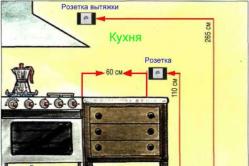
Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are situations of emergency care for fever, when the child needs to give the medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and apply antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? Which medications are the safest?
In modern electrical engineering there are many types and types of wires for various purposes. One of the most common power cables for applying an electrical line are wires marked BBG-Png and ABBG-Png. In this article we will look at the VVG cable, how the decoding is done, some of its features, specifications, as well as various designs.
First of all, it is necessary to determine exactly which design is called a cable. Usually it represents two or more supporting veins. Each vein is separately located in the insulating material, and then they are all enclosed in one common outer braid, which can vary in flexibility, strength, resistance to various external factors, and is standardized by GOST standards.
Practically all types of wires on the external insulation are marked with specific markings (for example, VVGng, AVVG-Png). The marking is an alphanumeric designation. This method is necessary in order to give a concise definition of the type of cable, its material, resistance to temperature or humidity, as well as other technical characteristics. Ability to decipher the marking on the outer braid will allow you to select the correct wire for electrical network, observing all the necessary requirements.
Specialists in the field of electrical engineering should know all the short notations that are applied on insulation. Also in stores, sales consultants should be able to read the markings in order to be able to quickly find a bay with a cable of interest to the customer. Consider several markings of common wires and their decoding. Cable ВВГ-Пнг and АВВГ-Пнг.
- A - the first letter means that the wires of the power wire are completely made of aluminum;
- On the BBGng marking, the first letters will determine the insulation material, and the absence of the letter "A" will make it clear that the core of this power cable uses copper wires;
- The first and second letter "B" in the BBGng marking means that the insulating material for the supporting strands, as well as the outer shell itself, are made of PVC (PVC);
- Letter "G" - determines that the power cable is of a flexible type, not armored (there are no protective covers on top of the shell);
- Letter "P" is a flat structure, veins in the bay are located in the same plane, parallel to each other.

If there is a "ng" prefix on the labeling, it means that in the production of insulation for the entire cable bay, a special stable PVC compound was used which can withstand high temperatures and can not be burned by contact with an open fire. "NG" - high refractoriness of the shell, low flammability.
The letters "ng-SL" - the insulation in the corresponding bay does not lend itself to burning, and also during melting it practically does not emit gas and smoke. Numerical designations allow to determine the diameter of the cross-section of the cord in the bay, the number of cores in the base of the structure. For example, АВВГ 3х4 - a bay with a three-strong power cable, section of each vein of 4 mm 2. Power structures are subject to mandatory certification in accordance with GOST.
Specifications
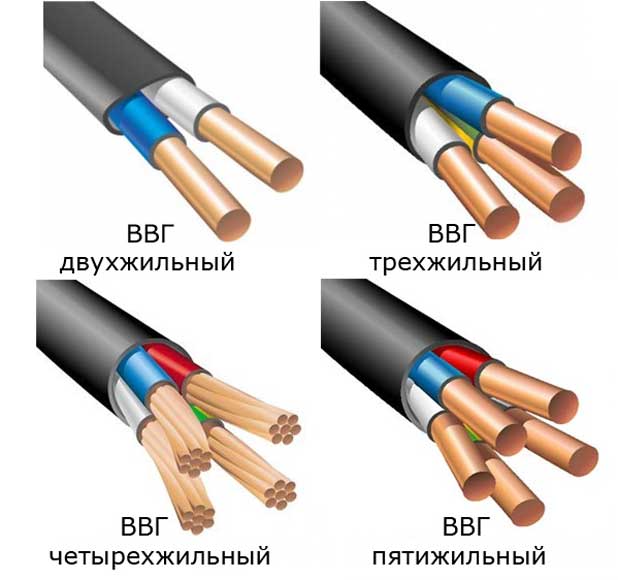
Cable ВВГ-Пнг and АВВГ-Пнг are made according to GOST standards. The cable ng consists of veins (copper or aluminum) of 1-2 classes in accordance with GOST, belt insulation for each conductor and outer shell. Current-carrying wires can be single-wire (monolithic), as well as multiwire (more flexible). The maximum number of veins in the braid is 5 pieces.

