Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are situations of emergency care for fever, when the child needs to give the medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and apply antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? Which medications are the safest?
Quite frankly, such a statement of the question, like "Which cables are better, multi-core or single-core?" Is incorrect in its essence.
This formulation strongly resembles another question: "What is better, a spoon or fork?" Obviously, the answer depends on what exactly a person will eat! So with the choice of a conductor in the cable - depending on the location and operating conditions, either a mono or multi-core version is used.
First consider their differences.
Wire single-stranded - as a conductive element, only one core is used, which has a section from the standard series.
Wire stranded - a conductive element are (most often) interwoven several conductors, having a total cross-section in standard values.

Among the conductive cores, a non-conductive thread (usually reminiscent of a capron) can be weaved to increase the elasticity of the cable.
Features of each type
Given that the same property of the wire can become both a virtue and a disadvantage (depending on the requirements for installation), we will not repeat the common error in the description of each of the two types. We simply indicate their features that help to make right choice.
1. Single-wire wire
Often it is preferred because of the relatively low price (in comparison with a multicore wire of equal cross-section).
The higher stiffness makes it possible to make the wiring in the shield much more beautiful than the loops from the flexible cable. In addition, rigid peeled ends do not require crimping when installed in circuit breakers and other devices.
Connection of lamps, sockets and switches (under the condition of using one or two conductors with a monobloc) is easier and faster than stranded wires.
The twisting, consisting of several rigid cores, is more easily subjected to crimping of terminals or welding, which are the basic requirements for the PUE.
When installed in a stroba or plastic box, the harder cable "keeps the shape" while remaining in place.
Power cables of larger cross-sections are preferable to choose from among single-core ones for reasons of price and mechanical strength.
In most cases, contrary to the opinion of some "home-grown" electricians, it is more reliable and efficient to use single-core wires.
2. Stranded wire
When stacked in plastic cable ducts (or ducts), a more flexible multi-wire wire is easier to "fit" into corner turns. In one such channel, it is easier to lay several flat flexible cables than rigid single-core counterparts of the same cross-section.
Flexible multicore wire is much easier to "pack" in the switching boxes, under the sockets and switches. This factor is critical for large quantities of connections in one box.
When using special equipment for crimping and ferrules, the contacts become no less durable and reliable than single-wire wires.
All conductors have a "surface conductivity" (or "skin effect"), implying a non-uniformity in the distribution of current across the cross-section: electricity "Is displaced" to the surface of the conductor. Since the total surface area of a multitude of wires in a stranded wire is greater than in a single-core wire, its conductivity is also significantly higher, while the heating is lower.
Field of application of wires
The above-mentioned different properties of solid and stranded wires dictate the expediency of their application.
Stationary wiring in the apartment, like the gasket power cables medium and large cross sections, is preferably carried out by single-wire wires. In industry, it is just such wires that power is supplied to the network. On the railway, all contact wires are produced only by single-core ones, providing reliable power supply to the rolling stock.
But where resistance to multiple bends and vibrations is particularly important, the use of stranded flexible conductors is justified.
This is especially true for household and industrial extension cords, which transmit power to mobile devices and units, wiring in cars, headphones and audio systems.
On materials of the site Promsnab
Solid wire with stranded?
The answers to these and many other questions you will get from this wonderful article.
First let me turn to the official version of the Terms and Definitions regulated in:
(the text is taken from GOST)
|
Photo for an example |
Term |
Definition |
|
One-, two-, three-core cable (wire, cord) |
||
|
|
Stranded cable (wire, cord) |
Cable (wire, cord), in which the number of veins more than three |
|
|
Necessary and sufficient signs of the concept are contained in the literal meaning of the term |
|
|
|
A conductor (conductor) consisting of two or more twisted wires or strands |
Before proceeding to an answer to the question which cable / wire is better: solid or stranded, you should correctly determine what we mean by residential.
