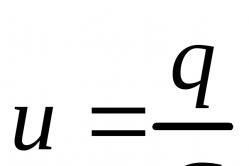Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are situations of emergency care for fever, when the child needs to give the medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and apply antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? Which medications are the safest?
Appointment
Notes
Sources of information
- "Theoretical Foundations of Electrical Engineering. Electrical circuits"Bessonov LA Moscow" Higher School "1996 ISBN 5-8297-0159-6
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Watch what is "Zero wire" in other dictionaries:
neutral wire - neutral wire - [Ya.N.Luginsky, M.S.Fezi Zhilinskaya, Y.S. Kabirov. English-Russian Dictionary of Electrical and Electrical Engineering, Moscow, 1999] Electrical Engineering, Basic Concepts Synonyms neutral wire EN inner mainneutral main ...
neutral wire - 3.35 zero wire (symbol N): A wire connected to a neutral (zero) point of the network and having the power transmission capability (MES 826 01 03) (ISO / TR 12100 1, 3.22 with changes). Source: GOST R IEC 60204.1 99: Security ... ... Dictionary-reference terms of normative and technical documentation
neutral wire - rus zero working conductor (m), neutral wire (m) eng neutral conductor fra conducteur (m) neutre, neutre (m) deu Neutralleiter (m), Nulleiter (m) spa conductor (m) neutro, neutro (m) ... Occupational safety and health. Translation into English, French, German, Spanish
neutral wire - nulinis laidas statusas T sritis automatika atitikmenys: angl. neutral conductor; neutral wire vok. Nulleiter, m rus. zero wire, m pranc. conducteur neutre, m; fil neutre, m; ligne neutre, f ... Automatikos terminų žodynas
zero wire (symbol N) - A wire connected to a neutral (zero) point of the network and having the ability to transmit electricity. [GOST R IEC 60204-1 2007] Electrical safety topics ... Technical Translator's Guide
A wire connected to the common junction point of the ends of the phase windings of machines and transformers. Technical railway dictionary. M .: State transport railway publishing house. NN Vasiliev, ON Isahakyan, NO Roginsky, Ya ... ... Technical Railway Dictionary
zero wire (N) - 3.57 null wire (N): A wire connected to a neutral (zero) network point and capable of transmitting electric power (cm. ). (See 3.35 of EN 60204-1.)
Beginners often have a question: "What wire is zero in the electricity supply system at home?" To answer this question, you should know that a zero wire is necessary to avoid a "phase skew". Experts are trying to achieve a uniform load in the electricity supply to consumers. To understand this phenomenon clearly, we take as an example apartment house, where an equal number of apartments are connected to one of the three phases. However, uneven consumption in this case still remains. After all, people in every apartment use different electrical appliances at different times of the day and night.
Principle of operation of the neutral wire
Electric power comes to consumers from a voltage transformer that is able to convert the voltage of an industrial network into a secondary winding of the transformer connected in a "star" scheme, that is, three wires are connected at one point "zero". The second end of the high-voltage wires is output to the terminals under the names A, B and C.
The ends connected together at the "zero" point are connected to the ground loop in the substation. There is also a separation of the high-voltage wire of zero resistance into:
- protective PE conductor (painted in yellow-green color);
- work zero (colored in blue).
According to the scheme described above, works in new buildings. It is referred to as the TN-S system. AT switchboard Electric buildings are supplied with 3 phases, PE conductor, and also a neutral wire.
In most old apartment buildings there is no RE-conductor. The power supply system consists of 4 wires, it is called TN-C. It is obsolete and is considered unsafe. Grounding of the neutral wire in this case is carried out at home.
The phases and zero from the voltage transformer are carried to the living quarters by underground or above-ground high-voltage wires, connecting them later to the input shield of the house. Thus a system of three phases with a voltage of 380/220 volts is formed. From the lead-in shield the electricians are wiring wires on the entrances and apartments. Consumers are supplied with electricity by means of wires connected to one of the three phases with a voltage of 220 volts. Also in the living room conduct a PE protective conductor (only with the new TN-S system) and a neutral wire.
When wires of zero resistance are conducted to each consumer of electricity, the uneven load on the power network practically disappears.
Why do you need a protective conductor PE?

A protective conductor or PE is required for additional protection at home. In the event of a short circuit, it removes the current from the place of destruction of the wiring, thereby protecting people from impact electric shock, and property from a fire.
In such a network, the load is distributed evenly, since on each floor of the apartment building there is a wiring for the phases.
The electrical system, led to the living quarters, is a "star" that repeats all the vector characteristics of the transformer substation.