Depending on the design of the wire, it has its own technical characteristics according to GOST. The fire hazard class of the line is standardized in accordance with GOST 31565. When laying cores in beams, the requirements of GOST 12176 Category A are met. Consider the parameters of VVGG wire.
This design has certain limitations on temperature. The limiting temperature at which the power cable will function stably is up to 70 degrees Celsius. Work in emergency mode - up to 80 degrees, and the maximum value of temperature in case of short circuit, so that the conductors do not ignite - 350 degrees. The maximum humidity level for such a wire is up to 98%. It is produced with a nominal voltage on the electrical line of 660 volts or 1000 volts with a frequency of up to 50 hertz. The tests are carried out at a voltage of 3.5 kV.
Permissible amplitude of ambient temperature for wiring from 50 degrees below zero to 50 degrees Celsius. The minimum wire bending radius without protective covers is not less than 7.5 from the diameter of the power cable. The service life is 30 years. When proper installation with the observance of all the rules, he can serve up to 45 years.
Such technical characteristics make the design quite versatile for building an electrical network or distributing electricity for connected equipment. You can conduct installation of electrical lines, both in the ground and in the air. The ABBG model is not so universal, since aluminum has less resistance. The lower resistance is compensated by the increase in the cable cross-section, but this solution is not suitable for all types of connection (terminals, racks).
Video "Cable Production"
Versions
Power cable ВВГ-Пнг and АВВГ are made by the company Open Company in the city of Krasnoyarsk (Russian Federation). In production there are many different types of structures, each of which fully complies with GOST standards. The thickness and characteristics of the layers are regulated by GOST R 53769-2010.

To date, you can choose a suitable design of the cord, as they are produced in a wide range - different design and insulation coating. This can be a normal VVG cable. The traditional design of the power cable without flame retardant properties. VVGng and -LS - separately with refractory sheath and PVC without halogens with reduced smoke emission.
Scope of use
The VVG and VVG-Png power cable allows it to be used in a variety of different spheres. So often it is used for laying an electrical line in the ground. When installing the circuit in the ground, a structure with additional protective covers is used to prevent mechanical damage to the wire, protect it from chemical and combustible substances.
The need to lay the power cable in the ground occurs quite often, and not only when building a new residential house. Applying the laying of VVG wires in the ground, the PVC sheath will protect the structure from excessive moisture. In the ground, the cable can lie for more than 30 years, the ambient temperature has a small amplitude and changes smoothly, which does not affect the service life. And another type with additional protective covers under the ground guarantees protection from rodents, mechanical friction, sharp stones and debris.

In addition to ground mounting, this type of power cable can be used for air laying of an electric line. In this case, it is rational to use AVVG, since aluminum wires are cheaper in production. Since air laying increases the consumption of material, AVVG will reduce the cost of installation work. In addition, modern polymers will protect cores from corrosion of metal.
It is used for the redistribution of electricity between electrical equipment and the distribution of electricity in industrial complexes, in factories, in public buildings, multi-storey apartment houses. The versatility of the design makes it possible to use the VVGng and AVVGGG wiring at power stations, blocks, specialized overpasses, in the ground, for connection of lighting and switchgears.
Most types of equipment, instruments, tools and equipment in production, trade and everyday life connected to the electrical network, which have an AC voltage of up to 1 kV. A this means that in these networks the distribution and supply of electricity is carried out via a secure cable. To date, one of the popular products for power and lighting in indoor and outdoor areas is the VVG cable. There are options for its execution.
Any cable or conductor has a special marking on which you can determine the characteristics of the product.
Beginning electricians, who first encounter abbreviations, often do not understand the difference between VVGng and VVG, and even from VVGng-LS. Let's figure it out:
- VVG is equipped with ordinary PVC insulation, which does not have fire-retardant and self-extinguishing qualities.
- In the insulating layer VVGng there are halogen elements, due to which the combustion process is neutralized.
