. Usually, the voltmeter's indices are equal and more than 9 indicate that the battery holds the load well. If the values are lower, the battery should be changed.
Depending on the amount of load used, the voltmeter readings may vary. Thus, the same battery, tested by two different load forks, can give values of both 8.5 V and 10.5 V.
The permissible range of values is indicated in the documentation accompanying the load plug.
3. Determination of leakage current. If you have a new battery, it is working, but in the morning after the previous normal operation you can not start an auto, then you should measure the leakage current. The presence is normal for the battery only if its value does not exceed the norm.
The leakage current level is determined using a multimeter. During the test, all consumers should be disconnected, turn off the ignition, disconnect the battery negative terminal. The multimeter is switched to the current measurement mode and connected to the gap between the negative terminal and the negative terminal, observing the polarity. The readings of the multimeter are considered normal at a level of 15-70 mA.
 If the resulting value is higher, you should look for a source of leakage. This is already a matter of a separate article, but you can start with the alternate removal of fuses. At the moment when the meter's parameters return to normal and a source of problems will be found.
If the resulting value is higher, you should look for a source of leakage. This is already a matter of a separate article, but you can start with the alternate removal of fuses. At the moment when the meter's parameters return to normal and a source of problems will be found.
Practice shows that the increase in leakage current is affected by:
- worn wiring, poor quality insulation;
- incorrect connection of electronic systems;
- dirt and oxide on the contacts.
4. Desulphation of the battery helps only at the initial stage of plate sulphation. If you encounter such a problem during the diagnostics, do not delay with the restoration of the battery performance. There are two types of desulphation.
- chemical. From the discharged battery drain the electrolyte and fill with a solution of Trilon B. Within an hour, a reaction occurs, then it is drained and rinsed with distilled water;
- impulse current. It is worth mentioning that this procedure is complex and it is necessary to have knowledge in the field of electrical engineering. The essence of this method is to connect the battery to a large power supply (more than 100 A). The impulse current excites electrons, thereby knocking out lead sulfate from the plates.
5. Check the density of the electrolyte. Also there is a term - "battery density". In fact, it's the same thing. The density is measured when the battery is fully charged. The average value differs by climatic zones. Thus, in the central band the norm is 1.27-1.29 g / cm3, and in the northern band 1.3 g / cm3.
 The test is carried out with a densimeter at a temperature of + 25 ° C. If the measurement occurs under a different temperature regime, then the values should be correlated with the table below.
The test is carried out with a densimeter at a temperature of + 25 ° C. If the measurement occurs under a different temperature regime, then the values should be correlated with the table below.
| The temperature of the electrolyte, in ° C | Correction to the indicator of the densimeter, in g / cm3 |
| -55 - 41 | -0,05 |
| -40 - 26 | -0,04 |
| -25 - 11 | -0,03 |
| -10 +4 | -0,02 |
| +5 +19 | -0,01 |
| +20 +30 | 0,00 |
| +31 +45 | +0,01 |
| + 46 +60 | +0,02 |
Metering is carried out in each compartment of the battery and the deviation in the indices should not be more than 0.01 g / cm 3.
The result of measuring the electrolyte density can be classified as:
- normal;
- overestimated (the situation can be corrected with a simple topping of distilled water);
- understated (raise the level is more difficult).
Increasing the density of electrolyte
Let us consider separately how to increase the density. After all, a low level reduces the voltage and makes it difficult to start the engine of the car.
- Preliminary it is necessary to measure the density in each bank of the battery, correlate with the norm according to the climatic zone.
- The increase in density occurs by adding an electrolyte of higher density. To do this, we remove the old solution with pears and fill it with new by volume twice as old.
- Shake the battery without turning it to mix fluids.
- The control density measurement is carried out, repeating the procedure, if necessary, until the required values are reached.
- The remainder of the volume is supplemented with distilled water.
Rechargeable batteries are filled with sulfuric acid and explosive gases (hydrogen and oxygen) are released in the course of a normal charge-discharge cycle. To avoid personal injury or damage to the vehicle, observe the following safety instructions:
- Before you start working with any electrical components of the car, disconnect the power cable from the negative battery terminal. With the power cable disconnected, all electrical circuits in the car will be opened, which will ensure that any electrical component is accidentally closed to ground. Electric spark creates a potential danger of injury and the occurrence of fire.
- Any work related to the battery must be carried out in safety glasses.
- To protect against the ingress of sulfuric acid, which is filled with a rechargeable battery, use protective clothing on your skin.
- Do not violate the safety rules specified in the maintenance procedures when handling equipment used for maintenance and testing of batteries.
- It is strictly forbidden to smoke or use open fire in the immediate vicinity of the battery.
Routine maintenance of the battery
Current maintenance battery is to check the cleanliness of the battery case and, if necessary, adding pure water to it. All battery manufacturers recommend using distilled water for this purpose, but if it is not available, you can use clean drinking water with a low salt content. Since water is the only consumable component of the battery, the acid is not allowed to be added to the battery. Some of the water from the electrolyte evaporates during the charging and discharging of the battery, but the acid contained in the electrolyte remains in the battery. Do not overfill the battery with electrolyte, because in this case the normal bubbling (gas generation) that occurs in the electrolyte during the operation of the battery will result in the leakage of the electrolyte, which causes corrosion of the battery terminals, its mounting brackets and the pallet. Batteries should be filled with electrolyte to a level about one and a half inches (3.8 cm) below the top of the filler neck.
The contact of the power cables connected to the battery and the terminals of the battery itself must be inspected and cleaned in order to avoid a voltage drop on them. One of the most common reasons that the engine does not start is the attenuation or corrosion of the contacts of the power cables connected to the battery terminals.
Fig. Strongly corroded battery terminal