Such a system is reliable and optimal, but there are also some disadvantages in it, since there are periodic failures. Most often, power outages are associated with poor wire quality, as well as poor connection quality.
Causes of the break in zero and phases
With poor contact of the wires and increased loads on the power supply system, the network breaks down.

If any of the three conductors feeding the house breaks, consumers connected to it will not receive electricity. At the same time, other consumers who are connected to the remaining two phases receive electricity in full. The current of the zero wire is summed from the remaining phases in the operating state, and will be equal to this value.
All the breaks in the network are connected with the disconnection of the power supply of the apartments from electricity. Such accidents can not damage electrical appliances. Hazardous situations that threaten a fire in the room and breakdown of machinery arise if the connection between the voltage transformer in the substation and the switchboard is terminated. This situation arises from a number of factors, but the most likely cause of power outages is by the mistake of the electricians team.
Causes of a short circuit
A short circuit becomes possible when the current does not pass through the "zero" to the ground loop A0, B0 and C0. Instead, the currents move along the outer contours of AB, BC and CA, which are powered by a voltage of 360 volts. Thus, on one flap can be too small voltage, since the economical lodger has turned off all electrical appliances, and on the other, a voltage approximating to the linear voltage is 360 volts. This is the cause of the damage to the wires. Instruments, in turn, overheat as a result of the receipt of unclear currents on them.
To avoid this situation and to protect yourself from a sudden surge in voltage, there are protection devices that are installed inside the housing shields. Also they are put in the case of expensive electrical appliances to prevent breakages, for example, in refrigerators and freezers.
Method for determining the zero and phase in the house

To identify a malfunction in the wiring at home, most often use a budget screwdriver with a light indicator. Such a device works by passing a capacitive current inside its housing. The internal part of such a device is equipped with the following components:
- metal bare tip, which serves to connect it to the phase or zero conductor;
- a resistor that reduces the amplitude of the current passing through the screwdriver to a safe value;
- a light indicator that lights when the current flows through the metal part of the device. A burning indicator indicates the presence of current in the phase;
- a platform through which the current passes through the human body and reaches the potential of the earth.
Experienced electricians for troubleshooting get more functional devices, for example, a multifunctional electronic indicator in the form of a screwdriver, working on two batteries, thanks to which the device is able to create a voltage of 3 volts. In addition to determining the phase, such devices perform other tasks.
If the light is lit when the device contacts the electrical contact, then a phase is detected. When the indicator contacts the PE and N conductors, the indicator light should not be on. If this is not the case, then electrical circuit is faulty.
Causes of zero damage in the circuit

Damage to the zero conductor occurs usually in those places where the connection is poor. If the resistance in the junction is large enough, the wires are heated. From elevated temperatures, the joint is oxidized, resulting in increased resistance. The wiring is heated to the melting point, which causes the problematic joint to be completely destroyed.
How to avoid a short circuit?
To ensure reliable connection of metal wires, it is necessary to increase the contact area. Connections of 1 cm in length will burn off after a month if the length of twisting is doubled, the wiring will last a year, but if you connect the wires with twisting in such a way that the contact length is 5 cm, then the conductor will work for many years. To secure the house even more, it is necessary to wrap the joint place with a non-insulated piece of wire.
Modern tools for connecting contacts

The twisting method as a connection of two conductive parts has long been obsolete, now electricians use connection tools (PPE). The case of such a product is made in the form of a cap, which winds the wires against each other, making the connection very reliable.
Even more convenient to use Enough ends of the two wires that need to be connected together, insert into special grooves until you click. After that, the connection is difficult to unhook.
The headache of any electrician is the disappearance of zero. In its absence, all consumers will be without electricity. Zero wire appears from the midpoint of the windings of a high-voltage transformer connected to a star. This point is bred to all cabinets and shields, and from this point the grounding bar extends. Zero wire is most important for the safety of electrical equipment.
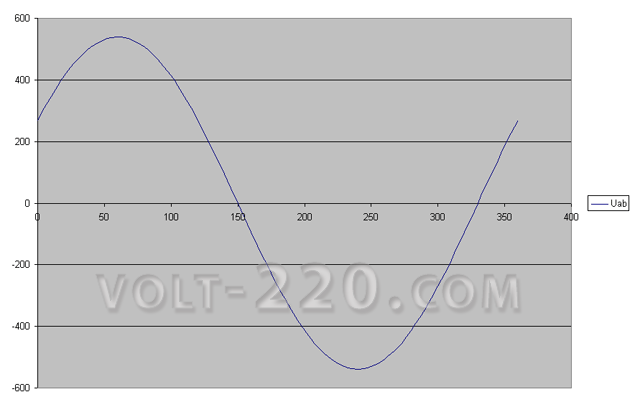
The alternating voltage in the network has a sinusoidal form. Three phases are shifted relative to each other by an angle of 120 *. This is a little incomprehensible, so these curves are illustrated here. If the voltage is measured with a standard voltmeter, this value between the phase conductor and zero will be 220 V, but this is the average value for half the period. The tester is not an oscilloscope, but only an average meter. In fact, instantaneous values of peak voltages greater than 220 V per square root of 2. In other words, 220 * 2 ^ 0.5 = 311 V.