- Sheath of current-carrying veins VVGng-ls in the event of a fire, smoke and gas are not released due to the use of halogen-free polyvinyl chloride (this is a big plus for VVGng-ls).
- VVGngfr-ls is a similar model, but fire-resistant. If there is a fire of this type of cable, the emission of gas and smoke is low. If you apply a group gasket, then there will be no spread of combustion.
- In manufacturing the conductor VVGng-fr-ls, halogen-free materials are used, which distinguish this product from other brands. Plastic from halogen-free material has a high level of insulation and forms a quantity of smoke within the limits of the norm. Fire safety is the main feature of VVG ngfr-ls type of cable.
What is VVG?
Often in various instructions for the work of wiring are offered to use a non-flammable conductor VVGng. On the quality / price ratio, it is the best option. This conductor VVGng is actually very versatile, because it is practical to use in buildings of flammable materials and in buildings that have high humidity.
What can marking say? First, let us consider what markings of the conductor exist. If you know the decoding of the letters in the above cable marking, you can easily determine its properties. Below is a list of the main features on which it is quite easy to divide all the conductors.
1. Material that is used for manufacture of a current-carrying vein:
- there is no designation, it is copper;
- if the letter A, it is aluminum.
2. Material from which the insulation is made for conductors:
- if the letter B, then polyvinyl chloride was used;
- if the letters Pv, then applied polyethylene;
- if the letter P, then used polymer insulation.
3. Armor of the cable:
- if the letter B, then armored;
- if the letter is G, then the armor is missing, the bare cable.
4. Sheath (outer insulation):
- if the letter is P, then the shell is made of polymer;
- if the letters Shp, that is, a protective hose made of polyethylene;
- if the letters Shv, then the protective hose;
- if the letter B, then the insulation is made of polyvinyl chloride.
5. Fire safety:
- if there is a marking ng-frhf, then in the case of a group conductor of the conductor, combustion does not propagate; in the case of burning and smoldering, corrosive substances are not formed in the form of a gas;
- if there is marking ngfr-ls, then in the case of a group conductor, combustion does not spread, the formation of smoke and gas is reduced;
- if there is a marking ng-hf, then in the case of a group conductor of the conductor, combustion does not propagate; during burning and smoldering, corrosive substances are not formed in the form of a gas;
- if there is a marking of ng-ls, then gas and smoke emission is reduced, in case of group conductivity of the conductor ng-ls, combustion does not propagate;
- if there is marking ng, then in the case of a group conductor, combustion does not spread;
- if there is no marking, then during the laying of a single conductor, combustion does not spread.
If you follow the above, then you can decipher the abbreviation VVGng: the first letter B means that the insulation of the conductors was made of polyvinyl chloride, the second letter B indicates that the insulation of the outer shell was also made of polyvinyl chloride, the third letter of G says that there is a special layer of protection, there is no armor.
In the professional language of electricians, the abbreviation VVG means approximately: the letter B is vinyl, the letter B is vinyl, the letter D is naked. And the letters ng say that if you apply the group gasket of this conductor, it will not support combustion. This is an important indicator for cases where it is necessary to make a conductor in places where there is a high probability of fire. After all, the most important thing is security. In the marking there is no letter A, which means that the conductor has conductive cores made of copper.
This guide happens is made in two modern modifications: with the end of ng-ls - this means that during combustion, there is a lower emission of smoke and gas (this is good ng-ls); with the end of ng-hf - this means that during the combustion of the cable, no corrosive-active substances are released in the form of gas. These modifications have improvements - it's fr (in other words - fire resistance, which differs from ng-ls).
Often with the usual VVG you can find cables that have the letter "P" at the end of the marking. Judging by the technical data, they do not differ, and a small difference lies in the structure - it is flat. And this means that cable decoding VVG n it sounds like this: the letter B is vinyl, the letter B is vinyl, the letter G is naked, the letter P is flat.
Cable options
Cable laying VVG open way
If you follow technical parameters This cable is only allowed to open on surfaces and constructions from hardly incombustible or incombustible materialseg gypsum, concrete, brick, plastered surface, etc.