Fig. It was found that this power cable connected to the battery is severely corroded under insulation. Although corrosion corroded through the insulation, but remained unnoticed until the cable was carefully inspected. This cable must be replaced

Fig. Carefully check all battery terminals for signs of corrosion. In this car, two power cables are connected to the positive terminal of the battery with a long bolt. This is a common cause of corrosion, which causes a violation of the electric starting of the engine
Battery emf measurement
Measurement of the electromotive force (EMF) of the battery using a voltmeter is simple way determine the degree of its charge. EMF battery is not an indicator that guarantees the performance of the battery, but this parameter more fully characterizes the state of the battery than simply inspecting it. A rechargeable battery, which looks quite workable in appearance, may not be as good as it seems.
This test is called the measurement of the voltage in idle mode (checking the emf) of the battery because the measurement is carried out at the terminals of the battery without the load connected to it, at zero current consumption.
- If the test is performed immediately after the battery is fully charged or in the car at the end of the trip, the battery must be emptied from the polarization emf before the measurement. EMF polarization - this is an increased, in comparison with the normal, voltage, which occurs only on the surface of the battery plates. EMF polarization quickly disappears when the battery works under load, so it does not give an accurate estimate of the degree of charge of the battery.
- To release the battery from the emf polarization, turn the headlamps into the driving mode for one minute, and then turn them off and wait a couple of minutes.
- With the engine and the rest of the electrical equipment switched off, with the doors closed (to turn off the light in the passenger compartment), connect the voltmeter to the battery terminals. Red, plus, the wire of the voltmeter connect to the positive terminal of the storage battery, and black, negative, a wire - to its minus terminal.
- Record the voltmeter reading and compare it with the battery charge table. The table below is suitable for estimating the degree of charge of the battery by the emf value at room temperature - from 70 ° F to 80 ° F (from 21 ° C to 27 ° C).
Table
| Emf of the battery (B) | Degree of charge |
| 12.6 V and higher | Charged to 100% |
| 12,4 | Charged by 75% |
| 12,2 | Charged by 50% |
| 12 | Charged by 25% |
| 11.9 and below | Unloaded |

Fig. The voltmeter shows the voltage of the battery one minute after the headlights are turned on (a). After turning off the headlights, the voltage measured on the battery was quickly restored to 12.6 V (b)
NOTE
If the voltmeter gives a negative indication, either the battery is charged in reverse polarity (and then it must be replaced), or the voltmeter is connected to the battery in reverse polarity.
Measure battery voltage under load
One of the most accurate ways to determine the working capacity of a battery is to measure the voltage of the battery under load. In most testers for starting and charging characteristics of car batteries, a carbon rheostat is used as the load of the battery. The load parameters are determined by the nominal capacity of the battery being tested. The nominal capacity of the battery is characterized by the amount of inrush current that the battery can provide at a temperature of 0 ° F (-18 ° C) for 30 seconds. Previously, the nominal capacity of the batteries in ampere-hours was used. The measurement of the voltage of the battery under load is carried out at a discharge current equal to half the rated current of the battery or three times the nominal capacity of the battery in ampere hours, but not less than 250 amperes. The voltage of the battery under load is measured after checking the degree of its charging by the built-in hydrometer or by measuring the EMF of the battery. The rechargeable battery must be charged at least 75%. The corresponding load is connected to the battery and after 15 seconds of battery operation under load the voltmeter readings are recorded with the load connected. If the battery is good, then the voltmeter should remain above 9.6 V. Many battery manufacturers recommend measuring twice:
- the first 15 seconds of battery operation under load are used to free from EMF polarization
- second 15 seconds - to get a more reliable estimate of the battery condition
Between the first and second cycle of work under load, it is necessary to make an exposure of 30 seconds to give the battery time to restore.