Based on the terminology described in GOST 15845-80, the number of cable cores and their concept design are separate, and in this case, I think it is the construction of the conductors themselves, which in turn are single-wire (mono) and multiwire.
If the question is asked correctly "which wire is the best one veined or many veined", Then the answer is simple, it will be better with the number of veins that the project provides.
If we are talking about the differences between single-wire and multi-stranded wires, then let's reliably understand this. The difference between single-wire and stranded wire will be demonstrated to us by a comparative table:
|
Stranded wire (conductor) |
Single-wire conductor |
|
in the photo we can clearly see the structural differences between the cores |
|
|
|
|
|
Cit consists of several conductors (current-conducting veins) twisted together. |
It consists of a single-wire (single-wire conductor) |
|
As a consequence of the design, there are differences in characteristics and purpose: |
|
|
Flexibility class:5 (at sections 4mm2 and above - a class of flexibility 4) |
Flexibility class: 1 and 2, depending on the cross-section of the cores |
|
Purpose:Temporary connections |
Purpose:Fixed gasket |
|
Life time:not more than 5 years |
Life time:not less than 30 years |
|
Ease of installation:excellent |
Ease of installation:is difficult due to low flexibility |
|
Price:more expensive monograms (more expensive) |
Price:cheaper multiwire (economical) |
So, we came close to resolving the question "what type of vein is better", although someone may already have made all the necessary conclusions about the pros and cons based on these dry tabular facts.
We know that the wire that is used to connect household appliances to the network, in extension cords, carriers and other temporary connections must meet the flexibility requirements and the use of a single-cable cable is not permissible.
Here the substitution will be noticeable, let's say an extension cable made on the VVG cable instead of the PVS wire will be more difficult to move from place to place and as a result, after a few bends the vein can be deformed.
It's obvious that for a temporary laying, use a multiwire construction, which has high flexibility.
What if, on the contrary, lay a multi-wire vein in places intended for the cable of a stationary installation? It seems logical, the convenience of installation is ensured (laying a flexible wire is much more convenient), the price in the scale of one bay is not very different, why not?
Here I ask you to carefully look at the lifetime of the multiwire conductor. This is not an accident or a mistake. During the operation of flexible cables and wires with a multiwire live, the oxidation process takes place more intensively and the effective cross-section of the conductive part of the vein is seriously reduced.
Thus, the need to replace the stationary gasket will come after 5 years, if a multi-wire wire structure is used. Cables with solid conductors have a service life of at least 30 years, which distinguishes them in this section.
therefore single-wire conductor design is the best solution for stationary installation, where there will be no mechanical effects during operation.
I suggest again using the table to determine examples of the use of single-wire and multiwire conductors:
"Examples of the use of stranded and single-core cable / wire, which marks are multiwire, which are single-wire"
|
Stranded wire (conductor) |
Single-wire conductor |
|
Laying in pipes and cable channels with a large number of bends for temporary power supply, including in office and industrial premises |
Laying in concrete and brick in a specially prepared "stroba" (groove), including in residential buildings and premises, as well as in industrial facilities, in the absence of mechanical influences |
|
Wires of PVS, SHVVP, POGV and other brands |
Cables of marks ВВГ, NYM, ПуВ, АВВГ and others |
|
Connection of devices, mobile industrial devices, household appliances, portable lamps, household and industrial extensions |
Armored cables are made on the basis of single-wire conductors and are used for laying in the ground, trenches, tunnels, mines, industrial premises with an aggressive environment. |
|
Cable KG, Wires MGSHV, GDP, PVS and others |
Cable АВБбШв, АСБ, СКл and others |
|
Car electrical wiring, audio (well withstand vibrational external loads) |
The wires of the contact network are used in vehicles using electric traction (locomotives, commuter trains, trams, trolley buses. |
|
PGVA, KPPT, PTL200, POGV and other |
MF, MK, NLF and othersa wire with multiwire cores is indispensable
For termination, you must use a special tool or you can use the usual pliers.