The installation of an open air VVG cable is allowed to be used under suspended structures, such as rope, etc. These facilities are required to provide a sufficiently reliable installation. When laying the cable, you should exclude any possibility of mechanical action on it.
If there is a risk of mechanical damage to the cable product, additional protection must be installed. It is necessary to use additional protection when laying an open cable on a burnt wood surface. Installation in this case should be made using a cable channel, corrugated hose, metal hose, pipe and other types of protection.
Wiring the VVG cable in a hidden way
This variant of cable laying remains the most popular for residential premises. Cable laying is done under the plaster, in voids, in furrows, etc.
With this version of the gasket, mechanical damage is practically impossible, therefore, the use of additional protection is not expected, except for the void walls in wooden houses.
It is allowed to perform hidden cable laying in pipes or other non-flammable materials. There are regulatory documents that relate to hidden electrical wiring. They determined the correct implementation of the hidden method of cable installation.
Execution of laying the cable VVG in the ground
It is known that it is not allowed to lay the cable of this brand under the ground without using special protection methods. All this is due to the fact that the protection, which will keep the cable from any mechanical influences, is not here.
The installation of underground VVG conductor is possible only in special sealed boxes and only over trestles and cable structures.
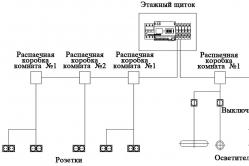
Marking electrical wires and cables The current range of wires and cables is quite wide. The buyer is presented with a wide range of cable-conductor products of various design versions of cores, as well as with a different insulation coating. As a rule, all conductors and cables have a special marking, which shows the characteristics of a particular product. Below is the decoding of the most common brands of wires and cables.
Marking of electrical cables
The modern range of wires and cables is quite wide. The buyer is presented with a wide range of cable-conductor products of various design versions of cores, as well as with a different insulation coating. As a rule, all conductors and cables have a special marking, which shows the characteristics of a particular product. Below is the decoding of the most common brands of wires and cables.
Alphanumeric marking of cables and wires
Marking electric cables and wires are produced by letters and numbers. Let's consider the letter abbreviations, that is, the marking, which is used to designate cables with polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and rubber insulation in accordance with GOST 16442-80, TU 16.K71-335-2004, TU16.71-277-98.
"A" (first letter) - indicates the material of the vein, in this case aluminum, and in the absence of this letter, the material is copper.
"AU" is an aluminum core with an additional sheathed cable made of lead.
"AA" is an aluminum core with an additional aluminum cable sheath.
"B" - indicates that this cable has a protective armor, which is made of two layers of steel tape with anti-corrosion coating. If the letter "n" stands, that is, the tongue has the form "B", then the steel shell has a special protective shell, which does not support combustion. Letter "b" - armor is made of profiled steel bands.
Marking of electrical cables and wires "B" - the first (in the presence of the first "A" - the second) - polyvinyl chloride insulation, the second (in the presence of the first "A" - the third) - polyvinylchloride shell.
"G" - at the end of the marking - a "bare" cable that does not have a protective cover. If the letter "G" stands at the beginning of the marking, then this cable is used in the mining industry. The lowercase letter "g", as a rule, is placed at the end of the marking and indicates that the metal shield of the cable is sealed with a water repellent tape. Marking "2g" - the presence of an additional aluminopolymer tape.
"Шв" - the presence of a cable protective sheath in the form of an extruded polyvinylchloride hose. "Шп" - the hose is made of polyethylene, "Шпс" - polyethylene, from which the hose is made, self-extinguishing.
"K" - at the beginning of the marking indicates that the control cable. "K" at the end of the marking - the cable armor is made with round steel wires, and a protective cover is put over them.
"C" - the lead sheath of the cable. "O" - the casing is made on top of each phase of the cable.
"P" - the insulation of the cable is made of rubber. If the letter H ("HP" marking) is in front, the cable insulation does not support combustion.
Labeling "ng" at the end - does not support combustion.