The voltage sine wave says that the average value of the voltage is 220 V, the peak value is 311 V. The measurements are made relative to the zero axis of abscissas.
The shape of the curve between the two phases is also a sinusoid. The average value of the line voltage is 380 V, and the peak value is 536 V.
At the sight of the common man in the street it is not clear why the loss of zero, the voltage in the network should increase. Logic suggests quite the opposite - complete loss of tension. And really, if you disconnect the zero wire to your apartment, then the light will go out and nothing terrible will happen with the equipment. But here it is a question of a break of zero in a substation or on distribution floor apartment blocks.
We start the unwinding of the tangle from the very beginning - the counter of active energy. At first glance - a standard device, but there is an underwater rock. In the meter there are two windings - the voltage, which is switched between phase and zero, and the current included in the phase break. The voltage between points A and B is 220 V, completely falling on the voltage winding.
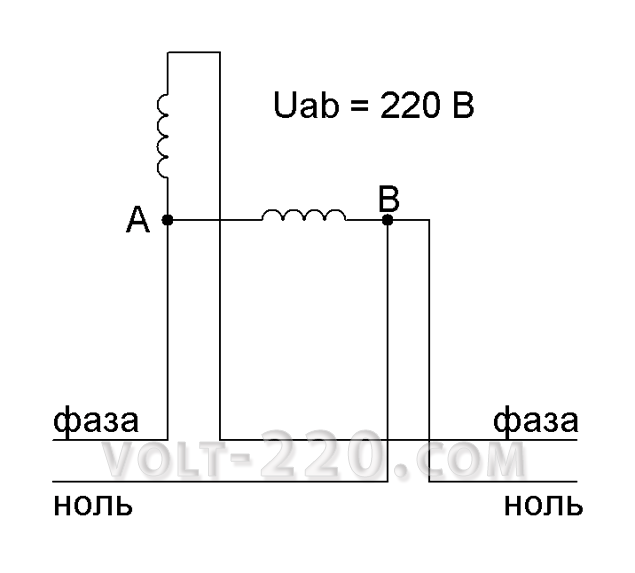
When the zero is cut, the phase will flow through the voltage winding and will flow to the consumer. If the consumer takes the indicator and pokes into the socket, it will immediately detect two phases, but the voltmeter will show a stable zero. It is possible that many people will start boiling from this information, but there is nothing magical about it. It's all about the counter.
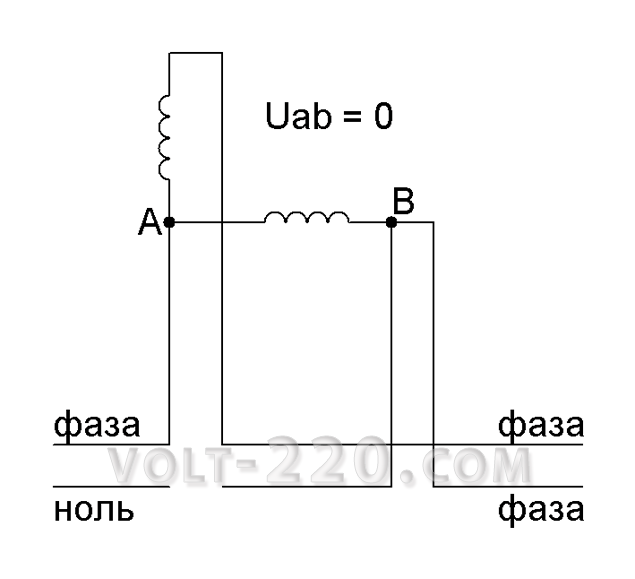
When the phase breaks off, everything is more logical - nothing will be observed anywhere.