And we get here such a wire:
In the next stage, after the termination of the stranded wire, it is possible to start connecting the conductor to the mono-strand and the stranded wire in the tip, say, for example, using terminals:
This is how the connection looks:
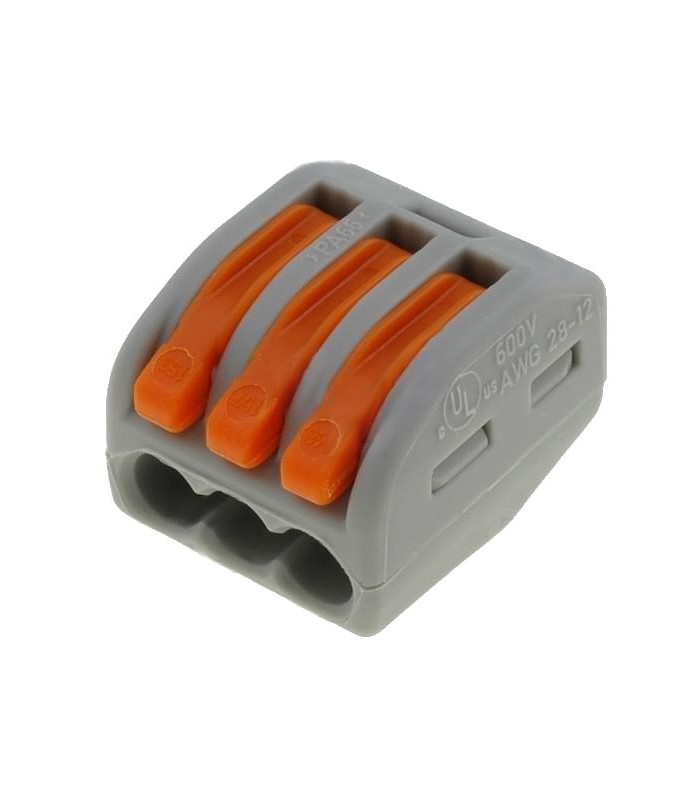
As an alternative, a simpler version, you can try using the WAGO 222 clamp terminals, which are just for multiwire conductors, but the conductor with the mono-pin can also be clamped. This connection will turn out to be less reliable than the previous one, but it is also quite suitable for connecting two copper conductors. Be sure to close the connection in the box, give it time to work under load and check if there is any heat. In the event that the connection gets warm, this indicates that the contact is bad and you need to re-connect the connection.
About connection types from detailed instructions execution, can be found thanks to the video shown here: |
This question is purely rhetorical. And the answer to it is known in advance. The choice of cable or wire will depend on many initial data, for example, on the purposes and conditions of work, and also on its localization. To proceed to the main issue, it is necessary to consider the properties of single-core and multi-core cables.
As it follows from the definition itself, the single-core cable contains one metal core with a certain cross-section. Accordingly, the multicore cable consists of several conductors interwoven with each other. The cross-section is determined in total by the standard scheme. Sometimes a thread is passed between the veins by the type of capron, which does not possess conductive properties, but improves the flexibility of the wire. Each of the mentioned types of cables has its own positive and negative points, which is determined for each specific case, based on which the choice should be made.
Let's start with a single-core cable, which is somewhat more popular, primarily due to the fact that it has a small price. But in addition to the relative cheapness, it has great rigidity, which facilitates installation work, and the ends of such a cable do not need to be crimped. Easier and more convenient connection of electric consumers (switches, sockets, etc.), in comparison with multicore cables. If the connection is made in the form of twisting, it is easier to subsequently compress the terminal or weld it. Easier laying of rigid single-core cable in the channel or stroba. Single-core cables with large cross-sections for power networks are better suited because of their greater strength and more favorable price. With a competent approach, solid wires can be used without violating the PUE, without losing efficiency and at the same time save money.