The numerical values in the cable marking show the number of cores and their cross-section. For example, 3x2.5 - three cores with a cross section of 2.5 square millimeters.
Examples of decoding alphanumeric marking of cables and wires
For clarity, we give a few examples of markings of the most common brands of cables.
АВВГнг 3x4 is a three-core cable with aluminum conductors cross-section of 4 squares, with a sheath and insulation made of PVC, without a protective cover, which does not support combustion.
PVG 3x2.5 is a three-core cable with copper conductors cross-section of 2.5 squares, with polyethylene insulation, PVC protective sheath, the cable has no protective cover.
ASB 7x2.5 is a seven-core cable with aluminum conductors cross-section of 2.5 square, in a lead sheath, the cable has armor, which is made by two steel strips that are not susceptible to corrosion.
Cable VVGng-LS Very often there are cable markings that contain English letters: HF and LS - they indicate a low level of gas and smoke emissions, respectively. For example, VVGng-LS-HF.
The marking of wires is somewhat similar to the marking of cable products, but it has some differences.
Here are some examples of marking the most common wires and cords in accordance with GOST 7399-97.
CIP - self-supporting insulated wire, the insulation of which is made of light-stabilized cross-linked polyethylene.
A - aluminum wire, which has no insulation coating. This wire is made from a variety of individual wires.
AC - steel-aluminum wire, not having an insulation coating. Structurally made of individual wires, which are located on the steel core (the base of the wire). PVS - wire with PVC sheath and insulation, flexible, with stranded conductors.
ШОГ - a cord with isolation from polyvinylchloride, with a parallel arrangement of veins, especially flexible.
PPV (APPV) - wire with copper (aluminum) flat cores, with single-layer PVC insulation.
Color coding of cables and wires
In addition to the alphanumeric marking of wires and cables, there is color marking. Below are the colors that mark the wire and the corresponding assignment of the core:
blue - neutral (neutral) wire;
yellow-green - protective conductor (grounding);
yellow-green with blue marks - grounding conductor, which is combined with zero;
black - phase wire.
In addition, according to PUE, the use of a different color for a phase conductor, for example, brown, is allowed.
When purchasing a cable, pay attention to the color marking of the cores, as in reality it may not meet the requirements. Correspondence of the colors of the veins to the generally accepted standards is, first of all, convenience for installation and further maintenance of the wiring.
In any case, the color marking of cores does not affect the quality of cable-conductor products. Therefore, if you purchased a cable (wire) with a non-standard color of cores, then before installing it, determine which color to which conductor will match.
Power cable VVG - choice and cost
Cable power flat, ВВГ-Пнг (А) 3х2, 5 bay 200м
Explanation of the abbreviation of VVG-Png (A) cable:
the absence of the first letter A speaks of copper veins (A-aluminum)
the first letter B denotes PVC insulation (vinyl)
the second letter B denotes a PVC shell (vinyl)
The third letter of G indicates the absence of a protective layer ("bare")
The fourth letter P denotes a flat form
the letters ng mean that the cable does not support burning
Index (A) in the name means that the cable does not spread combustion while laying in beams with a high concentration of combustible mass
Cable assignment For indoor installation
Type of equipment Power cable
Presence of a supporting wire No
Material of conductor Copper
PVC sheath material (PVC, PVC)
Conductor area 3 x 2.5 mm2
"Consumer properties"
Cable length 200 meters
"Logistics"
Packaging dimensions (measured in NICS) 40 x 10 x 40 cm
Gross weight (measured in NICS) is 17.4 kg
Power cable VVGng FRLS and VVGng FRHF
Cable ВВГнг FRLS and cable ВВГнг FRHF - power fireproof, a cover from PVC of orange color. Vng FRLS - with low smoke and gas evolution does not spread combustion. Vng FRHF - without halogen, does not spread combustion. The power cables vvng frls and vvng frhf are used for transmission and distribution electric power and electrical signals at an alternating voltage of 660V at a frequency of 50Hz. Cables remain operative in open flame conditions for 180 minutes on objects of mass gathering of people, on technically complex and especially dangerous objects.