Fig. The Car Battery Test and Charging Tester released by Bear Automotive automatically turns the battery under test into load mode for 15 seconds - to remove the emf polarization, then turns off the load for 30 seconds to restore the battery and reconnects the load to 15 seconds. Information on the state of the battery is displayed on the tester display

Fig. The tester VAT 40 (voltammeter, model 40) of Sun Electric, connected to a battery for testing under load. The operator uses the load current controller to set the discharge current equal to half the rated current of the battery by the ammeter. The battery operates under load for 15 seconds and at the end of this time interval, the battery voltage measured with the load connected must be at least 9.6 V
NOTE
Some testers to determine the degree of charging and the performance of the battery measure the capacity of the battery. Observe the testing procedure established by the manufacturer of the test equipment.
If the battery fails the test under load, recharge it and retest the test. If the second test fails, the battery must be replaced.
Charge the battery
If the battery is extremely discharged, it must be recharged. Charging the battery to avoid damage due to overheating is best done in the standard charging mode. Explanations regarding the standard charging mode of the battery are shown in the figure.

Fig. This battery charging device is regulated for charging the battery with a nominal charging current of 10 A. Charging the battery in the standard mode, as in the above photograph, does not affect the battery as much as the accelerated charging mode, which does not exclude battery overheating and warping of battery plates
It must be remembered that charging a fully discharged battery may take eight hours, or even more. Initially, it is necessary to maintain a charging current of about 35 A for 30 minutes - in order to facilitate the beginning of the process of charging the battery. In the mode of accelerated charging of the battery, its increased heating occurs and the risk of warping the battery plates increases. In the accelerated charging mode, there is also enhanced gas formation (release of hydrogen and oxygen), which creates a health hazard and a risk of fire. The temperature of the battery should not exceed 125 ° F (52 ° C, the battery pack is hot to the touch). It is recommended, as a rule, to charge the accumulator batteries with a charging current equal to 1% of the CCA current rating.
- Accelerated charging mode - maximum 15 A
- Standard charging mode - maximum 5 A
This can happen to anyone!
The owner of the Toyota car disconnected the battery. After connecting a new battery, the owner noticed that a yellow alarm lamp "airbag" was on the instrument panel, and the radio was blocked. The owner purchased a used car from the dealer and did not know the secret four-digit code needed to unblock the radio. Forced to look for a solution to this problem, he randomly tried to enter three different four-digit numbers in the hope that one of them would work. However, after three unsuccessful attempts, the radio completely disconnected.
The frustrated owner turned to the dealer. Elimination of the problem occurred cost more than three hundred dollars. To reset the "airbag" alarm, a special device was required. The radio had to be taken out of the car and sent to another state, to an authorized service center, and on return, reinstalled in the car.
Therefore, before disconnecting the battery, be sure to coordinate it with the owner of the car - you must make sure that the owner knows the secret code for the inclusion of the coded radio receiver, which is simultaneously used in the car security system. It may be necessary to use a backup power supply for the radio's memory when the battery is disconnected.

Fig. That's a good idea. The technician made a backup power source of memory from an old battery flashlight and a cable with an adapter to the cigarette lighter socket. He simply connected the wires to the battery terminals of his battery light. The flashlight battery is more convenient to use than a normal 9-volt battery - in case someone would think of opening the car door at a time when the backup power source of memory will be included in the circuit. A 9-volt battery with a small capacity, in this case, would quickly be discharged, while the capacity of the flashlight battery is large enough and it will be enough to ensure that even when the interior lighting is switched on, provide the necessary memory power
The bulk of vehicles, regardless of the model, year of manufacture and the manufacturer is equipped with such a necessary part as a rechargeable battery. This is one of the types of conventional electric battery. The main function of this device is to provide electric current to all systems and mechanisms of the machine or motorcycle with the inoperative on-board generator.
The battery is used in the following cases:
- power supply for the ignition system when the engine is first started;
- the supply of electric current to the onboard systems of a car or a motorcycle with an idle power unit;
- providing additional power for car devices when the generator is running.
The main principle of the battery, according to the laws of physics, is the process of creating a voltage between the contact plates placed in a special solution. Initially, the contacts in the battery were made of copper and zinc, but they were short-lived and quickly decomposed during operation.
The honor of creating this scheme, which in a somewhat modified form has survived to this day, belongs to the Frenchman named Plant. He first demonstrated a working prototype in 1859. 
Modern rechargeable battery for power supply electrical network The car consists of many different elements placed in a high-strength body made of polypropylene. Inside the case is divided into several cells filled with electrolyte.
In each cell of the battery, lead plates with different polarities are placed, which are coated with a special chemical reagent necessary for the generation of electric current. In order to prevent short circuits, the plates must be isolated from each other with a special material.
For ease of use and maintenance, some minor changes and improvements may be made to the basic design of the battery.
Types of batteries