Characterizing the properties of multicore cables and wires, the following points can be noted:
- Stranded cable due to its elasticity is well, compactly placed in boxes, under switches and sockets. This is very important when there are many connections in one place.
- When placed in cable channels with a multi-conductor cable, it is easier to pass turning angles along the line of the gasket. The number of such wires laid in one channel is greater than, respectively, single-core with a similar cross-section.
- To give strength to joints during crimping, there is a special equipment that allows to provide high-strength contact, not inferior to that of single-core cables.
- 4. By virtue of constructive features the stranded wires have a relatively higher conductive capacity and noticeably lower heating at the load
Based on the above characteristics, you can make the right choice in favor of a cable. In particular, the installation of electrical wiring in the apartment, house, as well as installation of power lines of large and medium cross sections is better done with single-core cables. Single-core cables are installed lines at production facilities and industrial enterprises. On the railway transport.
There are conditions when, undoubtedly, it is better to use multicore cables. These are, first of all, places where numerous bends and turns are assumed along the line. In particular, this is typical for extension cords, which are used when connecting power supplies in industry or at home, for example, connecting the cable to moving devices, or installing wiring in cars and special equipment, using many other household electric consumers (audio systems, fans, etc.).
Cable АВБбШв It is available in both single-core and multi-strand configurations.
All of you know that the cable that is used for wiring in apartments and houses consists of several insulated wires in general isolation. There are cables and other structures, but, as a rule, they are used for slightly different purposes.
Solid wire Is a wire in a cable that is a single copper or aluminum conductor.
Stranded wire Is a wire in the cable that is a set of veins of a small section.
So why do we need solid or multicore wires? If there are solid and stranded wires, then each of them is designed for a specific purpose. And to apply a single-wire wire where it is advisable to use multi-stranded wire would be erroneous and irrational.
Operating conditions for single-core wires.

In terms of its physical properties, a solid wire is stiffer with respect to a stranded wire, and for sufficiently large cross sections, even bend it an entire problem
The cable inside of which is used for a solid single-wire wire has a number of advantages when installing a residential electrical wiring. After all, if the wire, in a sense, keeps the form, then it is much more convenient to lay it in the rod, make twists of a large number of wires, etc.
And in general, from my experience I know that when installing electrical wiring and various fittings (sockets, switches, lamps, etc.), it is much more convenient to use single-core wires.
Operating conditions for stranded wires.
 If solid wires are used in electrical wiring of apartments, houses, etc., then where are the multicore wires used?
If solid wires are used in electrical wiring of apartments, houses, etc., then where are the multicore wires used?
To answer this question, you just have to think about the features of a stranded wire, and this is flexibility. After all, as I mentioned above, solid wires have more rigidity and they are more difficult to bend, etc. While stranded wires on the contrary - they are more elastic, they are easier to bend and, I would not say that they keep the shape, as do single-core ones.
In connection with these features of stranded wires they are used where such qualities of wires are necessary. For example, stranded wires are more convenient to use in cars, you could also notice that all wires of electrical appliances are multi-core - and it's convenient! Another example can be given various transfers, etc. I think you yourself can recall a number of cases where the use of stranded wires is much more convenient than single-core wires.
And so today we considered the advantages and disadvantages of single-core / stranded wires
Advantages of solid wire:
More convenient when installing electrical wiring in apartments and houses.
Have more rigidity, it is convenient to do twists.
Can be used in high-frequency circuits.
Advantages of stranded wire:
More flexible, which gives these wires more convenience, with appropriate use.
It has a higher conductivity and is often used in various equipment.
And, perhaps, it is more convenient to solder them.
Disadvantages of solid wire:
He does not tolerate repeated excesses and strong vibrations.
Disadvantages of stranded wires:
Limited use in high-frequency circuits
And remember that if you do not use it single-core or stranded wire, his dignity may well turn into shortcomings.