Description and decryption of the cable:
В - Insulation of cores from polyvinylchloride plastic compound
В - Polyvinylchloride plastic sheath
D - Absence of protective covers
FR - the presence of a thermal barrier in the form of a conductor winding with two mica-containing ribbons
LS - Core insulation and sheath of low-combustibility polyvinyl chloride plastic with reduced gas-smoke evolution
HF is a halogen-free polymer composition
Cable VVGng (A) -FRLS 2x1.5
Wholesale Price: 48.09 руб.
Cable VVGng (A) -FRLS 3x1.5
Wholesale Price: 64.62 руб.
Cable VVGng (A) -FRLS 3x4.0
Wholesale Price: 115.90 руб.
Cable VVGng (A) -FRLS 4x1.5
Wholesale Price: 91.03 руб.
Cable VVGng (A) -FRLS 4x2.5
Wholesale Price: 113.68 руб.
Cable VVGng (A) -FRLS 5x1.5
Wholesale Price: 102.87 руб.
Cable VVGng (A) -FRLS 5x2.5
Wholesale Price: 141.68 руб.
Cable VVGng (A) -FRHF 2x1.5
Wholesale Price: 75.13 руб.
Cable VVGng (A) -FRHF 2x2.5
Wholesale price: 100 руб.
Cable VVGng (A) -FRHF 3x1.5
Wholesale Price: 101.25 руб.
It is most expedient to use VVG-P cables in hidden wiring and with a single laying in rectangular cable channels of appropriate dimensions.
Construction and materials
1. A current-carrying vein - copper, single-wire 1 class in accordance with GOST 22483-77.
2. Insulation - made of polyvinyl chloride plastic.
Insulated conductors multicore cables must have a distinctive coloring or be marked with numbers starting from zero. The color of the insulation of the neutral wires is blue (light blue), the earth conductors are two-colored green-yellow. In the case of a digital marking, the earth conductor is indicated by the number "0". The marking is made by embossing or printing. The height of the digits should be not less than 4 mm, the intervals between the figures not exceeding 35 mm.
3. The insulated cores of the circular form are laid in parallel.
4. Cable sheath - made of polyvinylchloride plastic.
If you focus only on the letters that constitute the abbreviation of the cable name VVG, then you can and make a mistake. The fact is that depending on its type, occupied by a literal place in the name, the meaning of the notation can be completely different. How does the combination of VVG as applied to power cable and what are its technical characteristics?
Explanation
- 1 - the letter V is not on the first, about which many do not know. When marking cables (wires), the letter on it indicates which metal conductor is made of. If it is made of aluminum, it is marked A, but copper conductors are not indicated in any way. Consequently, in the VVG cable "by default" cores of copper.
- 2 (B) - material of internal insulation (conductors). For VVG cable, this is polyvinyl chloride.
- 3 (B) - shell. The same is PVC.
- 4 (D) - degree of protection against mechanical damage. This cable does not have it, that's why they say that VVG is "naked". It is easy to remember associatively.
- 5 (digits) - the first corresponds to the number of cores, the second - to their section. For example, 4 x 6.
Often, after an abbreviation with a universal cable type designation (VVG), additional symbols are placed. They reflect the individual properties of products or features of the design. For example, VVG ng. How do they decode?
- P is a flat cable.
- ng is a non-flammable modification. Such a cable is allowed to be laid without the use of ducts, pipes or other protective structures. For example, in strobes, under plaster.
- FR - increased fire resistance.
- LS - minimal release of toxic substances and smoke.
- HF - active substances that initiate corrosion of metals, with thermal exposure are not formed.
- h - with filling. It is not difficult to decipher - in the cable between current-carrying conductors there is additional insulation (dielectric "filler" of polymers).
Here, in fact, and the entire interpretation of VVG - it's simple and understandable. Knowing the meaning of all the letters, it is not difficult to choose the optimal cable modification.

VVG - technical specifications
The decision on whether to purchase and install any type of cable based on decoding alone is not acceptable. First, you need to know the basic properties of the product, and secondly, its range. Consequently, all this information will also be to the reader.