There are the following types of car batteries:
- serviced;
- little serviced;
- hybrid;
- not serviced.
- Serviced. This type of battery for the car is almost out of service and extremely rare in retail. Usually, these are models of domestic manufacturers. From other types of batteries (especially foreign production) they are distinguished by a large number of shortcomings, affecting the ease of operation.
The disadvantages of serviced batteries include a fragile, unprotected body (most often made of ebonite), which for isolation was covered with a special substance that lost its properties in sudden fluctuations in ambient air temperature. This is the cause of a sharp drop in battery power in the winter. The same was the reason for the drop in the level of liquid in the tanks, which required its constant replenishment.
- Low-maintenance. The most common in modern cars. Typically, these batteries are characterized by a very strong body of various types of plastic. In the process of operation, it is required to control the level of the electrolytic liquid and to replenish it approximately once per 30 thousand kilometers of run. The pluses can be attributed to their rather moderate cost.
- Hybrid. Hybrid car batteries are one of the modifications of the previous kind of batteries. But they have a significant difference: contact groups in cells consist of different metals, which allows to achieve certain advantages, namely:
- high current level during engine start-up;
- low liquid consumption in the battery;
- long life and unpretentiousness.
Hybrid car batteries are rare and not in high demand due to the high price.
- Maintenance free. The design of such batteries does not provide for the control and restoration of the water level in the cells, in connection with which the body lacks the necessary openings. However, to properly use unattended car batteries, you need to monitor other parts and mechanisms of the car that are part of the electrical system. It is important to regularly check the condition of the belts, monitor the serviceability of the generator and the entire electrical wiring of the machine. The combination of convenience and cheapness makes them an ideal choice for an automobile owner if he is confident in the technical condition of his iron horse.
Maintenance of car batteries
Long and high-quality work of the car depends on the technical serviceability of all its parts, units and mechanisms. The same applies to the battery. The battery requires attentive attitude and timely delivery of maintenance activities.
Measurement of electrolyte level
 If your car has a battery that requires maintenance, then to extend the life of the battery, you need to regularly check the electrolytic liquid level in the battery compartments.
If your car has a battery that requires maintenance, then to extend the life of the battery, you need to regularly check the electrolytic liquid level in the battery compartments.
To do this, it is enough to check with the marks on the body, marking the maximum and minimum level of liquid.
If they are not available, you can use a special glass tube of the correct size. For this:
- open the battery cell cap;
- immerse the tube in the corresponding hole;
- close the upper section of the tube with your finger and pull it out;
- set the liquid level in the tube.
The liquid level in the tube should be not less than 12 mm and not exceed 15 mm. If necessary, you can restore the required amount by adding distilled water.
Measurement of electrolyte density
 For the correct flow of chemical processes to generate electric current in the battery, it is important to control the density of the electrolyte in the battery. It should correspond to the value indicated in the technical characteristics of the battery.
For the correct flow of chemical processes to generate electric current in the battery, it is important to control the density of the electrolyte in the battery. It should correspond to the value indicated in the technical characteristics of the battery.
For this purpose a special device is used - hydrometer. It is a glass flask with a rubber pear on the end, inside which is placed a float.
To determine the density of the solution, the following sequence of actions should be carried out:
- open the plugs of the battery cell;
- release the air from the flask, squeezing the pear on its end;
- immersing the tip of the bulb in the hole on the battery to release the pear, as a result of which the hydrometer will fill with electrolyte;
- get the value of the density of the liquid in the battery, which is indicated on the float divisions
- check the resulting value with the battery specified in the documentation.
The density of the electrolyte in the battery depends on the model and manufacturer, but is usually 1.24 kg / l. When operating the device under severe climatic conditions, the density can be slightly increased.
If the figures obtained as a result of your measurements are lower than necessary, you should top up the required amount of distilled water and put the battery on charge.
Voltage of fully charged car battery should be 12.6 volts. This testifies to the correct operation of the battery and its readiness to perform the provided functions on the power supply of the vehicle's on-board system.
Safety measures for maintenance
Working with batteries is a rather dangerous procedure and requires certain safety measures:
- use protective gloves and glasses;
- work in well ventilated rooms;
- compliance with strict procedures for working with acids and alkalis;
- adherence to fire safety measures.
Long and high-quality work of the battery is a guarantee of the proper operation of all systems and mechanisms of the car. The electric power generated by the battery is necessary to start the engine, power electronic components and many other purposes.
Using the advice given above, any motorist will be able to independently carry out maintenance work on the battery, which guarantees its trouble-free service for a long time.