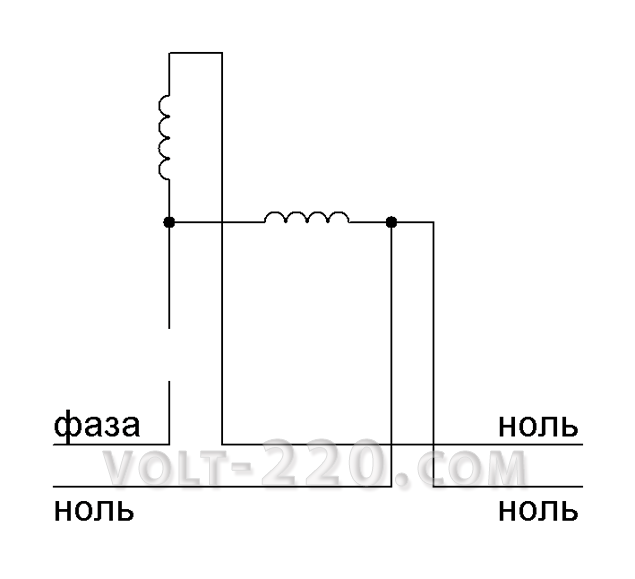
Now about the main thing. With the break of zero to the counters that feed two or more apartments an interesting process arises. Both counters will remain connected to zero wire, but there will be no zero. The situation will be aggravated by the fact that the counters are fed with different phases for a uniform load of the transformer. It turns out that one phase from the first counter will pass through the voltage winding and will start with another phase from the second counter, also passed through the voltage winding. Short circuit will not work, because two series-connected voltage windings, operating at 220 V, will be powered from 380 V, that is, each winding will have to 190 V. This is even less than the claimed, which is acceptable for windings. For the consumer it turns out that on one wire there will be a potential of 220 V, and on the second wire there is a potential of 190 V. And like everything is also not bad, because at first glance the voltage in the apartment will be equal to 220 - 190 = 30 V, but this is not so.
Depending on the load, the zero point will shift to the more loaded consumer and it will receive instead of 220 V, much less, for example, 100 V less, ie 120 V, but its neighbor will get 380-120 = 260 V. If one consumer is not loaded at all, then it will get all 380 V to its system. This does not mean that it is necessary to run all the devices to prevent skewing. A break of zero is an emergency and is rare.
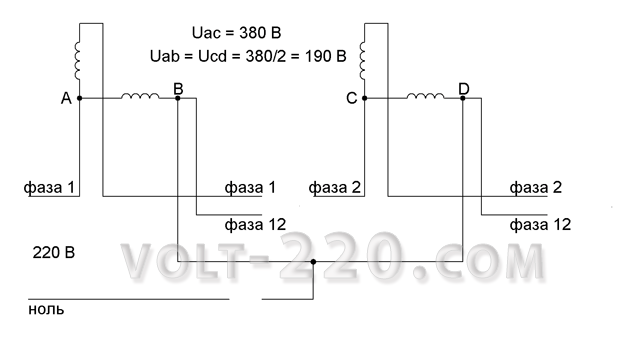
Often the literature describes a phase shift in which, because of the asymmetry of the phases, the zero potential point shifts and instead of zero on the wire it will hang 5-10 V, relative to the ground wire. In principle, this is normal. It is impossible to connect evenly a number of single-phase consumers so that the load is perfectly symmetrical. Personally, I measured the current in the ground wire from the high-voltage transformer to the earthing switches and it was 4 A. The phase irregularity itself is the norm.
As an experiment, you can take two transformers and connect them in series between the two phases. The wire from the middle point of both transformers must first be connected to the neutral wire. It is necessary to make sure of the voltage on the transformers. The voltage should be 220 V. If you disconnect the neutral wire and measure the voltage on the transformers, then the focus voltage will be different if the loads on the transformers are different, or if the power of the transformers is different, because the resistance of the primary windings will be different.
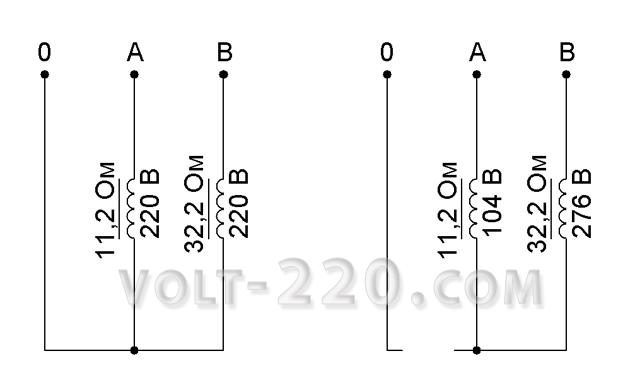
The results of the experiment are as follows: a zero break causes a phase skew between all consumers, shifting the zero point depending on the load of these consumers. The more the load, the less tension will come to the apartment.