- Cross-section of cores (mm²):
- basic - from 1.5 to 50 (in five-core), up to 95 (with the number of conductors 2 - 3), up to 240 (in a single- and four-wire cable);
- zero - from 1.5 to 25;
- grounding - from 1 to 16.
VVG is produced and with veins of different diameters (3 primary + 1 zero). Some samples may have a section more than those indicated. When buying, you should carefully read the range of this cable from the dealer (seller). Although, as a rule, "non-standard" VVG comes under the order.

- Load current (A) - from 19 to 208 (depends on the cross-section of the veins and their number).
- Temperature regime (ºС):
- operation - up to ± 50;
- installation of VVG - from -15 and above.
- Weight (kg / km) - from 7.6 to 10 526 (4 x 240).
- Storage conditions VVG (years):
- in closed rooms - 10;
- under canopies - 5;
- on platforms, under the open sky - no more than 2.
- Radius of bending - from 7.5 to 15 D ext.
- Shelf life (years) - up to 30.
Application of the cable VVG
This cable is used mainly for connecting equipment, laying power lines in circuits with voltage not exceeding 1 kV, mainly inside buildings, considering its mechanical insecurity. But this minus is leveled by a plus - unlike armored analogs, VVG has a smaller mass (1p.m.), therefore, it is much easier. In addition, it is more submissive to bending, which is important when installing power lines with a lot of changes in the direction of the route.
0 rub
Power cable flat VVG-P, VVG-Png (A), VVG-Png (A) - LS Number of cores from 2 to 3, section from 1,5 to 16 sq. M.
Explanation of the VVG-P cable:
В - Insulation of cores from polyvinylchloride plastic compound
В - Polyvinylchloride plastic sheath
D - Absence of protective covers
P - Flat, veins are located in the same plane parallel to each other
ng-LS - Insulation and sheath of polyvinylchloride plastic compound with reduced fire hazard with low gas emission
Elements of the construction of VVG-P cable:
- Copper round single-wire current-carrying veins: a single-wire (class 1) section 1,5-16 кв.мм- "ож";
- Insulation from PVC plastic, color marking of veins: white or yellow, blue or green, red or crimson;
- Sheath of PVC plastic compound of low combustibility.
The scope of application of VVG-P cable:
Power cables are intended for transmission and distribution of electrical energy in stationary installations for rated alternating voltage 0,66 kV and 1,0 kV of frequency 50Hz. Cables are designed for operation on land, rivers and lakes at altitudes up to 4300 m above sea level.
Cables are used for laying:
- in the air in the absence of danger of mechanical damage during operation;
- for laying in dry or damp premises (tunnels), channels, cable half-floors, mines, sewers, industrial premises, partially flooded structures in the presence of medium with weak, medium and high corrosive activity;
- for laying on special cable racks, on bridges and in blocks;
- for laying in explosive areas of class B-Ib, B-Ig, B-II, B-IIa;
- cables with copper cores are used for laying group lighting networks in explosive zones of class B-Ia.
Cables are designed for vertical, inclined and horizontal routes. Non-armored cables can be used in places subject to vibration. Cables can be used in nuclear power plants. Cables in tropical climatic design (index "-T") are resistant to mold fungi. Permissible heating of live conductors in emergency mode should not exceed + 80 ° С and the duration of operation in emergency mode should not be more than 8 hours per day, but not more than 1000 hours for the service life.
- Operating temperature range - from -50 ° С to + 50 ° С
- Minimum bend radius for laying 7.5 outside diameters
Cable VVG-P possible analogues / replacement *
* replacement data for VVG-P cable are reference, for their use, all necessary approvals and calculations by competent specialists must be carried out.
Permissible current loads VVG-P, VVG-Png (A), VVG-Png (A) -LS
The main design parameters of VVG-P, VVG-Png (A), VVG-Png (A) -LS
|
Number and cross-section of conductors, mm² |
Weight of cable kg / km |
Outer dimension, mm |